Tin bronze offers excellent wear resistance and corrosion protection, making it ideal for harsh environments and heavy-duty applications. Phosphor bronze provides superior strength and elasticity, along with increased fatigue resistance, suitable for electrical contacts and springs. Both alloys contain tin but differ in phosphorous content, influencing their mechanical properties and specific industrial uses.
Table of Comparison
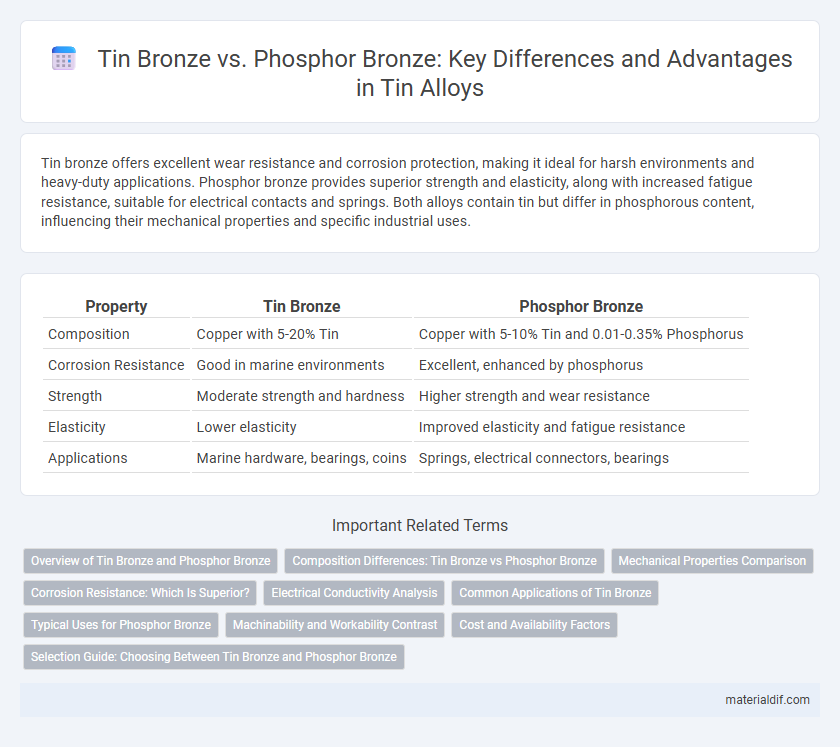
| Property | Tin Bronze | Phosphor Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper with 5-20% Tin | Copper with 5-10% Tin and 0.01-0.35% Phosphorus |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good in marine environments | Excellent, enhanced by phosphorus |
| Strength | Moderate strength and hardness | Higher strength and wear resistance |
| Elasticity | Lower elasticity | Improved elasticity and fatigue resistance |
| Applications | Marine hardware, bearings, coins | Springs, electrical connectors, bearings |
Overview of Tin Bronze and Phosphor Bronze
Tin bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, good strength, and wear resistance, making it suitable for bearings, bushings, and sculptures. Phosphor bronze contains copper, tin, and a small amount of phosphorus, which enhances its stiffness, fatigue resistance, and lubricity, ideal for springs, electrical connectors, and precision instruments. Both alloys are widely used in industrial applications, with tin bronze favored for durability and phosphor bronze valued for mechanical strength and resilience in dynamic environments.
Composition Differences: Tin Bronze vs Phosphor Bronze
Tin bronze primarily consists of copper alloyed with 5-20% tin, enhancing its corrosion resistance and hardness. Phosphor bronze includes 0.5-11% tin combined with 0.01-0.35% phosphorus, which improves wear resistance and stiffness. The key compositional difference lies in the presence of phosphorus, providing phosphor bronze with superior fatigue resistance compared to tin bronze.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Tin bronze exhibits superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance compared to phosphor bronze, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Phosphor bronze offers excellent elasticity and fatigue resistance due to its higher phosphorous content, which enhances wear resistance and reduces friction. The mechanical properties of phosphor bronze contribute to its widespread use in springs and electrical connectors, whereas tin bronze is preferred in marine environments and bearing applications for its durability.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Is Superior?
Phosphor bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to tin bronze due to its higher phosphorous content, which enhances its ability to withstand oxidation and chemical exposure in harsh environments. Tin bronze is more prone to corrosion, especially in marine or acidic conditions, making phosphor bronze the preferred choice for applications requiring long-term durability and resistance to rust. The enhanced corrosion resistance of phosphor bronze makes it ideal for electrical connectors, springs, and marine hardware.
Electrical Conductivity Analysis
Tin bronze exhibits moderate electrical conductivity typically ranging from 15% to 25% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), primarily due to its higher tin content which increases hardness but reduces conductivity. Phosphor bronze displays slightly lower conductivity, around 10% to 20% IACS, as phosphorus additions enhance corrosion resistance and strength but further impede electron flow. Electrical conductivity analysis reveals that both alloys are less conductive than pure copper, with tin bronze generally outperforming phosphor bronze in applications prioritizing electrical efficiency.
Common Applications of Tin Bronze
Tin bronze is widely used in manufacturing bearings, bushings, and gears due to its excellent wear resistance and low friction properties. It is commonly applied in marine hardware, musical instruments, and coins because of its corrosion resistance and attractive finish. The alloy's combination of strength and ductility makes it ideal for architectural applications and sculptures.
Typical Uses for Phosphor Bronze
Phosphor bronze is commonly used in electrical connectors, springs, and marine hardware due to its excellent fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. Unlike tin bronze, which is often utilized for bearings and bushings, phosphor bronze's superior strength and wear resistance make it ideal for precision instruments, musical instruments, and fasteners. Its applications extend to aerospace and automotive components where durability and resistance to environmental stresses are critical.
Machinability and Workability Contrast
Tin bronze offers superior machinability compared to phosphor bronze due to its lower hardness and reduced tendency to work-harden, allowing easier cutting and shaping during manufacturing processes. Phosphor bronze, while more challenging to machine because of its higher strength and wear resistance, excels in workability with enhanced fatigue resistance and better spring properties for applications requiring durability. The choice between tin bronze and phosphor bronze hinges on the balance between ease of machining and mechanical performance needs in specific industrial applications.
Cost and Availability Factors
Tin bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, tends to be more cost-effective and widely available due to the abundance of tin as a raw material. Phosphor bronze, which includes tin with a small amount of phosphorus, generally incurs higher costs because of added alloying elements and more complex manufacturing processes. Availability of phosphor bronze is comparatively limited, impacting its price and accessibility in large-scale industrial applications.
Selection Guide: Choosing Between Tin Bronze and Phosphor Bronze
Tin bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance and good wear properties, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in marine and chemical environments. Phosphor bronze provides superior strength, fatigue resistance, and elasticity, suitable for springs, clips, and electrical components demanding high mechanical performance. Selection between tin bronze and phosphor bronze depends on specific application requirements such as load-bearing capacity, corrosion exposure, and electrical conductivity.
Tin bronze vs phosphor bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com