Extruded PTFE offers superior mechanical strength and is ideal for applications requiring tight dimensional tolerances and consistent performance, while molded PTFE provides enhanced chemical resistance and is better suited for complex shapes or custom parts. Extrusion creates uniform sheets or rods with excellent ductility, whereas molding allows for intricate geometries that extrusion cannot achieve. Choosing between extruded and molded PTFE depends on the specific requirements for durability, shape complexity, and chemical exposure in Teflon pet applications.
Table of Comparison
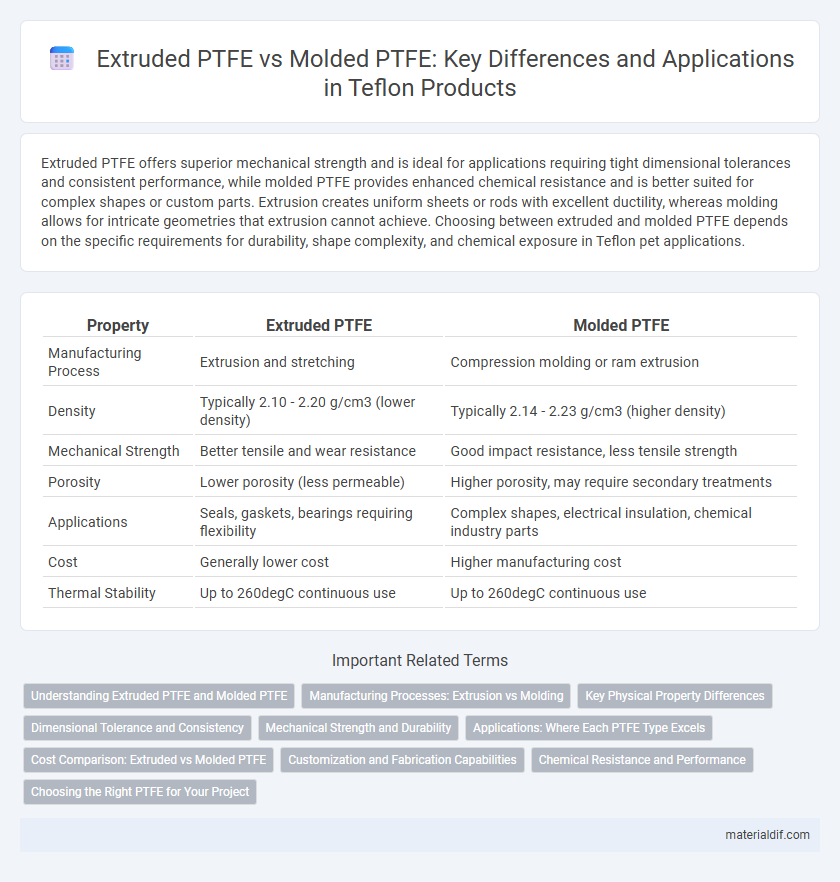
| Property | Extruded PTFE | Molded PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Extrusion and stretching | Compression molding or ram extrusion |
| Density | Typically 2.10 - 2.20 g/cm3 (lower density) | Typically 2.14 - 2.23 g/cm3 (higher density) |
| Mechanical Strength | Better tensile and wear resistance | Good impact resistance, less tensile strength |
| Porosity | Lower porosity (less permeable) | Higher porosity, may require secondary treatments |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, bearings requiring flexibility | Complex shapes, electrical insulation, chemical industry parts |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 260degC continuous use | Up to 260degC continuous use |
Understanding Extruded PTFE and Molded PTFE
Extruded PTFE is produced by pushing softened PTFE resin through a die, resulting in a dense, uniform material with excellent dimensional stability and mechanical strength ideal for seals and gaskets. Molded PTFE, formed by compression molding PTFE powder in heated molds, offers intricate shapes and superior chemical resistance but may have slightly less mechanical strength than extruded variants. Understanding the differences in manufacturing processes helps select the right PTFE type based on application requirements like flexibility, strength, and chemical exposure.
Manufacturing Processes: Extrusion vs Molding
Extruded PTFE is produced by forcing raw PTFE resin through a shaped die, resulting in continuous, uniform sheets or rods with enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Molded PTFE involves compressing powdered resin in a mold under heat and pressure, producing complex shapes with precise dimensional accuracy but often lower tensile strength. The choice between extrusion and molding impacts the final product's structure, surface finish, and suitability for applications requiring specific mechanical and thermal properties.
Key Physical Property Differences
Extruded PTFE typically exhibits higher tensile strength and elongation due to its continuous extrusion process, making it more flexible and impact-resistant compared to molded PTFE. Molded PTFE often demonstrates superior dimensional stability and higher density, resulting in better chemical resistance and compression strength. These physical property differences influence their suitability for applications requiring specific mechanical performance and durability under stress.
Dimensional Tolerance and Consistency
Extruded PTFE typically offers tighter dimensional tolerance and greater consistency compared to molded PTFE due to its continuous manufacturing process, which allows for uniform molecular alignment. Molded PTFE, while versatile, often exhibits more dimensional variability and less precise tolerance because of the batch-based molding and sintering steps. For applications requiring exact dimensions and consistent performance, extruded PTFE is generally the preferred choice.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Extruded PTFE exhibits superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to molded PTFE, making it ideal for applications requiring higher tensile strength and resistance to deformation. The extrusion process aligns polymer chains, increasing structural integrity and wear resistance, while molded PTFE often contains microvoids that reduce mechanical performance. Consequently, extruded PTFE is preferred in demanding industrial environments where long-term durability and consistent mechanical properties are critical.
Applications: Where Each PTFE Type Excels
Extruded PTFE offers superior mechanical properties, making it ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength and flexibility such as seals, gaskets, and tubing in chemical processing industries. Molded PTFE excels in producing complex or thick-walled parts like valve seats, flanges, and custom shapes where intricate design and high chemical resistance are crucial. Both PTFE types provide excellent thermal stability and chemical inertness, but application choice depends on mechanical demands and part geometry.
Cost Comparison: Extruded vs Molded PTFE
Extruded PTFE generally offers a more cost-effective solution due to lower tooling and production expenses compared to molded PTFE, which requires expensive molds and longer setup times. The extrusion process allows for continuous production, reducing material waste and operational costs, making extruded PTFE ideal for large-volume applications. Molded PTFE provides superior dimensional accuracy but at a higher price point, making it less economical for high-volume, low-complexity parts.
Customization and Fabrication Capabilities
Extruded PTFE offers superior uniformity and enhanced mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and precise dimensional control. Molded PTFE allows complex geometries and integrated features through custom mold designs, supporting intricate component fabrication with reduced post-processing. Both formats provide extensive customization options, but extruded PTFE excels in producing continuous profiles while molded PTFE is preferred for specialized, high-precision parts.
Chemical Resistance and Performance
Extruded PTFE exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its dense molecular structure, making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments where corrosion is a concern. Molded PTFE offers enhanced mechanical strength and dimensional stability, which improves performance in applications involving high pressure or mechanical stress. Both forms maintain exceptional resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents, but extruded PTFE is preferred when maximum chemical inertness is critical.
Choosing the Right PTFE for Your Project
Extruded PTFE offers superior flexibility and is ideal for applications requiring intricate shapes or detailed machining, while molded PTFE provides enhanced chemical resistance and structural integrity for high-stress environments. Selecting the right PTFE depends on factors such as mechanical load, chemical exposure, and dimensional tolerance, with extruded grades favored for dynamic sealing and molded grades suitable for heavy-duty components. Evaluating project-specific requirements ensures optimal performance, durability, and cost-efficiency when choosing between extruded and molded PTFE materials.
Extruded PTFE vs Molded PTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com