Pit sand is coarse-textured with sharp edges, making it ideal for construction and concrete work due to its excellent bonding properties. Desert sand features fine, rounded grains that lack the roughness needed for strong adhesion, rendering it unsuitable for standard building applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate sand type in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
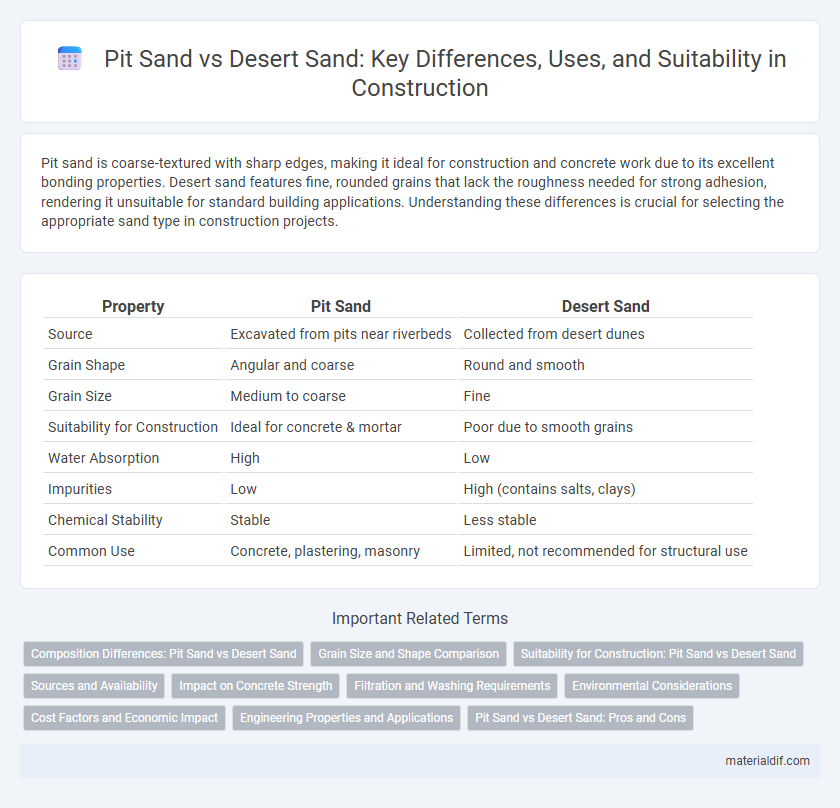
| Property | Pit Sand | Desert Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Excavated from pits near riverbeds | Collected from desert dunes |
| Grain Shape | Angular and coarse | Round and smooth |
| Grain Size | Medium to coarse | Fine |
| Suitability for Construction | Ideal for concrete & mortar | Poor due to smooth grains |
| Water Absorption | High | Low |
| Impurities | Low | High (contains salts, clays) |
| Chemical Stability | Stable | Less stable |
| Common Use | Concrete, plastering, masonry | Limited, not recommended for structural use |
Composition Differences: Pit Sand vs Desert Sand
Pit sand contains coarse, angular grains primarily composed of quartz and feldspar, making it ideal for construction due to its better binding properties and strength. Desert sand, by contrast, consists of fine, rounded grains shaped by wind erosion, often resulting in smooth particles with lower silica content and less effective bonding capabilities. This distinct difference in grain size, shape, and mineral composition directly affects their suitability for concrete and mortar applications.
Grain Size and Shape Comparison
Pit sand features coarse, angular grains typically ranging from 0.5 to 2 mm in size, providing excellent binding properties for construction purposes. Desert sand grains are finer and smoother, often less than 0.5 mm, with rounded edges due to natural wind erosion, resulting in poor adhesion in concrete mixtures. The grain shape and size difference makes pit sand preferable for structural applications, while desert sand is generally unsuitable for conventional concrete.
Suitability for Construction: Pit Sand vs Desert Sand
Pit sand, characterized by its coarse texture and angular grains, is highly suitable for construction due to its excellent binding properties and ability to provide strong concrete and mortar mixes. In contrast, desert sand has fine, rounded grains that lack the necessary cohesion and grip, making it unsuitable for traditional construction purposes without extensive processing. The difference in grain morphology directly impacts their usability, with pit sand preferred for structural stability and desert sand often requiring blending or modification for construction applications.
Sources and Availability
Pit sand, extracted from riverbeds and pits, is characterized by its coarse grains and abundant availability in regions near water bodies, making it a preferred choice for construction due to its strength and binding properties. Desert sand, sourced from arid desert environments, has fine, rounded grains with limited angularity, which reduces its suitability for concrete but is abundant in vast desert regions. The availability of pit sand is often seasonal and geographically restricted, whereas desert sand is plentiful but requires processing to improve its binding capability for construction uses.
Impact on Concrete Strength
Pit sand, known for its angular grains and rough texture, significantly enhances concrete strength by improving the bond between cement and aggregates. Desert sand, characterized by its smooth, rounded particles and fine size, often leads to weaker concrete due to poor interlocking and reduced adhesion. Using pit sand in concrete mixes results in higher compressive strength, making it preferable over desert sand for structural applications.
Filtration and Washing Requirements
Pit sand possesses angular, coarse grains ideal for effective filtration and minimal washing due to low clay content, making it suitable for concrete applications. Desert sand, characterized by smooth, rounded particles with high silt and salt content, requires extensive washing to remove impurities and enhance its filtration performance. Proper washing ensures desert sand's usability in construction by reducing fines that otherwise impair water permeability and structural strength.
Environmental Considerations
Pit sand, known for its angular grains and high durability, is often extracted through mining processes that lead to land degradation, habitat disruption, and increased carbon emissions. Desert sand, characterized by its smooth, rounded particles, is abundant but less suitable for construction; however, its use can significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with extensive pit sand mining. Sustainable alternatives and recycling of desert sand in concrete production are gaining attention to minimize ecological damage and promote resource conservation.
Cost Factors and Economic Impact
Pit sand, sourced from riverbeds and pits, is characterized by its coarse texture and angular grains, making it ideal for construction but generally more costly due to extraction and transportation expenses. Desert sand, with its smooth, rounded grains, is less suitable for concrete-making and is often cheaper, though its limited applicability can lead to higher long-term project costs. The economic impact of choosing pit sand over desert sand hinges on balancing initial material costs against durability and structural integrity in construction projects.
Engineering Properties and Applications
Pit sand, characterized by its coarse texture and angular grains, offers excellent strength and compaction properties ideal for concrete and masonry work. Desert sand, with its fine, smooth, and rounded particles, lacks sufficient cohesion and does not bond well in construction applications, making it unsuitable for structural concrete. Engineering projects favor pit sand for its superior load-bearing capacity and durability in foundations and structural frameworks.
Pit Sand vs Desert Sand: Pros and Cons
Pit sand offers superior strength and workability in construction due to its coarse texture and angular grains, enhancing concrete bonding and durability. Desert sand, characterized by its fine, rounded particles, often lacks the necessary binding properties, resulting in weaker concrete mixes and higher cement consumption. However, desert sand is abundant in arid regions and can be environmentally beneficial when used with specific admixtures to improve its performance in masonry.
Pit sand vs Desert sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com