Volcanic sand features dark, dense particles rich in minerals like basalt and obsidian, providing excellent drainage and natural fertility for plants. Quartz sand, composed mainly of clear or white silica, offers durability and a neutral pH that supports a wide range of garden and aquarium plants. Choosing between volcanic and quartz sand depends on the desired texture, mineral content, and aesthetic preferences for pet habitats.
Table of Comparison
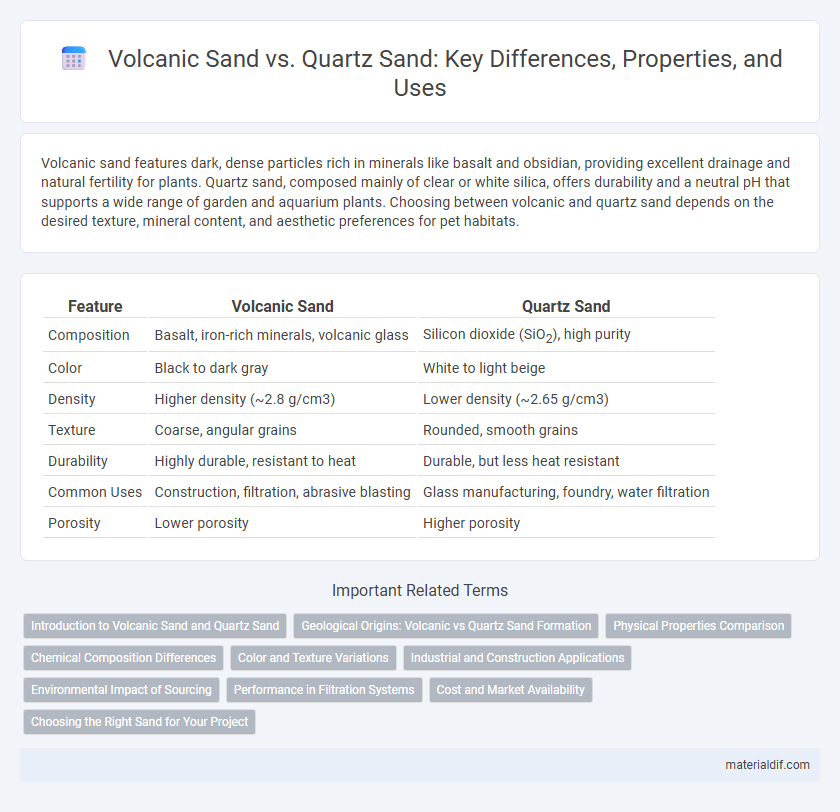
| Feature | Volcanic Sand | Quartz Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Basalt, iron-rich minerals, volcanic glass | Silicon dioxide (SiO2), high purity |
| Color | Black to dark gray | White to light beige |
| Density | Higher density (~2.8 g/cm3) | Lower density (~2.65 g/cm3) |
| Texture | Coarse, angular grains | Rounded, smooth grains |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to heat | Durable, but less heat resistant |
| Common Uses | Construction, filtration, abrasive blasting | Glass manufacturing, foundry, water filtration |
| Porosity | Lower porosity | Higher porosity |
Introduction to Volcanic Sand and Quartz Sand
Volcanic sand originates from the rapid cooling and fragmentation of volcanic rocks, characterized by its dark color and high mineral content, including basalt and obsidian fragments. Quartz sand, primarily composed of silicon dioxide, is known for its hard, durable grains that have been weathered and rounded over time. These distinct compositions influence their use in construction, landscaping, and industrial applications, with volcanic sand offering higher density and heat resistance, while quartz sand provides high purity and consistent granularity.
Geological Origins: Volcanic vs Quartz Sand Formation
Volcanic sand originates from the rapid cooling and fragmentation of volcanic rocks, primarily basalt and andesite, during volcanic eruptions, resulting in dark-colored, dense grains rich in iron and magnesium. Quartz sand forms through the weathering and erosion of continental rocks like granite, leading to light-colored, durable grains predominantly composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2). The geological processes behind volcanic sand involve pyroclastic activity and lava flows, whereas quartz sand is shaped by sedimentary processes including abrasion and transport by water and wind over extended geological timescales.
Physical Properties Comparison
Volcanic sand features dark, dense grains with high iron and magnesium content, making it heavier and coarser than quartz sand. Quartz sand is typically lighter in color, composed primarily of silicon dioxide with rounded, smooth grains due to extensive weathering. The angular, rough texture of volcanic sand enhances its cohesion and drainage, whereas quartz sand's uniformity supports broad industrial applications like glass manufacturing.
Chemical Composition Differences
Volcanic sand primarily consists of basaltic and andesitic minerals rich in iron and magnesium, with high amounts of ferromagnesian silicates like olivine and pyroxene, imparting a dark color. Quartz sand is predominantly composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), forming nearly pure crystalline quartz grains with minimal impurities, resulting in its lighter, often white or translucent appearance. The chemical composition differences influence durability, reactivity, and suitability for various industrial and construction applications.
Color and Texture Variations
Volcanic sand typically exhibits dark hues ranging from black to deep brown due to its basaltic origin, while quartz sand is characterized by lighter tones such as white, beige, or pale yellow, reflecting its high silica content. The texture of volcanic sand often feels coarse and gritty with irregular, sharp fragments resulting from rapid lava cooling, whereas quartz sand is generally smoother and more rounded due to prolonged weathering and erosion processes. These color and texture differences affect the sand's suitability for construction, landscaping, and industrial applications.
Industrial and Construction Applications
Volcanic sand, composed mainly of basalt and other volcanic minerals, offers superior heat resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for refractory materials and specialized concrete in high-temperature industrial environments. Quartz sand, abundant in silica content, provides excellent strength and is widely used in glass manufacturing, foundry casting, and high-performance concrete due to its hardness and stability. Both sands serve crucial roles in construction and industry, with volcanic sand preferred for thermal applications and quartz sand favored for structural and manufacturing processes.
Environmental Impact of Sourcing
Volcanic sand sourcing often involves extraction from active or dormant volcanic regions, which can disrupt fragile ecosystems and increase erosion risk. Quartz sand mining typically occurs in riverbeds or coastal areas, leading to habitat destruction and water pollution from sediment runoff. Both types of sand extraction contribute to biodiversity loss and require sustainable management practices to mitigate environmental damage.
Performance in Filtration Systems
Volcanic sand exhibits superior filtration performance due to its high porosity and irregular particle shapes, enhancing water flow and trapping impurities more effectively than quartz sand. Quartz sand, with its uniform grain size and chemical stability, provides consistent filtration but may allow faster water passage, reducing contact time with contaminants. Volcanic sand's mineral composition and rough texture improve filtration efficiency in water treatment systems requiring enhanced impurity removal.
Cost and Market Availability
Volcanic sand typically costs more than quartz sand due to its limited geographic distribution and specialized extraction processes. Quartz sand is widely available globally, making it more affordable and accessible for large-scale construction and industrial applications. The higher market demand for quartz sand ensures consistent supply, while volcanic sand remains a niche product with fluctuating availability.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Project
Volcanic sand, rich in basalt and other dark minerals, offers superior drainage and is ideal for landscaping requiring quick water runoff, while quartz sand, composed primarily of silica, provides durability and a clean aesthetic suitable for construction and glassmaking. Selecting the right sand depends on project needs--volcanic sand excels in erosion control and acidic soil environments, whereas quartz sand enhances structural integrity and is chemically inert. Assessing factors like grain size, mineral composition, and environmental impact ensures the optimal sand choice for landscaping, concrete mixing, or filtration systems.
Volcanic Sand vs Quartz Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com