Glassmaking sand is primarily composed of high-purity silica, essential for producing clear, strong glass with minimal impurities. Foundry sand, on the other hand, requires a high silica content but emphasizes grain shape and thermal stability to withstand repeated heating cycles in metal casting molds. These differences in composition and physical properties ensure optimal performance tailored to the specific demands of glass production versus metal foundry applications.
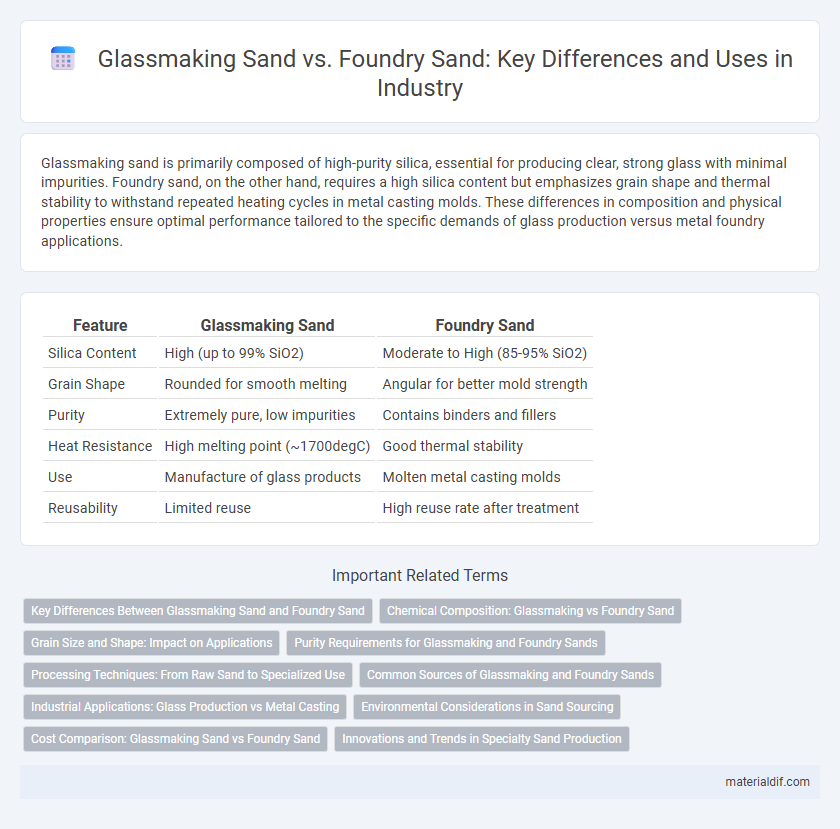
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glassmaking Sand | Foundry Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Silica Content | High (up to 99% SiO2) | Moderate to High (85-95% SiO2) |
| Grain Shape | Rounded for smooth melting | Angular for better mold strength |
| Purity | Extremely pure, low impurities | Contains binders and fillers |
| Heat Resistance | High melting point (~1700degC) | Good thermal stability |
| Use | Manufacture of glass products | Molten metal casting molds |
| Reusability | Limited reuse | High reuse rate after treatment |
Key Differences Between Glassmaking Sand and Foundry Sand
Glassmaking sand, primarily composed of high-purity silica (quartz) with low impurities, is essential for producing clear, strong glass with consistent melting properties. Foundry sand contains a mix of silica and other minerals, optimized for mold strength, thermal resistance, and reclaimability in metal casting processes rather than purity or clarity. The key differences lie in composition, particle size distribution, and functional properties tailored to glass clarity versus foundry mold performance.
Chemical Composition: Glassmaking vs Foundry Sand
Glassmaking sand primarily consists of high-purity silica (SiO2) with minimal impurities such as iron oxides and alumina to ensure clarity and strength in the final glass product. Foundry sand, while also rich in silica, contains higher levels of clay, feldspar, and other minerals that enhance mold stability and thermal resistance during metal casting. The distinct chemical compositions of these sands tailor their properties for specific industrial applications, with glassmaking sand emphasizing purity and foundry sand prioritizing binding and thermal properties.
Grain Size and Shape: Impact on Applications
Glassmaking sand features uniformly fine, rounded grains that enhance transparency and durability in glass products, while foundry sand consists of coarser, angular grains optimized for mold stability and permeability. The fine grain size in glassmaking sand ensures a smooth surface finish and reduces impurities, crucial for high-quality glass fabrication. In contrast, the larger, irregular grain shape in foundry sand promotes better air flow and strength in casting molds, improving metal casting accuracy and surface texture.
Purity Requirements for Glassmaking and Foundry Sands
Glassmaking sand requires exceptionally high silica purity, typically exceeding 95% SiO2 content, to ensure clarity and prevent discoloration in the final glass product. Foundry sand, while also predominantly silica-based, tolerates higher impurities like alumina and iron oxides, as these do not critically impact molding processes. Rigorous purification methods such as washing and magnetic separation are employed in glassmaking sand production to meet stringent purity standards essential for optical quality.
Processing Techniques: From Raw Sand to Specialized Use
Glassmaking sand undergoes extensive washing, sorting, and chemical purification to eliminate impurities such as iron and alumina, ensuring high silica content for clear, strong glass production. Foundry sand is processed through screening, crushing, and thermal reclamation, enhancing grain uniformity and strength for molding and casting applications. Specialized treatments like coating or resin bonding further tailor the sand's surface properties to meet the precise demands of glassmaking or foundry industries.
Common Sources of Glassmaking and Foundry Sands
Common sources of glassmaking sand include high-purity quartz sands that contain minimal iron content to ensure clear, high-quality glass production, typically extracted from riverbeds, beaches, and silica-rich sandstone deposits. Foundry sand primarily originates from naturally occurring silica sand, often sourced from inland sand dunes, river deposits, and specialized mining operations known for providing sands with appropriate grain size and refractory properties critical for mold durability in metal casting. Both types require stringent quality control to remove impurities that could affect the final product's properties in glass or metal foundry applications.
Industrial Applications: Glass Production vs Metal Casting
Glassmaking sand, primarily composed of high-purity silica (SiO2), is essential for producing clear, durable glass used in windows, bottles, and optical instruments. Foundry sand, characterized by its refractory properties and thermal stability, is specifically engineered for metal casting processes to create precise molds and cores for automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery components. The distinct chemical composition and particle size distribution of glassmaking sand versus foundry sand directly influence their performance in glass manufacturing and metal casting industries.
Environmental Considerations in Sand Sourcing
Glassmaking sand typically requires high-purity silica with low impurities to ensure clarity and strength in glass products, often sourced from carefully regulated deposits to minimize environmental disruption. Foundry sand, while also silica-based, can include recycled sand and varies in grain size and composition, which impacts the environmental footprint of mining and waste management practices. Sustainable sand sourcing involves balancing extraction impacts such as habitat disruption and groundwater depletion against the demand for high-quality materials in both glass and foundry industries.
Cost Comparison: Glassmaking Sand vs Foundry Sand
Glassmaking sand typically commands a higher price due to its superior purity, lower iron content, and consistent grain size essential for transparent, defect-free glass products. Foundry sand, used primarily in metal casting, is generally less expensive as it tolerates higher impurity levels and coarser grains without compromising mold quality. Cost differences also stem from processing methods, with glassmaking sand requiring more intensive refining to meet strict industry standards.
Innovations and Trends in Specialty Sand Production
Innovations in specialty sand production focus on enhancing the purity and particle size distribution of both glassmaking sand and foundry sand to improve end-product quality. Advanced beneficiation techniques, such as magnetic separation and attrition scrubbing, are increasingly employed to remove impurities and achieve higher silica content, crucial for glass clarity and foundry mold strength. Trends indicate a growing demand for eco-friendly processing methods and the development of tailored sand blends, optimizing performance and sustainability in glass manufacturing and metal casting industries.
Glassmaking Sand vs Foundry Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com