Silica sand, composed primarily of quartz, offers high heat resistance and excellent strength, making it ideal for precision molds in metal casting. Molding sand, often a mixture of silica sand with clay and other additives, provides greater plasticity and cohesiveness, allowing for easy shaping and reuse in foundry processes. The choice between silica sand and molding sand depends on the specific casting requirements, balancing strength, permeability, and moldability.
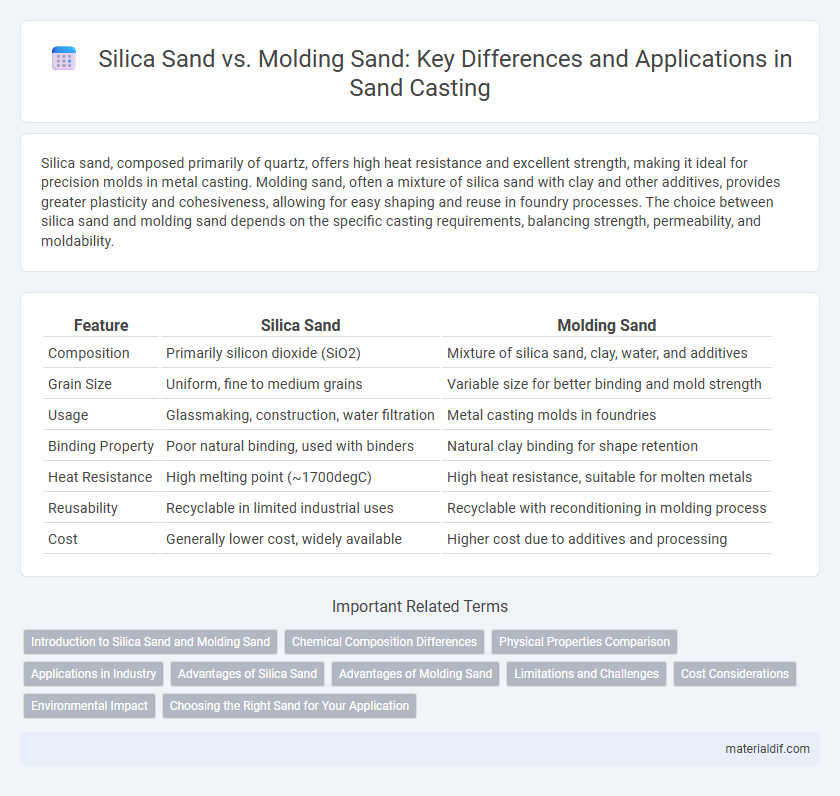
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Silica Sand | Molding Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Mixture of silica sand, clay, water, and additives |
| Grain Size | Uniform, fine to medium grains | Variable size for better binding and mold strength |
| Usage | Glassmaking, construction, water filtration | Metal casting molds in foundries |
| Binding Property | Poor natural binding, used with binders | Natural clay binding for shape retention |
| Heat Resistance | High melting point (~1700degC) | High heat resistance, suitable for molten metals |
| Reusability | Recyclable in limited industrial uses | Recyclable with reconditioning in molding process |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to additives and processing |
Introduction to Silica Sand and Molding Sand
Silica sand primarily consists of quartz grains and is known for its hardness, high melting point, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for industrial applications like glassmaking and foundry molds. Molding sand, often a mixture of silica sand, clay, and water, is specifically designed for shaping metal casts due to its binding properties and ability to withstand high temperatures. The fundamental difference lies in silica sand's purity and physical characteristics versus molding sand's composite nature tailored to support casting processes.
Chemical Composition Differences
Silica sand primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with a purity typically above 95%, making it highly resistant to heat and chemical reactions. Molding sand contains a mixture of silica, clay minerals like bentonite, and other impurities, which provide the necessary plasticity and cohesiveness for shaping molds. The key chemical composition difference lies in silica sand's high SiO2 content versus the diverse mineralogical components of molding sand that influence its binding properties.
Physical Properties Comparison
Silica sand features a high quartz content with a hardness of 7 on the Mohs scale, offering superior heat resistance and uniform grain size ideal for casting processes. Molding sand, often composed of a mixture of silica sand, clay, and other materials, exhibits greater plasticity and retains moisture to enhance moldability but has lower thermal stability. The porosity of silica sand allows for efficient gas permeability, whereas molding sand balances permeability with cohesion to maintain shape during metal pouring.
Applications in Industry
Silica sand is primarily used in glass manufacturing, foundry casting, and hydraulic fracturing due to its high silica content and durability, which provide excellent heat resistance and chemical stability. Molding sand, composed of natural or synthetic materials with high clay content, is essential in metal casting industries for forming molds that hold molten metal during solidification. Both types of sand play critical roles in industrial processes but serve distinct functions based on their physical and chemical properties.
Advantages of Silica Sand
Silica sand offers superior heat resistance and high purity, making it ideal for precision molding applications in foundries. Its consistent grain size ensures excellent permeability and surface finish, which reduces defects in castings compared to molding sand. The chemical stability of silica sand also enhances mold durability and reusability, optimizing production efficiency.
Advantages of Molding Sand
Molding sand offers superior plasticity and cohesiveness compared to silica sand, making it ideal for complex mold shapes in metal casting. Its high refractory properties ensure better heat resistance, reducing defects and improving casting quality. The natural binding components in molding sand also allow for easier reuse and environmentally-friendly disposal.
Limitations and Challenges
Silica sand faces limitations such as high thermal expansion and poor moisture resistance, which can cause cracking and reduced casting quality in foundry applications. Molding sand, while offering better plasticity and bonding properties, often contains impurities that limit its reusability and can lead to inconsistent mold strength. Both sands pose challenges in controlling grain size distribution and maintaining optimal moisture levels to ensure mold stability and surface finish quality.
Cost Considerations
Silica sand typically incurs higher costs due to its purity and extensive processing requirements, making it more expensive than molding sand commonly used in foundry applications. Molding sand, often composed of natural sand mixed with clay and water, offers a cost-effective solution for metal casting because of its availability and reusability. When budgeting for industrial processes, the choice between silica sand and molding sand hinges on balancing performance needs against material and processing expenses.
Environmental Impact
Silica sand mining generates significant environmental impacts, including habitat disruption, dust pollution, and groundwater contamination from excessive extraction. Molding sand, often recycled within foundries, reduces the need for virgin sand mining and minimizes waste disposal issues, resulting in a lower environmental footprint. Proper management of silica sand extraction and increased recycling of molding sand are critical for sustainable industrial practices.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Application
Silica sand is prized for its high quartz content and consistent grain size, making it ideal for applications requiring excellent thermal resistance and strength, such as glassmaking and foundry molds. Molding sand, often composed of silica mixed with binders like clay, offers superior moldability and surface finish, essential for casting complex metal shapes with precision. Selecting between silica sand and molding sand depends on the specific requirements of permeability, refractoriness, and surface finish in your manufacturing or construction process.
Silica sand vs Molding sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com