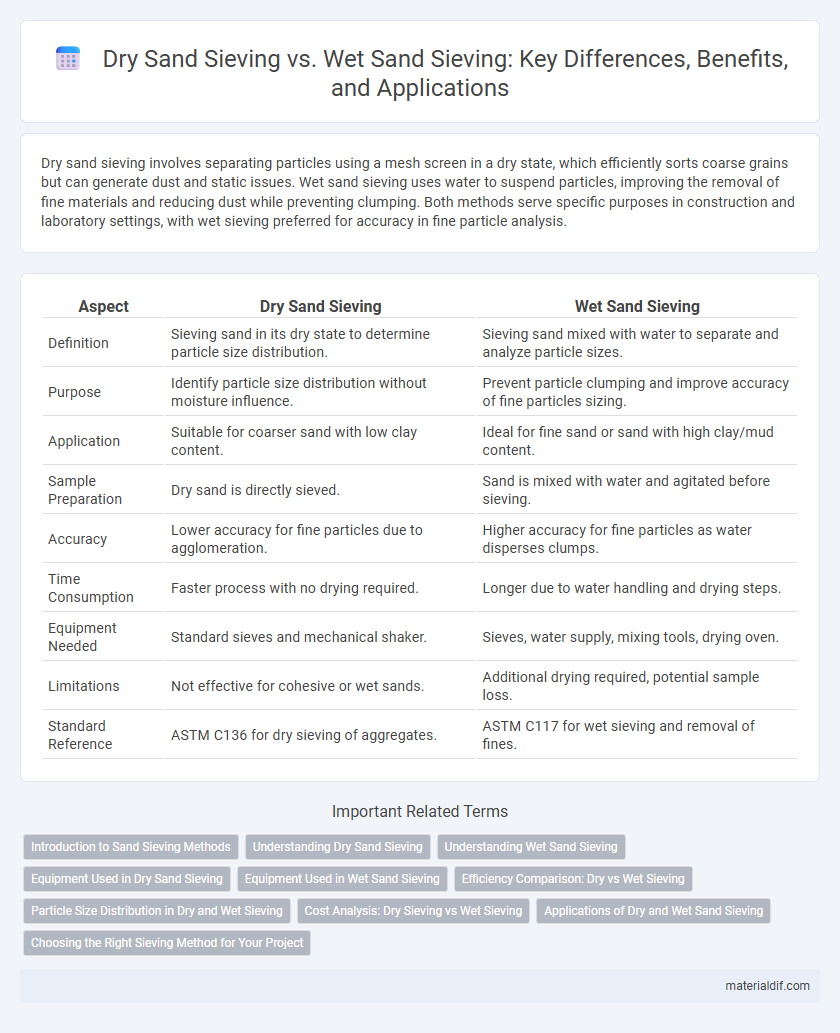
Dry sand sieving involves separating particles using a mesh screen in a dry state, which efficiently sorts coarse grains but can generate dust and static issues. Wet sand sieving uses water to suspend particles, improving the removal of fine materials and reducing dust while preventing clumping. Both methods serve specific purposes in construction and laboratory settings, with wet sieving preferred for accuracy in fine particle analysis.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dry Sand Sieving | Wet Sand Sieving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sieving sand in its dry state to determine particle size distribution. | Sieving sand mixed with water to separate and analyze particle sizes. |
| Purpose | Identify particle size distribution without moisture influence. | Prevent particle clumping and improve accuracy of fine particles sizing. |
| Application | Suitable for coarser sand with low clay content. | Ideal for fine sand or sand with high clay/mud content. |
| Sample Preparation | Dry sand is directly sieved. | Sand is mixed with water and agitated before sieving. |
| Accuracy | Lower accuracy for fine particles due to agglomeration. | Higher accuracy for fine particles as water disperses clumps. |
| Time Consumption | Faster process with no drying required. | Longer due to water handling and drying steps. |
| Equipment Needed | Standard sieves and mechanical shaker. | Sieves, water supply, mixing tools, drying oven. |
| Limitations | Not effective for cohesive or wet sands. | Additional drying required, potential sample loss. |
| Standard Reference | ASTM C136 for dry sieving of aggregates. | ASTM C117 for wet sieving and removal of fines. |
Introduction to Sand Sieving Methods
Dry sand sieving involves passing sand through a mesh screen to separate particles by size without moisture, ensuring quick results and minimal preparation. Wet sand sieving uses water to wash and separate finer particles, reducing dust and improving particle dispersion for more accurate analysis. Both methods are essential in geotechnical and construction applications to determine sand gradation and quality for optimal material performance.
Understanding Dry Sand Sieving
Dry sand sieving involves separating sand particles using a mesh sieve without any moisture, allowing for precise measurement of particle size distribution by preventing clumping or aggregation. This method is crucial in construction and manufacturing industries where accurate sand grading ensures consistent strength and stability of concrete or molding materials. Dry sieving is preferred for its simplicity, speed, and ability to deliver reliable results when assessing dry, free-flowing sand samples.
Understanding Wet Sand Sieving
Wet sand sieving improves particle separation by reducing dust and preventing fine particles from clumping, resulting in more accurate grain size analysis. This method is essential in construction and geotechnical engineering for ensuring soil stability and concrete quality. Utilizing water during sieving enhances the efficiency of separating fine sand particles compared to dry sand sieving.
Equipment Used in Dry Sand Sieving
Dry sand sieving primarily employs mechanical sieves with rigid mesh screens designed to separate particles based on size without moisture interference. Equipment such as vibratory sieve shakers and rotary sifters are commonly used to ensure efficient classification and prevent clumping in dry sand samples. High-quality stainless steel frames and calibrated mesh sizes enhance precision and durability in dry sand sieving operations.
Equipment Used in Wet Sand Sieving
Wet sand sieving utilizes specialized equipment such as slurry tanks, water sprays, and vibrating sieves with corrosion-resistant stainless steel meshes to ensure accurate particle size separation and prevent clogging. High-frequency vibrating sieves equipped with water jets enhance the removal of finer particles, improving classification efficiency in wet sand analysis. This equipment is designed to handle damp or submerged sand samples, providing precise grading essential for construction and industrial applications.
Efficiency Comparison: Dry vs Wet Sieving
Dry sand sieving offers rapid separation with minimal equipment, ideal for coarse particles but may cause dust generation and particle agglomeration. Wet sand sieving improves accuracy by preventing dust and loosening fine particles, enhancing size distribution analysis efficiency. The choice depends on sample characteristics and desired precision, with wet sieving generally preferred for fine or cohesive sands due to superior particle dispersion and reduced sieve clogging.
Particle Size Distribution in Dry and Wet Sieving
Dry sand sieving typically results in a broader particle size distribution due to the presence of dust and fine particles that can inflate smaller size fractions. Wet sand sieving reduces particle agglomeration and dust, leading to a more accurate and narrower particle size distribution by effectively separating finer particles suspended in the water. Measuring particle size distribution via wet sieving provides greater precision for applications requiring uniform grain sizes, such as concrete production and sand grading.
Cost Analysis: Dry Sieving vs Wet Sieving
Dry sand sieving incurs lower upfront equipment costs and reduced water usage, making it more economical for small-scale projects. Wet sand sieving requires investment in water supply and drainage systems, increasing operational expenses, but improves accuracy by preventing particle agglomeration. Cost analysis reveals dry sieving is cost-effective in low-contamination scenarios, while wet sieving justifies higher costs through enhanced precision in fine sand grading.
Applications of Dry and Wet Sand Sieving
Dry sand sieving is ideal for applications requiring precise particle size analysis in construction materials, concrete production, and quality control where moisture presence may interfere with accurate measurement. Wet sand sieving is preferred in mineral processing, environmental testing, and sedimentology to separate fine particles suspended in water, providing clearer differentiation of grain size distributions. Both methods are essential in industries where sand texture and granularity impact product performance and compliance with industry standards.
Choosing the Right Sieving Method for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate sieving method depends on the sand's moisture content and project requirements; dry sand sieving is ideal for free-flowing, dry particles, ensuring rapid particle-size analysis without clumping. Wet sand sieving prevents particle aggregation in fine or moist sand samples, delivering more accurate gradation data critical for concrete mix design and construction standards. Understanding project-specific factors such as sand type, required precision, and testing standards ensures optimal method selection for reliable and consistent results.
Dry Sand Sieving vs Wet Sand Sieving Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com