Industrial sand is primarily used for manufacturing glass, construction materials, and hydraulic fracturing, characterized by its high silica content and uniform grain size. Foundry sand, on the other hand, is specifically selected for metal casting processes, requiring good thermal stability, refractoriness, and the ability to withstand high temperatures without deforming. Both types differ in composition and application, with industrial sand emphasizing purity and uniformity while foundry sand prioritizes heat resistance and molding properties.
Table of Comparison
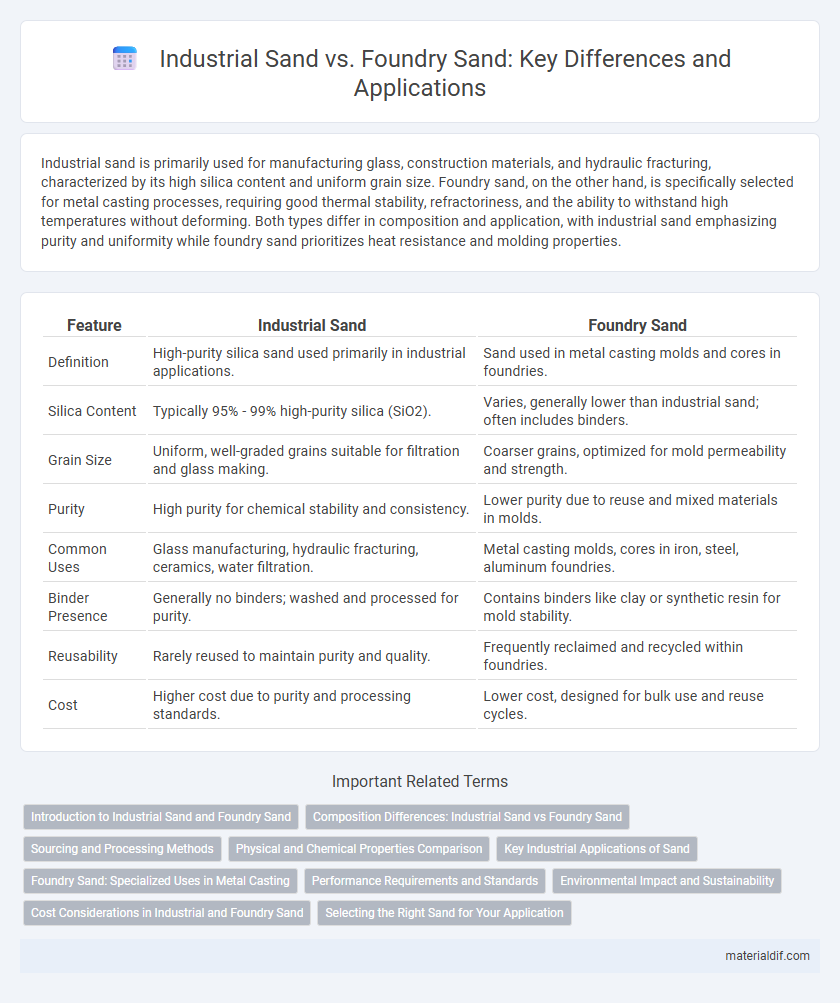
| Feature | Industrial Sand | Foundry Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-purity silica sand used primarily in industrial applications. | Sand used in metal casting molds and cores in foundries. |
| Silica Content | Typically 95% - 99% high-purity silica (SiO2). | Varies, generally lower than industrial sand; often includes binders. |
| Grain Size | Uniform, well-graded grains suitable for filtration and glass making. | Coarser grains, optimized for mold permeability and strength. |
| Purity | High purity for chemical stability and consistency. | Lower purity due to reuse and mixed materials in molds. |
| Common Uses | Glass manufacturing, hydraulic fracturing, ceramics, water filtration. | Metal casting molds, cores in iron, steel, aluminum foundries. |
| Binder Presence | Generally no binders; washed and processed for purity. | Contains binders like clay or synthetic resin for mold stability. |
| Reusability | Rarely reused to maintain purity and quality. | Frequently reclaimed and recycled within foundries. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and processing standards. | Lower cost, designed for bulk use and reuse cycles. |
Introduction to Industrial Sand and Foundry Sand
Industrial sand, primarily composed of high-purity quartz, is essential for manufacturing glass, ceramics, and construction materials due to its consistent grain size and chemical composition. Foundry sand, a specific type of industrial sand, is specialized for metal casting processes, offering properties like high refractoriness and molding strength to withstand molten metal temperatures. Both sands are crucial in their respective industries for ensuring product quality, performance, and efficiency in manufacturing applications.
Composition Differences: Industrial Sand vs Foundry Sand
Industrial sand primarily consists of high-purity quartz grains with uniform particle size, making it ideal for glass manufacturing and hydraulic fracturing. Foundry sand contains a mixture of silica, clay, and other minerals, providing the necessary binding properties for metal casting molds. The distinct compositions influence their performance, with industrial sand emphasizing cleanliness and uniformity, while foundry sand focuses on thermal stability and mold strength.
Sourcing and Processing Methods
Industrial sand, primarily sourced from silica-rich quartz sandstone deposits, undergoes rigorous washing, sorting, and drying to achieve high purity and consistent particle size for use in glassmaking, construction, and hydraulic fracturing. Foundry sand is typically procured from natural or chromite sand quarries and processed through screening, attrition scrubbing, and thermal reclamation to ensure optimal grain shape and strength for molding and casting applications. Both sands require precise extraction and conditioning techniques tailored to their specific industrial functions to maintain material performance standards.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Industrial sand typically consists of high-purity silica with a uniform grain size, low moisture content, and excellent strength, making it suitable for construction and manufacturing applications. Foundry sand, containing higher clay and carbon content, exhibits enhanced bonding properties and thermal stability essential for mold making and casting processes. Chemically, industrial sand has minimal impurities such as iron oxide, whereas foundry sand may contain binders and additives that influence its reusability and performance in metal foundries.
Key Industrial Applications of Sand
Industrial sand is primarily used in hydraulic fracturing for oil and gas extraction, glass manufacturing, and water filtration due to its high silica content and uniform grain size. Foundry sand is specialized for metal casting processes, providing mold stability and heat resistance essential for producing automotive parts, machinery, and industrial equipment. Both types of sand are critical in construction, but their specific applications depend on their physical and chemical properties tailored to distinct industrial needs.
Foundry Sand: Specialized Uses in Metal Casting
Foundry sand, specifically engineered for metal casting, features high silica content and precise grain size distribution to withstand extreme temperatures and metal flow. This sand's exceptional thermal stability and refractoriness ensure defect-free molds, critical in producing intricate metal parts with fine surface finish. Unlike general industrial sand, foundry sand often undergoes reclamation to maintain its properties and reduce environmental impact in casting operations.
Performance Requirements and Standards
Industrial sand must meet strict performance requirements such as high silica content, uniform grain size, and minimal impurities to ensure optimal strength and permeability in construction applications. Foundry sand requires even more rigorous standards, including thermal stability, refractoriness, and grain shape consistency, to withstand high casting temperatures and produce defect-free metal castings. Compliance with ASTM standards like ASTM C144 for industrial sand and ASTM E11 for foundry sand ensures quality control and suitability for specific industrial uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Industrial sand and foundry sand vary significantly in their environmental impact and sustainability profiles. Industrial sand, often sourced from natural deposits, can lead to habitat disruption and groundwater depletion if mined excessively, whereas foundry sand is frequently reclaimed and recycled, reducing waste and minimizing landfilling. Sustainable practices in foundry sand usage, such as reclamation systems and reuse in construction, enhance environmental performance compared to the more extractive nature of industrial sand mining.
Cost Considerations in Industrial and Foundry Sand
Industrial sand generally incurs lower costs compared to foundry sand due to its widespread availability and less stringent quality requirements. Foundry sand demands higher purity and specific grain size distribution, leading to increased processing expenses and higher market prices. Cost considerations in both industrial and foundry sands mainly depend on extraction, processing, and transportation factors, with foundry sand typically reflecting more specialized application-driven investments.
Selecting the Right Sand for Your Application
Industrial sand, typically composed of high-purity quartz, is selected for applications requiring uniform particle size and chemical inertness, such as glass manufacturing and hydraulic fracturing. Foundry sand, often silica-based but mixed with binders, is essential for creating molds in metal casting due to its refractoriness and thermal stability. Choosing between industrial and foundry sand depends on specific attributes like grain size, thermal resistance, and strength to meet the demands of your manufacturing or construction process.
Industrial sand vs Foundry sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com