Molding sand is specifically formulated for shaping and supporting metal castings during the casting process, offering fine grain size and high strength to maintain detailed impressions. Foundry sand, while similar, is a broader category that includes various types of sand used in foundries, often chosen for their refractory properties and durability to withstand high temperatures. The primary difference lies in the precise composition and intended use, with molding sand optimized for surface finish and mold integrity, whereas foundry sand emphasizes thermal resistance and reuse.
Table of Comparison
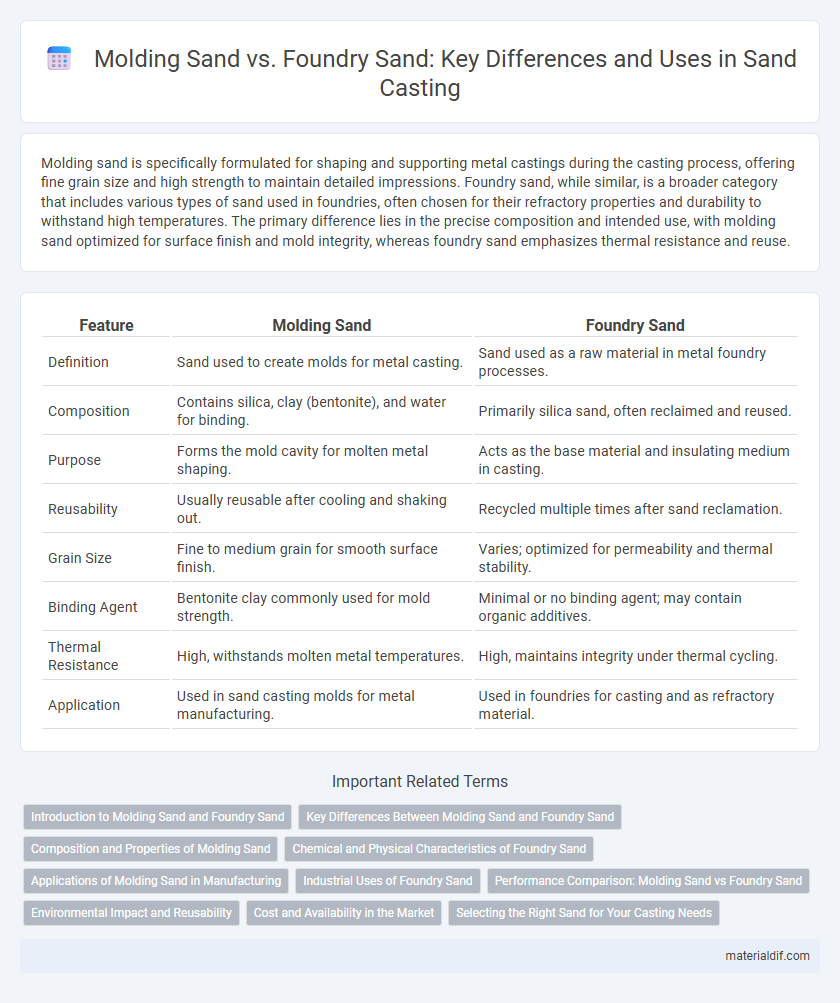
| Feature | Molding Sand | Foundry Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sand used to create molds for metal casting. | Sand used as a raw material in metal foundry processes. |
| Composition | Contains silica, clay (bentonite), and water for binding. | Primarily silica sand, often reclaimed and reused. |
| Purpose | Forms the mold cavity for molten metal shaping. | Acts as the base material and insulating medium in casting. |
| Reusability | Usually reusable after cooling and shaking out. | Recycled multiple times after sand reclamation. |
| Grain Size | Fine to medium grain for smooth surface finish. | Varies; optimized for permeability and thermal stability. |
| Binding Agent | Bentonite clay commonly used for mold strength. | Minimal or no binding agent; may contain organic additives. |
| Thermal Resistance | High, withstands molten metal temperatures. | High, maintains integrity under thermal cycling. |
| Application | Used in sand casting molds for metal manufacturing. | Used in foundries for casting and as refractory material. |
Introduction to Molding Sand and Foundry Sand
Molding sand, primarily used in metal casting processes, is formulated to create precise and durable molds capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures during metal pouring. Foundry sand, a broader category, includes various types such as green sand, resin-bonded sand, and oil sand, each selected based on specific casting requirements like permeability, strength, and surface finish. Understanding the distinct properties and applications of molding sand versus foundry sand is crucial for optimizing casting quality and minimizing defects in metal fabrication industries.
Key Differences Between Molding Sand and Foundry Sand
Molding sand primarily consists of silica sand mixed with clay and water to create a mold that shapes molten metal, offering excellent moldability and surface finish. Foundry sand, typically a high-purity silica sand, is used mainly as a refractory material lining molds and cores, with higher heat resistance and chemical stability. The key differences lie in composition, intended use, and physical properties, with molding sand emphasizing pliability and foundry sand prioritizing thermal resilience.
Composition and Properties of Molding Sand
Molding sand primarily consists of silica sand, clay (commonly bentonite), and water, offering a balance of plasticity and cohesion essential for shaping durable molds. Its fine grain size and moisture content allow it to retain intricate details and resist deformation under metal casting temperatures. Unlike foundry sand, which is optimized for reclamation and thermal stability, molding sand emphasizes workability and surface finish quality to produce precise castings.
Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Foundry Sand
Foundry sand exhibits high silica content, typically above 90%, providing excellent thermal stability and refractoriness crucial for metal casting molds. Its grain size distribution and shape ensure optimal permeability and compactability, essential for gas escape and mold strength during the casting process. Chemical impurities like clay, moisture, and iron oxides are minimal in foundry sand, maintaining consistent physical properties and reducing defects in the final cast product.
Applications of Molding Sand in Manufacturing
Molding sand is primarily used in the casting process to create precise molds for metal components, offering excellent thermal stability and surface finish quality. Its applications include manufacturing automotive parts, machinery components, and complex industrial equipment where accurate replication of patterns is critical. Foundry sand, often silica-based, serves as a reusable base material but lacks the specialized binding properties essential for high-detail molding sand applications.
Industrial Uses of Foundry Sand
Foundry sand is specifically engineered for metal casting applications due to its high purity, grain size, and thermal stability, enhancing mold strength and surface finish quality in foundries. Unlike general molding sand, foundry sand's consistent silica content and refractoriness enable it to withstand extreme temperatures during molten metal pouring without deformation. Industrial uses of foundry sand include creating molds for ferrous and non-ferrous metal castings, core making in automotive and aerospace manufacturing, and producing precision components requiring intricate detail and durability.
Performance Comparison: Molding Sand vs Foundry Sand
Molding sand and foundry sand differ significantly in performance attributes, with molding sand offering superior plasticity and cohesiveness essential for shaping intricate patterns. Foundry sand excels in thermal stability and permeability, ensuring efficient gas escape and maintaining mold integrity during metal casting. The choice between molding and foundry sand directly impacts casting quality, surface finish, and defect reduction in metal fabrication processes.
Environmental Impact and Reusability
Molding sand, primarily composed of clay, silica, and water, often contains additives that can introduce pollutants during casting, affecting local soil and water quality. Foundry sand, repurposed from high-quality silica, offers superior reusability with reduced environmental impact due to its ability to be recycled multiple times without significant degradation. Both sands require proper handling and waste management to minimize ecological footprint, but foundry sand's recyclability makes it a more sustainable choice in metal casting industries.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Molding sand typically offers lower costs due to its widespread availability and common use in basic casting processes, making it suitable for small to medium production runs. Foundry sand, often specially treated or reclaimed for high-performance casting, is generally more expensive but provides superior quality and reusability in industrial applications. Market availability of molding sand is consistently high, while foundry sand supply depends on specialized processing facilities, influencing overall cost and accessibility.
Selecting the Right Sand for Your Casting Needs
Molding sand typically consists of clay, silica, and water, providing excellent cohesiveness and surface finish ideal for detailed patterns, while foundry sand, often high-purity silica sand, offers superior thermal stability and permeability essential for metal casting processes. Selecting the right sand depends on factors such as casting size, metal type, mold complexity, and desired surface texture, where molding sand suits smaller, intricate castings and foundry sand best supports high-temperature metal pours. Understanding the chemical composition, grain size, and bonding properties of each sand type ensures optimal mold strength, dimensional accuracy, and defect-free castings.
Molding sand vs Foundry sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com