Angular sand features sharp, jagged edges that provide excellent interlocking properties, making it ideal for construction and concrete applications requiring strong mechanical bonding. In contrast, round sand has smooth, curved grains that promote better drainage and ease of compaction, often preferred in landscaping and recreational uses such as playgrounds and golf courses. The choice between angular and round sand depends on the specific requirements for stability, water flow, and surface texture in a project.
Table of Comparison
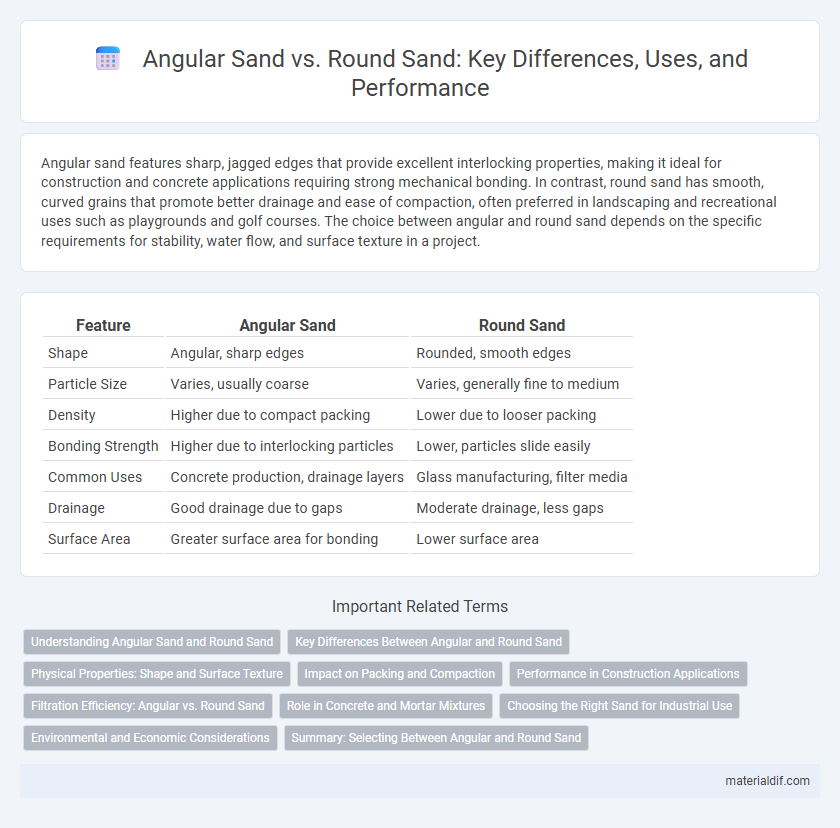
| Feature | Angular Sand | Round Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Angular, sharp edges | Rounded, smooth edges |
| Particle Size | Varies, usually coarse | Varies, generally fine to medium |
| Density | Higher due to compact packing | Lower due to looser packing |
| Bonding Strength | Higher due to interlocking particles | Lower, particles slide easily |
| Common Uses | Concrete production, drainage layers | Glass manufacturing, filter media |
| Drainage | Good drainage due to gaps | Moderate drainage, less gaps |
| Surface Area | Greater surface area for bonding | Lower surface area |
Understanding Angular Sand and Round Sand
Angular sand features sharp, irregularly shaped grains with rough edges, providing superior mechanical bonding in concrete and mortar applications. Round sand consists of smooth, rounded particles formed by natural abrasion, offering better workability but weaker adhesion in construction mixes. Understanding the distinct granulometry and surface texture of angular versus round sand is crucial for optimizing strength and durability in building projects.
Key Differences Between Angular and Round Sand
Angular sand has sharp, irregular edges that provide superior interlocking and stability in construction applications, making it ideal for concrete mixes and asphalt. Round sand features smooth, rounded grains formed by natural weathering, offering better drainage but less binding strength compared to angular sand. The key differences lie in particle shape, compaction ability, and suitability for specific uses such as durable concrete versus drainage layers.
Physical Properties: Shape and Surface Texture
Angular sand particles exhibit sharp edges and rough surfaces, contributing to higher interlocking potential and improved compaction. Round sand particles have smooth, curved surfaces with minimal angularity, resulting in lower internal friction and easier flowability. The surface texture and shape differences significantly impact their suitability for construction and soil stabilization applications.
Impact on Packing and Compaction
Angular sand particles interlock more effectively due to their irregular shapes, resulting in higher packing density and improved compaction strength. Round sand, characterized by smooth and spherical grains, offers lower internal friction, which can reduce stability and increase void spaces during compaction. The choice between angular and round sand significantly affects soil mechanics, influencing load-bearing capacity and settlement behavior in construction applications.
Performance in Construction Applications
Angular sand provides superior mechanical interlocking compared to round sand, enhancing the strength and stability of concrete structures. Round sand, with its smooth and rounded grains, offers better workability but results in lower bonding strength in construction applications. Choosing angular sand improves load-bearing capacity and durability, making it the preferred choice for high-performance building projects.
Filtration Efficiency: Angular vs. Round Sand
Angular sand exhibits higher filtration efficiency compared to round sand due to its irregular, sharp edges which create more void spaces and increase surface area for particle capture. The angular shape enhances mechanical retention of contaminants, making it preferable in filtration systems requiring fine particulate removal. In contrast, round sand's smooth, uniform grains allow faster water flow but reduce filtration effectiveness because of lower particle adhesion.
Role in Concrete and Mortar Mixtures
Angular sand provides superior interlocking and bonding properties in concrete and mortar mixtures, enhancing overall structural strength and durability. Round sand, with its smooth, spherical particles, improves workability and flowability but can reduce the mixture's mechanical strength due to weaker particle interlocking. The choice between angular and round sand directly influences the compressive strength, bonding capacity, and finish quality of concrete and mortar applications.
Choosing the Right Sand for Industrial Use
Angular sand offers superior mechanical interlock and higher load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for concrete and asphalt production in industrial applications. Round sand, characterized by its smooth texture and lower friction, is preferred for filtration systems and foundry molding where flowability is critical. Selecting the right sand depends on factors like intended use, particle shape, and performance requirements within specific industrial processes.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
Angular sand, characterized by its sharp edges and irregular shapes, provides superior compaction and strength, reducing the need for chemical stabilizers and thus lessening environmental impact. Round sand, with its smooth, rounded grains, often requires less energy-intensive processing, making it a more cost-effective option but potentially increasing long-term maintenance expenses due to reduced structural integrity. Choosing between angular and round sand depends on balancing upfront economic costs against environmental sustainability and project durability requirements.
Summary: Selecting Between Angular and Round Sand
Angular sand offers superior interlocking properties and higher surface area, making it ideal for concrete and asphalt mixtures requiring strength and stability. Round sand, characterized by its smooth texture and better flowability, is preferred for applications like plastering and sandblasting where ease of movement is crucial. Choosing between angular and round sand depends on the structural requirements and specific performance needed in construction or industrial processes.
Angular sand vs Round sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com