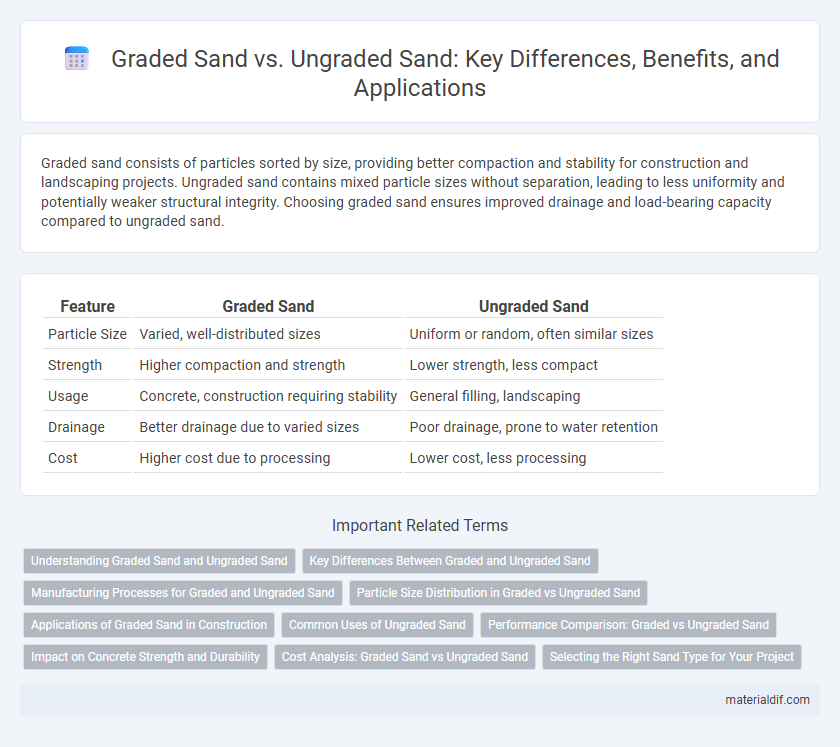
Graded sand consists of particles sorted by size, providing better compaction and stability for construction and landscaping projects. Ungraded sand contains mixed particle sizes without separation, leading to less uniformity and potentially weaker structural integrity. Choosing graded sand ensures improved drainage and load-bearing capacity compared to ungraded sand.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graded Sand | Ungraded Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Varied, well-distributed sizes | Uniform or random, often similar sizes |
| Strength | Higher compaction and strength | Lower strength, less compact |
| Usage | Concrete, construction requiring stability | General filling, landscaping |
| Drainage | Better drainage due to varied sizes | Poor drainage, prone to water retention |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing | Lower cost, less processing |
Understanding Graded Sand and Ungraded Sand
Graded sand consists of a mix of particle sizes that enhances compaction and stability in construction applications, providing better load distribution and reduced voids. Ungraded sand, with uniform particle size, offers consistent texture but may result in weaker bonding and higher porosity. Understanding the gradation of sand is crucial for selecting the right material to optimize strength and durability in concrete or mortar mixes.
Key Differences Between Graded and Ungraded Sand
Graded sand consists of particles sorted by size, ensuring a uniform distribution that enhances compaction and stability in construction applications. Ungraded sand has a random particle size distribution, which can lead to voids and reduced strength in concrete and mortar mixes. The key difference lies in their particle size uniformity, affecting workability, strength, and durability of construction materials.
Manufacturing Processes for Graded and Ungraded Sand
Manufacturing graded sand involves precise screening and washing processes to separate particles into specific size ranges, ensuring uniformity and consistency in grain size distribution. Ungraded sand, produced through minimal processing, undergoes basic washing and coarse filtration without strict particle size separation. Advanced technology in graded sand production enhances performance in construction by providing controlled granulometry, while ungraded sand suits applications requiring less precision and lower production costs.
Particle Size Distribution in Graded vs Ungraded Sand
Graded sand features a well-structured particle size distribution, encompassing a range of sizes from fine to coarse, which improves compaction and stability in construction applications. Ungraded sand consists primarily of particles of similar size, resulting in poor compaction and higher void content. The diverse particle sizes in graded sand create a denser packing arrangement, enhancing load-bearing capacity and reducing permeability compared to ungraded sand.
Applications of Graded Sand in Construction
Graded sand offers a well-defined particle size distribution, making it ideal for concrete, mortar, and plaster applications where strength and durability are critical. Its consistent gradation improves compaction and reduces voids, resulting in enhanced bonding between cement and aggregate. Construction projects such as road bases, bricklaying, and flooring benefit from graded sand due to its ability to provide superior load-bearing capacity and structural integrity.
Common Uses of Ungraded Sand
Ungraded sand is commonly used in landscaping projects, filling low spots in yards, and as a base material for paving stones due to its varied particle sizes that provide good compaction. It's also frequently applied in concrete mixing for non-structural applications and as a backfill material around pipes and utility lines. Its irregular particle distribution helps improve drainage and stability in these practical uses.
Performance Comparison: Graded vs Ungraded Sand
Graded sand, featuring a well-distributed range of particle sizes, typically offers superior compaction and stability compared to ungraded sand, which consists of particles mostly uniform in size. This variation in size distribution in graded sand improves load-bearing capacity and reduces void spaces, enhancing the material's overall strength and durability. Ungraded sand, while easier to work with for some applications, often exhibits lower mechanical performance due to higher permeability and reduced cohesiveness.
Impact on Concrete Strength and Durability
Graded sand, with its well-distributed particle sizes, enhances concrete strength by improving compaction and reducing voids, resulting in a denser and more durable matrix. Ungraded sand, lacking uniform particle size distribution, can lead to higher porosity and weaker bonding within the concrete, compromising overall durability and load-bearing capacity. Concrete mixed with graded sand exhibits superior resistance to cracking and environmental stresses compared to that made with ungraded sand.
Cost Analysis: Graded Sand vs Ungraded Sand
Graded sand typically incurs a higher upfront cost due to its processing and sorting, which ensures particle size uniformity essential for structural applications. Ungraded sand, being less processed, is generally cheaper but may lead to increased material waste and potential quality issues, raising long-term expenses. Evaluating the total cost should consider both initial price and performance efficiency to determine the most economical choice for construction projects.
Selecting the Right Sand Type for Your Project
Choosing the right sand type depends on the specific requirements of your project, with graded sand offering a well-sorted mixture of particle sizes that provides better compaction and stability for concrete and masonry work. Ungraded sand, containing a range of particle sizes without sorting, is suitable for applications where fine grading is less critical, such as fill or backfill. Understanding the particle size distribution and intended use helps ensure optimal strength, durability, and performance in construction tasks.
Graded Sand vs Ungraded Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com