Dry sand is loose and flows easily, making it ideal for activities like building sandcastles or running on the beach. Wet sand, containing moisture, is heavier and sticks together, providing better stability for molding shapes and supporting weight. The presence of water changes the sand's texture and behavior, significantly affecting its usability in construction and recreational purposes.
Table of Comparison
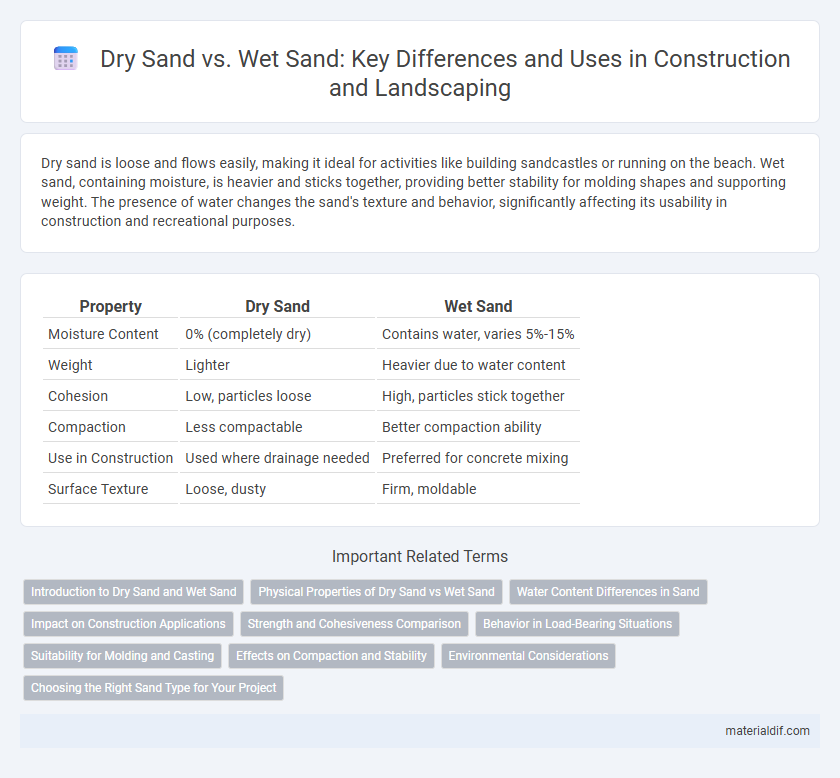
| Property | Dry Sand | Wet Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | 0% (completely dry) | Contains water, varies 5%-15% |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier due to water content |
| Cohesion | Low, particles loose | High, particles stick together |
| Compaction | Less compactable | Better compaction ability |
| Use in Construction | Used where drainage needed | Preferred for concrete mixing |
| Surface Texture | Loose, dusty | Firm, moldable |
Introduction to Dry Sand and Wet Sand
Dry sand consists of granular particles that are free from moisture, offering excellent drainage and strong structural stability ideal for construction and landscaping. Wet sand contains varying amounts of water, which alters its weight, compaction, and cohesive properties, making it essential for applications like concrete mixing and sandcastle building. The presence or absence of moisture fundamentally affects the physical behavior and utility of sand in different engineering and recreational contexts.
Physical Properties of Dry Sand vs Wet Sand
Dry sand consists of individual grains with minimal cohesion, resulting in high permeability, low density, and loose texture that allows air and water to pass through easily. Wet sand exhibits increased cohesion due to surface tension from water film around particles, which reduces permeability, increases density, and enables firmer compaction and stability. The presence of moisture changes the angle of repose and shear strength, making wet sand more suitable for construction and molding applications compared to dry sand.
Water Content Differences in Sand
Dry sand contains minimal water content, typically less than 1%, resulting in loose, free-flowing particles with low cohesion. In contrast, wet sand has higher water content, ranging from about 2% to 6%, which fills the voids between sand grains and increases particle adhesion, enhancing its stability and compaction. The water content in wet sand significantly affects its mechanical properties, influencing applications such as construction, landscaping, and sandcastle building.
Impact on Construction Applications
Dry sand improves workability and cement bonding in construction applications, ensuring easier mixing and stronger adhesion in concrete and mortar. Wet sand increases the risk of uneven curing and weakens structural integrity due to excess moisture interfering with hydration processes. Selecting dry sand is crucial for achieving optimal strength and durability in building foundations and masonry.
Strength and Cohesiveness Comparison
Dry sand exhibits lower cohesiveness and reduced strength due to the absence of moisture acting as a binding agent between particles. Wet sand gains enhanced strength and cohesiveness as water creates surface tension that binds grains together, improving load-bearing capacity. This moisture-induced cohesion makes wet sand ideal for structural applications like sandcastles and foundational bases.
Behavior in Load-Bearing Situations
Dry sand exhibits lower cohesion and increased friction, resulting in less stability under load-bearing conditions. Wet sand gains apparent cohesion due to capillary forces between water and sand grains, enhancing its load-bearing capacity. Optimal moisture levels help wet sand maintain shape and resist deformation better than dry sand in structural applications.
Suitability for Molding and Casting
Dry sand offers superior mold stability and is preferred for casting intricate details due to its lack of moisture, which prevents shrinkage and distortion. Wet sand, containing a precise amount of water, enhances cohesion and compaction, making it suitable for molds requiring higher strength and resistance to collapse during metal pouring. The choice between dry and wet sand depends on the casting process, with dry sand favored for fine finishes and wet sand for heavy-duty molds.
Effects on Compaction and Stability
Dry sand exhibits higher friction between particles, resulting in lower compaction density and reduced stability under load. Wet sand allows water to act as a binding agent, increasing cohesion and compaction but may compromise stability if saturation leads to excess pore water pressure. Optimal moisture content balances these effects, enhancing sand's overall strength and load-bearing capacity.
Environmental Considerations
Dry sand absorbs less water, reducing its ability to support vegetation and increasing erosion risks in coastal and desert environments. Wet sand retains moisture, which helps stabilize soil structure and supports plant roots, promoting biodiversity and reducing dust pollution. Managing sand moisture levels is crucial for maintaining ecosystem balance and preventing habitat degradation.
Choosing the Right Sand Type for Your Project
Choosing between dry sand and wet sand depends largely on the specific requirements of your project; dry sand offers excellent drainage and ease of handling, making it ideal for construction or concrete mixing. Wet sand provides better compaction and stability, which is crucial for laying foundations or creating sand molds in metal casting. Understanding the moisture content and particle consistency of the sand ensures optimal performance and durability in your project.
Dry sand vs Wet sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com