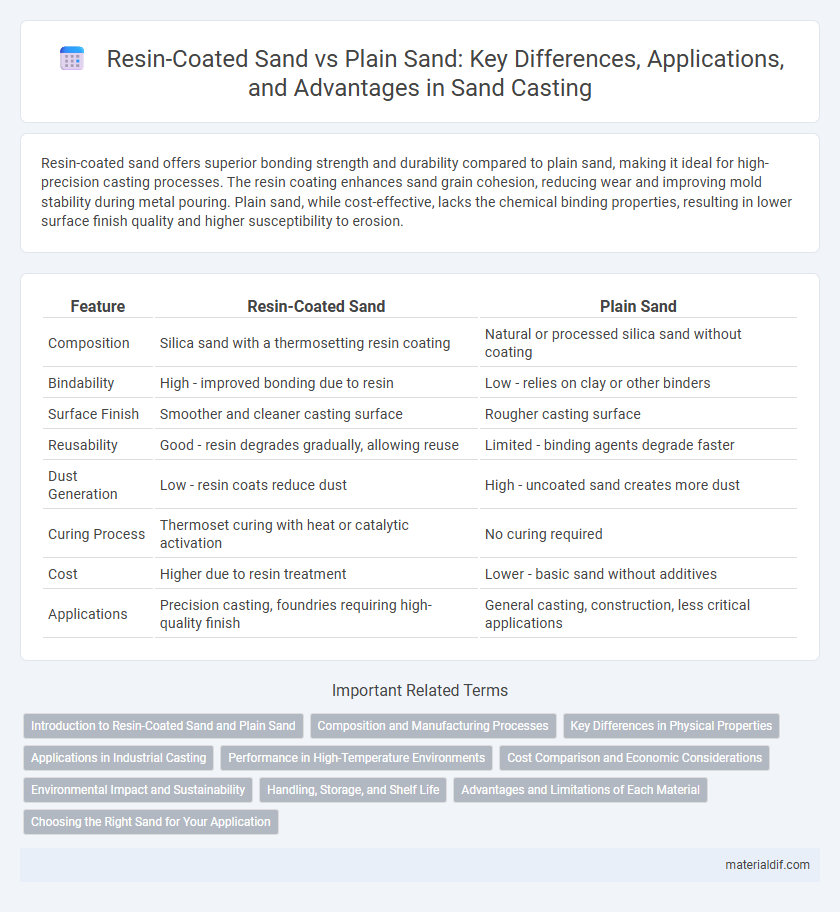
Resin-coated sand offers superior bonding strength and durability compared to plain sand, making it ideal for high-precision casting processes. The resin coating enhances sand grain cohesion, reducing wear and improving mold stability during metal pouring. Plain sand, while cost-effective, lacks the chemical binding properties, resulting in lower surface finish quality and higher susceptibility to erosion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Resin-Coated Sand | Plain Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica sand with a thermosetting resin coating | Natural or processed silica sand without coating |
| Bindability | High - improved bonding due to resin | Low - relies on clay or other binders |
| Surface Finish | Smoother and cleaner casting surface | Rougher casting surface |
| Reusability | Good - resin degrades gradually, allowing reuse | Limited - binding agents degrade faster |
| Dust Generation | Low - resin coats reduce dust | High - uncoated sand creates more dust |
| Curing Process | Thermoset curing with heat or catalytic activation | No curing required |
| Cost | Higher due to resin treatment | Lower - basic sand without additives |
| Applications | Precision casting, foundries requiring high-quality finish | General casting, construction, less critical applications |
Introduction to Resin-Coated Sand and Plain Sand
Resin-coated sand consists of natural sand particles bonded with synthetic resin, enhancing strength and recyclability in foundry applications. Plain sand, or natural silica sand, is uncoated and primarily valued for its high silica content but lacks the enhanced binding properties of resin-coated varieties. The resin coating improves mold stability and reduces defects in casting processes.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Resin-coated sand consists of silica grains bonded with synthetic resin, creating a durable and cohesive material used predominantly in foundry molds, while plain sand is composed of natural silica grains without any binders. The manufacturing process for resin-coated sand involves mixing sand with a polymer resin and curing it under controlled conditions to achieve a uniform coating, enhancing strength and surface finish of molds. In contrast, plain sand requires minimal processing, primarily cleaning and grading, making it less expensive but also less structurally robust for detailed casting applications.
Key Differences in Physical Properties
Resin-coated sand features a smooth surface with enhanced strength and durability due to the resin binder, resulting in higher abrasion resistance compared to plain sand. Plain sand, composed of naturally occurring grains without any binding agent, exhibits lower cohesiveness and is more prone to degradation under mechanical stress. The key physical differences lie in the coated sand's improved flowability, reduced dust generation, and consistent particle size distribution, making it preferable for precise molding applications.
Applications in Industrial Casting
Resin-coated sand is widely preferred in industrial casting due to its superior mold strength and surface finish compared to plain sand, enabling high-precision and complex casting shapes. Plain sand, while cost-effective and abundant, often requires binders and results in rougher surfaces, limiting its use to simpler castings and less demanding industrial applications. The enhanced dimensional accuracy and reduced defects associated with resin-coated sand make it ideal for automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery castings.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Resin-coated sand exhibits superior thermal stability compared to plain sand, maintaining its strength and shape under high-temperature casting conditions. Its enhanced binder properties reduce defects such as sand erosion and cracking during metal solidification. This performance advantage makes resin-coated sand ideal for high-temperature applications in foundry and metal casting industries.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Resin-coated sand generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to plain sand due to the expense of resin materials and the coating process, but it offers enhanced properties like improved strength and reduced defects which can lower overall production costs. Plain sand, while cheaper initially, may lead to increased waste and longer cycle times, impacting cost efficiency in foundry operations. Economic considerations should weigh the balance between initial investment in resin-coated sand and potential savings from improved casting quality and productivity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Resin-coated sand reduces dust emissions and minimizes waste due to its higher reclamation rate compared to plain sand, enhancing sustainability in foundry applications. Unlike plain sand, resin-coated sand's binder systems require fewer processing chemicals and generate less airborne particulate matter, lowering environmental pollution. Efficient reuse of resin-coated sand decreases the need for raw sand extraction, preserving natural resources and reducing ecological disturbance.
Handling, Storage, and Shelf Life
Resin-coated sand offers superior handling and storage advantages compared to plain sand due to its improved flowability and reduced dust generation, minimizing health hazards and equipment wear. It maintains its properties longer during storage, extending shelf life by preventing moisture absorption and clumping, unlike plain sand which degrades quickly under similar conditions. These characteristics make resin-coated sand a more efficient and cost-effective choice for foundry and casting processes.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Material
Resin-coated sand offers superior binding strength and reduced dust, making it ideal for high-precision foundry molds, while plain sand provides better permeability and cost-effectiveness for simpler casting processes. Resin-coated sand improves surface finish and reduces defects but may involve higher material costs and limited recyclability. Plain sand is more environmentally friendly and easier to reuse, yet it can lead to inferior mold stability and increased sand erosion during casting.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Application
Resin-coated sand offers superior strength, enhanced durability, and improved molding precision compared to plain sand, making it ideal for complex casting applications. Plain sand is more cost-effective and suitable for simpler projects where surface finish and dimensional accuracy are less critical. Selecting the right sand depends on factors such as casting complexity, desired surface quality, and budget constraints, with resin-coated sands preferred for high-performance molds.
Resin-Coated Sand vs Plain Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com