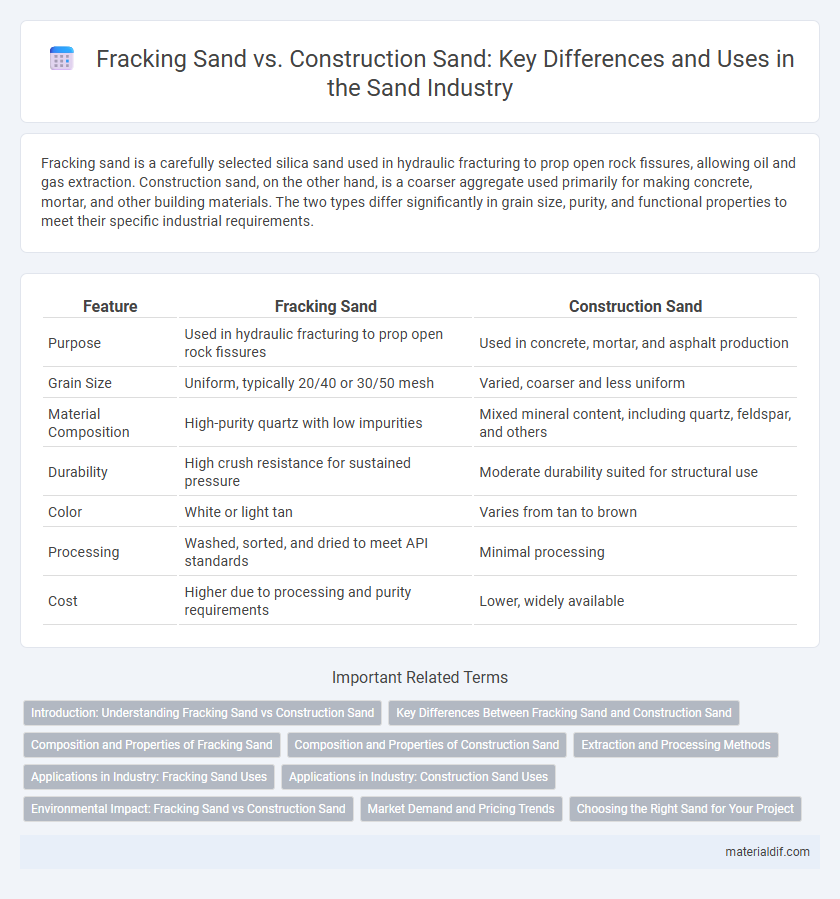
Fracking sand is a carefully selected silica sand used in hydraulic fracturing to prop open rock fissures, allowing oil and gas extraction. Construction sand, on the other hand, is a coarser aggregate used primarily for making concrete, mortar, and other building materials. The two types differ significantly in grain size, purity, and functional properties to meet their specific industrial requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fracking Sand | Construction Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used in hydraulic fracturing to prop open rock fissures | Used in concrete, mortar, and asphalt production |
| Grain Size | Uniform, typically 20/40 or 30/50 mesh | Varied, coarser and less uniform |
| Material Composition | High-purity quartz with low impurities | Mixed mineral content, including quartz, feldspar, and others |
| Durability | High crush resistance for sustained pressure | Moderate durability suited for structural use |
| Color | White or light tan | Varies from tan to brown |
| Processing | Washed, sorted, and dried to meet API standards | Minimal processing |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and purity requirements | Lower, widely available |
Introduction: Understanding Fracking Sand vs Construction Sand
Fracking sand is a high-purity quartz sand with uniform grain size essential for hydraulic fracturing, providing proppant strength and permeability in oil and gas extraction. Construction sand, typically coarser and less uniform, is used for concrete, mortar, and asphalt production, prioritizing durability and compaction properties. Understanding the distinct mineral composition, grain size, and application requirements highlights the specialized roles of fracking sand versus construction sand in industrial processes.
Key Differences Between Fracking Sand and Construction Sand
Fracking sand, also known as frac sand, is primarily composed of high-purity quartz grains with round shapes and high crush resistance, making it ideal for hydraulic fracturing in oil and gas extraction. Construction sand, typically sourced from riverbeds or quarries, often contains a mixture of mineral types and varies in grain size and shape, suited for concrete, mortar, and road base applications. The key differences lie in the grain roundness, silica content, and strength requirements, with fracking sand demanding stringent quality standards for permeability and durability.
Composition and Properties of Fracking Sand
Fracking sand, primarily composed of high-purity quartz grains, exhibits a uniform size, roundness, and high crush resistance essential for withstanding extreme subsurface pressures during hydraulic fracturing. Unlike construction sand, which often contains diverse mineral impurities and irregular shapes suited for general use in concrete and masonry, fracking sand's durability and high silica content (typically over 99% SiO2) ensure optimal permeability and proppant strength. These unique compositional and physical properties enable fracking sand to maintain fracture openness and enhance hydrocarbon extraction efficiency.
Composition and Properties of Construction Sand
Construction sand primarily consists of silica (quartz) grains with angular to sub-angular shapes, contributing to its high strength and stability in concrete and mortar mixes. It typically has a well-graded particle size distribution that enhances compaction and reduces voids, providing durability and resistance to weathering. Unlike fracking sand, construction sand is characterized by higher purity and lower crush resistance, making it ideal for structural applications but less suitable for hydraulic fracturing.
Extraction and Processing Methods
Fracking sand is extracted primarily from high-purity sandstone quarries, undergoing rigorous washing, drying, and sorting to achieve uniform grain size and strength essential for hydraulic fracturing. Construction sand is typically sourced from riverbeds or pits and requires minimal processing, such as simple screening and washing, to remove impurities like clay and silt for use in concrete and masonry. The extraction of fracking sand involves more specialized equipment and environmental controls compared to the relatively straightforward methods used for construction sand.
Applications in Industry: Fracking Sand Uses
Fracking sand, characterized by its high purity and roundness, is primarily used in the oil and gas industry to prop open fractures in shale formations, enhancing hydrocarbon extraction efficiency. Unlike construction sand, which is coarser and irregular, fracking sand's uniform grain size ensures optimal permeability and strength under high pressure during hydraulic fracturing. This specialized sand supports critical industrial processes by maintaining fracture conductivity and preventing collapse, essential for maximizing production rates in fracking operations.
Applications in Industry: Construction Sand Uses
Construction sand, primarily composed of finely crushed quartz, is essential in the building industry for producing concrete, mortar, and asphalt due to its strength and durability. Unlike fracking sand, which must have high purity and spherical shape to withstand subsurface pressures, construction sand is valued for its angular texture that enhances bonding in cement mixes. This versatility makes construction sand a fundamental material for foundations, road bases, and masonry work in infrastructure projects.
Environmental Impact: Fracking Sand vs Construction Sand
Fracking sand, typically sourced from high-purity quartz deposits, involves intensive mining processes that disrupt ecosystems, increase water consumption, and release silica dust, posing significant health risks to workers and nearby communities. Construction sand, often obtained from riverbeds or dunes, can lead to habitat destruction and water table depletion but generally has a lower environmental footprint compared to fracking sand extraction. Sustainable practices and regulatory measures are critical to minimizing the ecological damage associated with both types of sand mining.
Market Demand and Pricing Trends
Fracking sand, used primarily in hydraulic fracturing for energy extraction, has experienced volatile market demand driven by fluctuations in oil and gas production, often commanding higher prices than construction sand due to its specific grain size and purity requirements. Construction sand, essential in concrete, asphalt, and building materials, maintains a relatively stable demand linked to global infrastructure development, typically priced lower than fracking sand because of its broader availability and lesser processing needs. Pricing trends show fracking sand markets are heavily influenced by energy sector dynamics, while construction sand pricing correlates more closely with urbanization and real estate growth patterns.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Project
Fracking sand, characterized by its high quartz content and uniform round grains, ensures optimal permeability and strength for hydraulic fracturing operations, while construction sand prioritizes durability and angularity for concrete and masonry stability. Choosing the right sand depends on project requirements such as grain size, shape, and chemical purity to maximize performance and cost-efficiency. Evaluating the specific mechanical and chemical properties of fracking sand versus construction sand is essential for structural integrity and operational success.
Fracking sand vs Construction sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com