Foundry sand is a specialized type of sand used in metal casting molds due to its high heat resistance and grain shape, which ensures precise mold formation and smooth surface finishes. Construction sand, on the other hand, is coarser and primarily utilized in concrete production and building applications for its strength and durability. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right sand based on thermal properties and structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
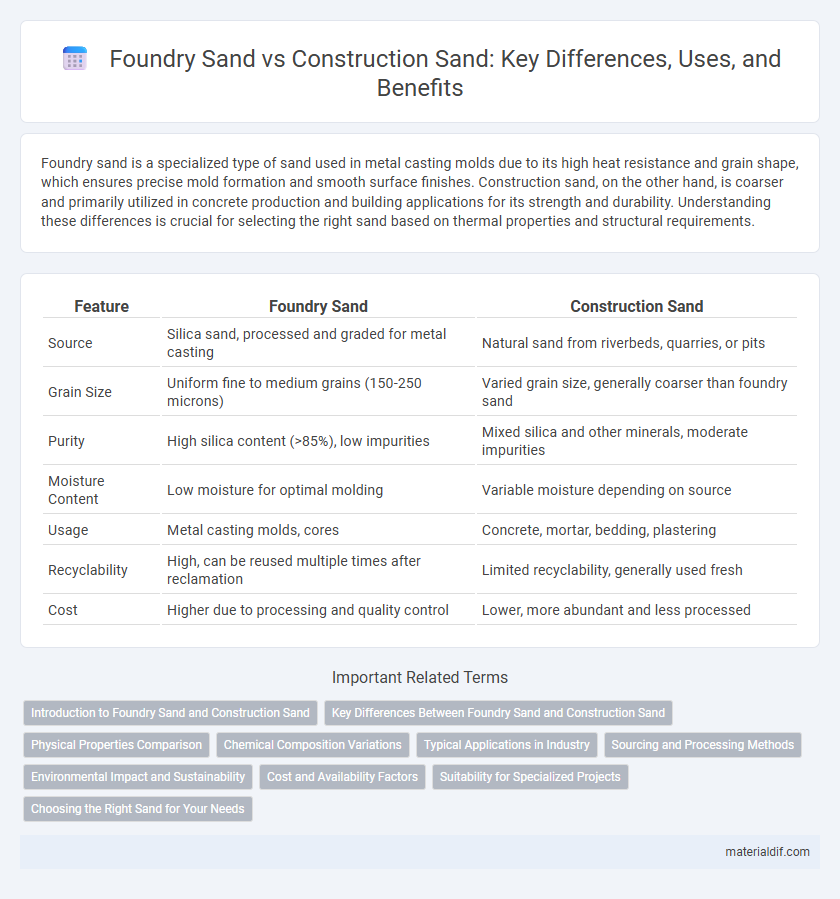
| Feature | Foundry Sand | Construction Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Silica sand, processed and graded for metal casting | Natural sand from riverbeds, quarries, or pits |
| Grain Size | Uniform fine to medium grains (150-250 microns) | Varied grain size, generally coarser than foundry sand |
| Purity | High silica content (>85%), low impurities | Mixed silica and other minerals, moderate impurities |
| Moisture Content | Low moisture for optimal molding | Variable moisture depending on source |
| Usage | Metal casting molds, cores | Concrete, mortar, bedding, plastering |
| Recyclability | High, can be reused multiple times after reclamation | Limited recyclability, generally used fresh |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and quality control | Lower, more abundant and less processed |
Introduction to Foundry Sand and Construction Sand
Foundry sand, characterized by its high silica content and grain shape, is specifically engineered for mold casting in metal foundries, offering excellent thermal stability and refractoriness. Construction sand, typically composed of natural quartz grains or manufactured quartz, is optimized for concrete, mortar, and asphalt applications, providing essential strength and durability. Understanding the distinct physical and chemical properties of foundry sand versus construction sand is crucial for selecting the right aggregate in industrial and building projects.
Key Differences Between Foundry Sand and Construction Sand
Foundry sand is specifically engineered with high silica content and precise grain size for metal casting molds, ensuring thermal stability and permeability, while construction sand typically has a wider grain size distribution suitable for concrete and mortar applications. Foundry sand undergoes rigorous testing for chemical composition and grain shape to withstand high temperatures, unlike construction sand, which prioritizes strength and workability in structural builds. The key differences lie in their intended use, composition, and physical properties tailored to meet industry-specific requirements.
Physical Properties Comparison
Foundry sand exhibits a higher grain size uniformity and thermal stability compared to construction sand, making it ideal for mold making in metal casting. Construction sand typically has a wider particle size distribution and higher impurity levels, affecting its compaction and load-bearing capacity. The angularity and silica content of foundry sand contribute to its superior permeability and refractoriness, critical for metal solidification processes.
Chemical Composition Variations
Foundry sand typically contains higher silica content (SiO2) around 85-95%, along with minor amounts of alumina (Al2O3) and iron oxide (Fe2O3), providing high thermal stability necessary for metal casting molds. Construction sand, also known as concrete sand, often features a more varied mineral composition with lower silica levels and higher quantities of feldspar, calcium carbonate, and other impurities, affecting its strength and binding properties. These chemical composition variations influence the suitability of each sand type for specific industrial applications, where foundry sand's purity ensures mold integrity, while construction sand supports structural bonding.
Typical Applications in Industry
Foundry sand is primarily used in metal casting industries due to its high thermal stability and fine grain structure, which ensures precise mold formation and smooth metal surfaces. Construction sand, typically coarser and less uniform, is widely applied in concrete production, mortar mixing, and groundwork for infrastructure projects. Each type's granularity and composition dictate its specific suitability for industrial tasks requiring different strength, permeability, and heat resistance characteristics.
Sourcing and Processing Methods
Foundry sand is typically sourced from high-purity silica deposits and undergoes rigorous processing methods such as washing, drying, and screening to meet specific particle size and chemical composition requirements essential for metal casting. Construction sand is often sourced from riverbeds, quarries, or marine environments and generally requires simpler processing, including basic washing and grading, to ensure proper texture and strength for concrete and masonry applications. The distinct sourcing and processing techniques reflect the specialized performance criteria of foundry sand compared to the broader, structural role of construction sand.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foundry sand, often reclaimed and recycled within industrial processes, typically presents lower environmental impact compared to construction sand, which is extracted in large quantities from natural sources leading to significant habitat disruption and resource depletion. The reuse of foundry sand reduces landfill waste and conserves natural sand reserves, enhancing sustainability in metal casting industries. In contrast, sustainable construction practices are increasingly promoting alternatives like manufactured sand and recycled aggregates to mitigate the ecological footprint associated with traditional construction sand mining.
Cost and Availability Factors
Foundry sand typically costs more than construction sand due to its specialized properties and stringent quality requirements suited for metal casting processes. Construction sand is more widely available and less expensive, as it is sourced from common riverbeds and quarries for general building purposes. Availability of foundry sand is often limited by strict environmental regulations and recycling practices, impacting overall cost efficiency.
Suitability for Specialized Projects
Foundry sand, characterized by its high silica content and refractoriness, is highly suitable for specialized casting projects requiring precise mold properties and high-temperature resistance. Construction sand, typically coarser with varying compositions, is better suited for structural applications like concrete and mortar but lacks the refined qualities needed for precision foundry work. The distinct particle size distribution and chemical purity of foundry sand ensure optimal performance in specialized industrial processes compared to the broader versatility of construction sand.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Needs
Foundry sand, known for its high silica content and thermal stability, is specially designed for metal casting processes requiring precise mold performance and heat resistance. Construction sand, with its coarser texture and angular grains, is ideal for concrete production, masonry work, and infrastructure projects due to its excellent binding properties and structural support. Selecting the right sand depends on factors like grain size, purity, and application requirements to ensure optimal strength, durability, and performance in your specific industry.
Foundry sand vs Construction sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com