Foundry sand is specifically engineered for high-temperature applications and molds in metal casting, offering excellent thermal stability and refractory properties. Glass sand, primarily composed of high-purity silica, is used in the manufacturing of glass products due to its low impurity levels and consistent grain size that ensures clarity and strength in the final glass. Both types of sand serve distinct industrial purposes, with foundry sand optimized for metal molding and glass sand tailored for glassmaking processes.
Table of Comparison
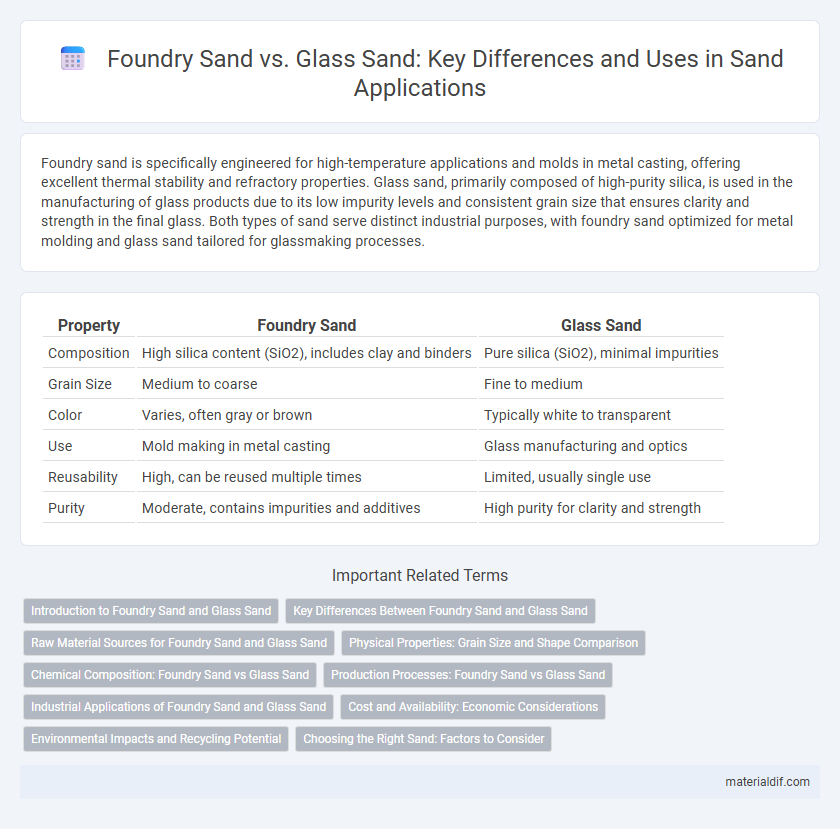
| Property | Foundry Sand | Glass Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High silica content (SiO2), includes clay and binders | Pure silica (SiO2), minimal impurities |
| Grain Size | Medium to coarse | Fine to medium |
| Color | Varies, often gray or brown | Typically white to transparent |
| Use | Mold making in metal casting | Glass manufacturing and optics |
| Reusability | High, can be reused multiple times | Limited, usually single use |
| Purity | Moderate, contains impurities and additives | High purity for clarity and strength |
Introduction to Foundry Sand and Glass Sand
Foundry sand is specifically processed silica sand used in metal casting molds to shape molten metals, valued for its high thermal resistance and grain shape that supports excellent mold permeability. Glass sand, primarily composed of high-purity silica, is essential in the manufacture of glass products, offering a uniform grain size and low iron content to ensure clarity and strength in the final glass. Both types of sand are crucial industrial materials but differ significantly in their physical characteristics and applications.
Key Differences Between Foundry Sand and Glass Sand
Foundry sand is specifically processed for metal casting and possesses high refractoriness, fine grain size, and excellent molding properties, whereas glass sand is primarily composed of high-purity silica essential for producing clear, durable glass products. Foundry sand contains binders like clay or resin to maintain shape during casting, while glass sand requires minimal impurities such as iron oxide to ensure translucency. The key differences lie in their mineral composition, grain characteristics, and intended industrial applications.
Raw Material Sources for Foundry Sand and Glass Sand
Foundry sand is primarily sourced from high-purity silica deposits found in sandstone and quartz-rich beach sands, emphasizing angular grains ideal for metal casting molds. Glass sand, on the other hand, is extracted from silica sand deposits with exceptionally low iron and other impurities, predominantly from quartz-rich sandstone formations or riverbeds. The raw material quality impacts the thermal and chemical properties essential for foundry molds and glass manufacturing, driving distinct sourcing criteria.
Physical Properties: Grain Size and Shape Comparison
Foundry sand typically exhibits a coarser grain size ranging from 0.1 to 1 mm with angular, irregular shapes that enhance mold strength and permeability. Glass sand features finer grains, about 0.02 to 0.5 mm, with smoother, more rounded particles that improve glass melting and clarity. The distinct differences in grain size and shape between foundry sand and glass sand are critical for their respective applications in metal casting and glass manufacturing.
Chemical Composition: Foundry Sand vs Glass Sand
Foundry sand primarily consists of high-purity silica (SiO2) around 85-95% with minor amounts of alumina (Al2O3) and iron oxides, optimized for thermal stability and binding during metal casting; glass sand, also rich in silica (above 95%), contains low levels of iron oxide to prevent discoloration and includes additional minerals like soda ash and lime to aid in melting and glass formation. The chemical composition of foundry sand is tailored to withstand high temperatures without reacting with molten metals, while glass sand's composition prioritizes purity and fluxing agents to produce clear, uniform glass. Variations in minor elements such as Fe2O3 directly affect the suitability of each sand type for their respective industrial applications.
Production Processes: Foundry Sand vs Glass Sand
Foundry sand undergoes a molding process where high-purity silica sand is mixed with binders to create molds capable of withstanding extreme temperatures during metal casting. Glass sand production requires precise beneficiation steps including washing, screening, and acid leaching to achieve the high silica content and low impurities essential for clarity in glass manufacturing. The foundry sand's process emphasizes thermal stability and binders, while glass sand production prioritizes purity and chemical composition for optical quality.
Industrial Applications of Foundry Sand and Glass Sand
Foundry sand, primarily composed of high-purity silica, is engineered for metal casting applications due to its high thermal stability and refractory properties, enabling precise molding of metal parts in industries such as automotive and aerospace. Glass sand, characterized by its uniform grain size and chemical purity, is essential for manufacturing high-quality glass products including windows, bottles, and fiberglass, where clarity and strength are critical. Both foundry and glass sands play crucial roles in industrial processes, with foundry sand focusing on mold creation and heat resistance, and glass sand optimized for melting efficiency and final product quality.
Cost and Availability: Economic Considerations
Foundry sand is generally more expensive than glass sand due to its specialized processing and high-quality refractory properties, which are critical for metal casting applications. Glass sand, primarily composed of high-purity silica, is more abundantly available and less costly, making it a preferred choice for large-scale glass manufacturing. The price difference reflects not only the raw material sourcing but also the treatment and handling requirements specific to each type of sand.
Environmental Impacts and Recycling Potential
Foundry sand, composed primarily of silica and used in metal casting, generates waste with potential heavy metal contamination requiring careful disposal to prevent soil and water pollution. Glass sand, typically higher-purity silica used in glass manufacturing, offers greater recycling potential as cullet can be melted and remolded, reducing raw material extraction and energy consumption. Both sands impact the environment differently; foundry sand's limited recyclability raises landfill concerns, while glass sand supports circular economy practices through efficient recovery and reuse.
Choosing the Right Sand: Factors to Consider
Foundry sand boasts high refractoriness and thermal stability, making it ideal for metal casting molds that require precision and durability. Glass sand, characterized by its high silica content and purity, is optimized for producing clear, strong glass with minimal impurities. When selecting the right sand, consider factors such as grain size, composition, thermal resistance, and the specific industrial application to ensure optimal performance and quality.
Foundry sand vs Glass sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com