Desert sand tends to be finer, more rounded, and uniformly sized due to constant wind erosion, making it less suitable for construction purposes. Beach sand is coarser, contains more varied mineral compositions, and often includes shell fragments, resulting from water's natural sorting action. Understanding these differences is crucial for applications in landscaping, concrete production, and ecological studies.
Table of Comparison
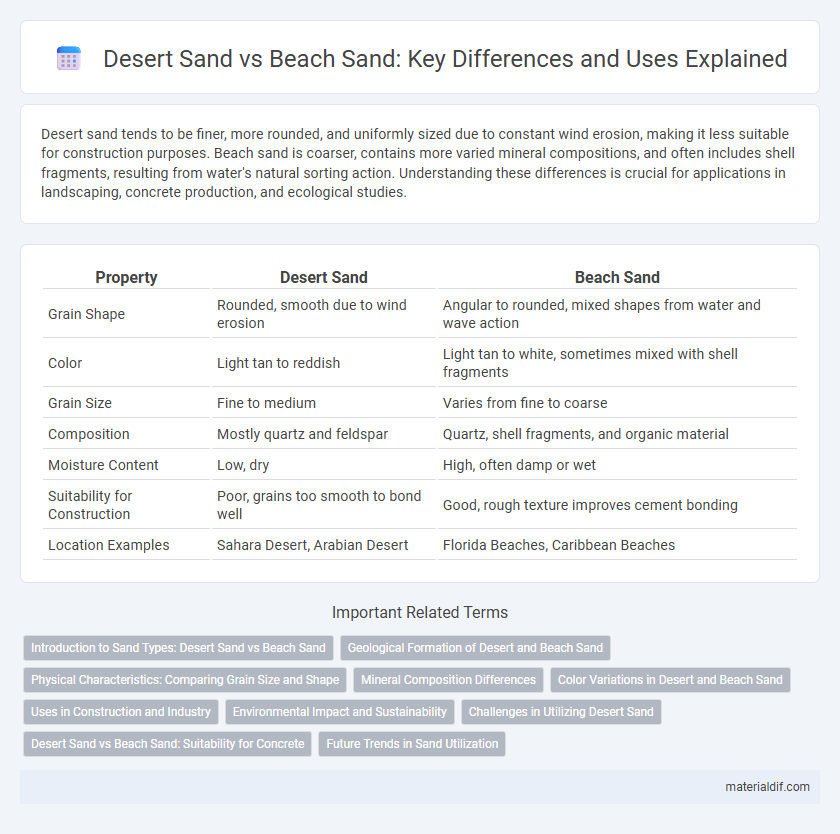
| Property | Desert Sand | Beach Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Shape | Rounded, smooth due to wind erosion | Angular to rounded, mixed shapes from water and wave action |
| Color | Light tan to reddish | Light tan to white, sometimes mixed with shell fragments |
| Grain Size | Fine to medium | Varies from fine to coarse |
| Composition | Mostly quartz and feldspar | Quartz, shell fragments, and organic material |
| Moisture Content | Low, dry | High, often damp or wet |
| Suitability for Construction | Poor, grains too smooth to bond well | Good, rough texture improves cement bonding |
| Location Examples | Sahara Desert, Arabian Desert | Florida Beaches, Caribbean Beaches |
Introduction to Sand Types: Desert Sand vs Beach Sand
Desert sand primarily consists of fine, well-rounded grains shaped by wind erosion, resulting in smooth, uniform particles with high silica content. Beach sand typically contains a mix of quartz, shell fragments, and various minerals, leading to coarser, more angular grains shaped by water action. Understanding the distinct composition and texture of these sand types is crucial for applications in construction, landscaping, and environmental studies.
Geological Formation of Desert and Beach Sand
Desert sand forms primarily through the weathering and erosion of rocks in arid environments, characterized by wind-driven processes that create well-rounded, fine grains with a high quartz content. Beach sand results from the mechanical breakdown of rocks and shells by wave action, leading to coarser, more angular grains composed of a mix of quartz, feldspar, and biogenic materials. The distinct geological formations reflect the contrasting depositional environments, with desert sand shaped by aeolian forces and beach sand influenced by hydraulic dynamics.
Physical Characteristics: Comparing Grain Size and Shape
Desert sand grains are typically finer and more rounded due to prolonged wind erosion, resulting in smoother particles compared to beach sand. Beach sand grains tend to be coarser and more angular because they are constantly broken down by wave action and tidal forces. The grain size and shape differences significantly affect sediment transport and soil permeability in their respective environments.
Mineral Composition Differences
Desert sand primarily consists of quartz grains with a high degree of angularity due to wind erosion, leading to a more uniform mineral composition. Beach sand contains a diverse mixture of minerals, including quartz, feldspar, and shell fragments, influenced by wave action and marine organisms. The distinct mineralogy of desert sand results in coarser texture, while beach sand is finer and often richer in calcium carbonate.
Color Variations in Desert and Beach Sand
Desert sand typically exhibits warm hues such as golden yellow, reddish-brown, and orange due to iron oxide and mineral content, while beach sand often varies in color from white and pale tan to dark gray or black, influenced by the presence of quartz, shell fragments, and volcanic minerals. The bright, uniform colors of desert sand reflect the arid environment and the dominance of weathered rock particles, whereas beach sand's color diversity results from constant wave action and diverse mineral sources. These color variations not only indicate the geological composition but also the environmental processes shaping each sand type.
Uses in Construction and Industry
Desert sand, characterized by its fine, rounded grains, is generally unsuitable for construction due to poor compaction and weak bonding properties, limiting its use in concrete and masonry. Beach sand, with its coarser texture and higher mineral content, is preferred in construction because it provides better strength and durability for concrete mixes and industrial applications. Industrially, beach sand's consistent grain size and composition make it suitable for glass manufacturing and foundry molds, whereas desert sand's lack of angularity reduces its efficacy in these sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Desert sand typically has fine, smooth grains that are less suitable for construction, often leading to increased extraction of beach sand, which disrupts coastal ecosystems and accelerates erosion. Beach sand extraction directly impacts marine biodiversity by destroying habitats of numerous species and increasing vulnerability to storm surges. Sustainable alternatives, such as recycled construction materials or manufactured sand, reduce dependency on natural sand sources and mitigate environmental degradation.
Challenges in Utilizing Desert Sand
Desert sand poses significant challenges for construction due to its fine, rounded grains that lack the angularity required for strong bonding in concrete mixtures. Unlike beach sand, which contains coarser, more angular particles and natural salts aiding cohesion, desert sand often leads to weaker structural integrity and increased material usage. The scarcity of suitable desert sand complicates sustainable development in arid regions, necessitating innovative processing techniques for effective utilization.
Desert Sand vs Beach Sand: Suitability for Concrete
Desert sand particles are typically smooth, rounded, and fine, making them less suitable for concrete as they reduce the bonding strength with cement. Beach sand contains salt and organic materials, which can cause corrosion and weaken concrete structures if not properly washed. For concrete production, river sand or specially processed beach sand is preferred over desert sand to ensure optimal strength and durability.
Future Trends in Sand Utilization
Desert sand, characterized by its fine, angular grains, is increasingly being explored for use in sustainable construction materials due to its high silica content and abundance, contrasting with the coarser, rounded grains of beach sand that often suffer from environmental extraction regulations. Innovations in industrial applications are driving research into desert sand's potential in 3D printing concrete and high-strength composites, addressing global shortages of suitable sand for infrastructure development. Future trends indicate a shift towards maximizing desert sand utilization through advanced processing techniques to reduce environmental impacts while meeting escalating demand in urbanization and green building initiatives.
Desert Sand vs Beach Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com