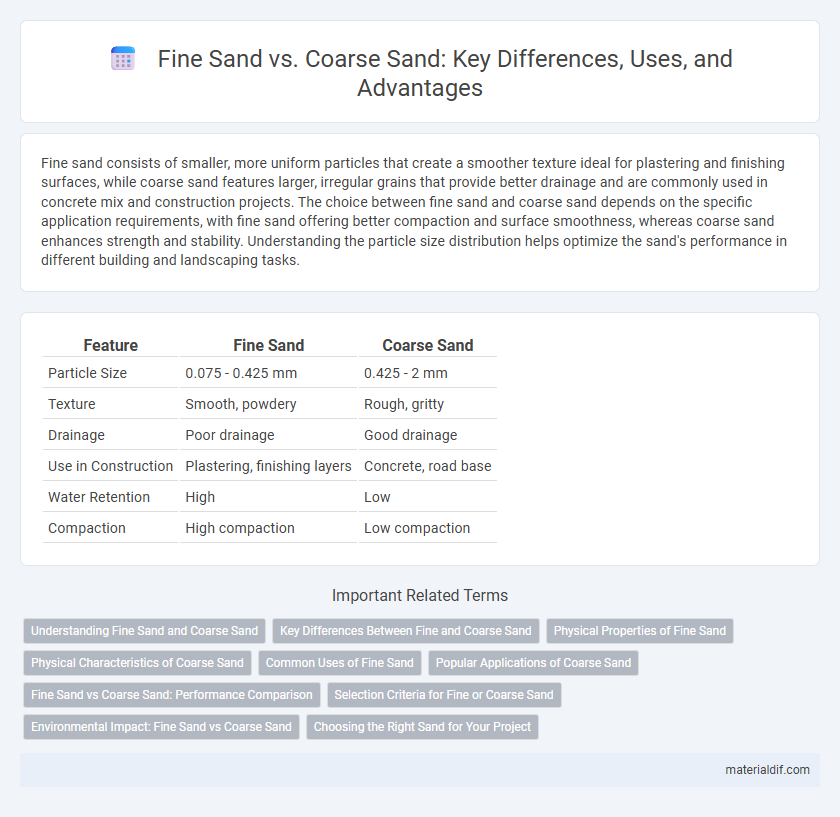
Fine sand consists of smaller, more uniform particles that create a smoother texture ideal for plastering and finishing surfaces, while coarse sand features larger, irregular grains that provide better drainage and are commonly used in concrete mix and construction projects. The choice between fine sand and coarse sand depends on the specific application requirements, with fine sand offering better compaction and surface smoothness, whereas coarse sand enhances strength and stability. Understanding the particle size distribution helps optimize the sand's performance in different building and landscaping tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fine Sand | Coarse Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 0.075 - 0.425 mm | 0.425 - 2 mm |
| Texture | Smooth, powdery | Rough, gritty |
| Drainage | Poor drainage | Good drainage |
| Use in Construction | Plastering, finishing layers | Concrete, road base |
| Water Retention | High | Low |
| Compaction | High compaction | Low compaction |
Understanding Fine Sand and Coarse Sand
Fine sand consists of small, smooth particles typically ranging from 0.05 to 0.25 millimeters in diameter, making it ideal for detailed plastering and masonry work due to its ability to produce a smooth finish. Coarse sand, with particle sizes between 0.5 and 2 millimeters, offers better drainage and structural strength, making it suitable for concrete mixing and foundation laying. Understanding the particle size and texture differences between fine and coarse sand is crucial for selecting the right material in construction and landscaping projects.
Key Differences Between Fine and Coarse Sand
Fine sand consists of smaller particles typically less than 0.25 millimeters in diameter, providing a smoother texture and better compaction for concrete and plaster applications. Coarse sand features larger particles usually between 0.25 to 2 millimeters, offering superior drainage and strength in construction projects like masonry and road building. The key differences lie in particle size, texture, water retention, and suitability for specific construction and landscaping purposes.
Physical Properties of Fine Sand
Fine sand consists of smaller grain sizes ranging from 0.075 to 0.425 millimeters, resulting in a smooth texture and higher surface area compared to coarse sand. Its particles have greater cohesion and compaction ability, making fine sand ideal for use in concrete, plastering, and masonry work where a dense and strong mix is required. The porosity of fine sand is lower than that of coarse sand, which reduces water permeability and enhances the material's binding properties in construction applications.
Physical Characteristics of Coarse Sand
Coarse sand is characterized by larger grain size, typically ranging from 0.5 mm to 2 mm in diameter, which results in a rough texture and higher permeability compared to fine sand. Its irregularly shaped particles create more voids, enhancing drainage and reducing water retention in construction applications. These physical properties make coarse sand ideal for concrete mixes, road bases, and drainage layers where strength and stability are crucial.
Common Uses of Fine Sand
Fine sand is commonly used in construction for plastering walls, providing a smooth finish essential for painting and wallpaper application. It plays a crucial role in making concrete and mortar mixes, improving workability and strength. Landscaping projects also utilize fine sand for leveling surfaces and enhancing soil drainage.
Popular Applications of Coarse Sand
Coarse sand is widely used in construction for concrete production due to its superior strength and durability compared to fine sand. It is also popular in road base layers and drainage systems, where its larger particle size enhances stability and water flow. Landscaping projects often utilize coarse sand to improve soil aeration and prevent compaction.
Fine Sand vs Coarse Sand: Performance Comparison
Fine sand features smaller particle size, resulting in higher surface area and better compaction, which enhances strength and smoothness in masonry work. Coarse sand, with larger grains, provides superior drainage and reduces shrinkage in concrete applications, improving structural durability. Performance differences depend on project requirements, with fine sand suited for plastering and fine finishing, while coarse sand excels in concrete and foundational mixes.
Selection Criteria for Fine or Coarse Sand
Selection criteria for fine or coarse sand primarily depend on the intended construction application and desired structural properties. Fine sand, characterized by particle sizes typically less than 0.5 mm, is preferred for plastering and masonry due to its smooth texture and better compaction, whereas coarse sand with particle sizes ranging from 0.5 mm to 2 mm is favored in concrete production for enhanced strength and reduced shrinkage. The choice also hinges on factors such as gradation, purity, moisture content, and compatibility with cement to ensure optimal bonding and durability.
Environmental Impact: Fine Sand vs Coarse Sand
Fine sand, characterized by smaller particles and higher surface area, tends to retain more water and nutrients, which can affect soil permeability and contribute to localized moisture retention but may lead to compacted soil issues. Coarse sand, with larger particles and better drainage, enhances aeration and reduces waterlogging risks, promoting healthier root growth and minimizing erosion potential. Environmentally, coarse sand extraction often causes greater habitat disruption and sediment displacement compared to fine sand, making sustainable sourcing practices critical for both types.
Choosing the Right Sand for Your Project
Fine sand offers a smooth texture ideal for plastering and masonry work, providing better workability and surface finish. Coarse sand, with its larger particles, enhances strength and drainage, making it suitable for concrete and road construction. Selecting the right sand depends on project requirements such as desired strength, texture, and environmental conditions.
Fine Sand vs Coarse Sand Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com