Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, elasticity, and load-bearing capacity compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for demanding applications like seals and gaskets. Chloroprene rubber, also known as neoprene, excels in chemical stability and weather resistance, providing excellent performance in automotive and industrial products exposed to oils and outdoor conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the specific requirements for durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure in each application.
Table of Comparison
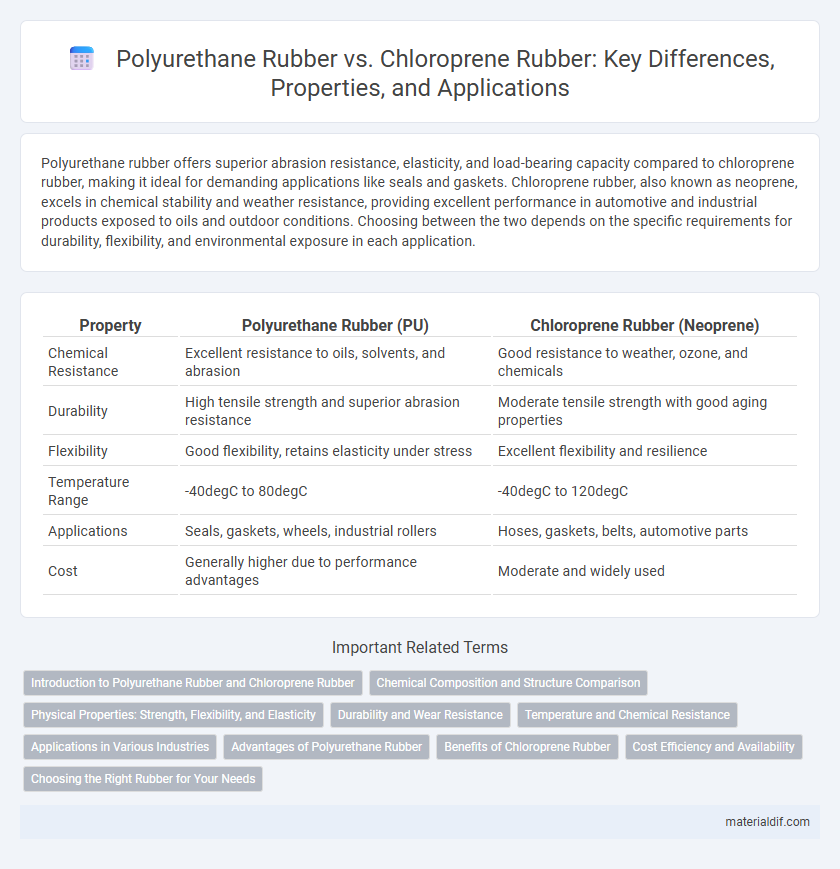
| Property | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) | Chloroprene Rubber (Neoprene) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and abrasion | Good resistance to weather, ozone, and chemicals |
| Durability | High tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength with good aging properties |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, retains elasticity under stress | Excellent flexibility and resilience |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, wheels, industrial rollers | Hoses, gaskets, belts, automotive parts |
| Cost | Generally higher due to performance advantages | Moderate and widely used |
Introduction to Polyurethane Rubber and Chloroprene Rubber
Polyurethane rubber is a versatile elastomer known for its exceptional abrasion resistance, elasticity, and resistance to oil and solvents, making it ideal for industrial applications such as seals, gaskets, and wheels. Chloroprene rubber, commonly referred to as Neoprene, offers excellent chemical stability, weather resistance, and flame retardancy, widely used in automotive parts, hoses, and protective gear. Both materials deliver specialized performance properties tailored to distinct operational environments, with polyurethane excelling in mechanical durability and chloroprene providing strong environmental resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyurethane rubber consists of segmented block copolymers with alternating soft and hard segments, providing high abrasion resistance and elasticity due to its urethane linkages formed from polyols and diisocyanates. Chloroprene rubber, composed of polychloroprene chains derived from chloroprene monomers, exhibits strong chemical stability and weather resistance attributed to chlorine atoms in its backbone. The chemical structure of polyurethane offers superior mechanical flexibility, while chloroprene's carbon-chlorine bonds deliver enhanced resistance to oils and chemicals.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Elasticity
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability. Chloroprene rubber offers excellent flexibility and good elasticity over a wide temperature range, providing reliable performance in dynamic environments. Both materials balance strength and elasticity differently, with polyurethane excelling in toughness and chloroprene favoring resilience and stretchability.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to chloroprene rubber, making it ideal for applications demanding prolonged abrasion resistance and load-bearing performance. Its molecular structure provides excellent tensile strength and resistance to oils, solvents, and fatigue, outperforming chloroprene in harsh environments. Chloroprene rubber, while offering good weather and chemical resistance, generally falls short in long-term wear applications where polyurethane rubber excels.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane rubber offers superior chemical resistance to oils, solvents, and abrasives, maintaining performance in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 90degC. Chloroprene rubber excels in high-temperature resistance, enduring continuous use up to 120degC and exposure to weathering, ozone, and moderate chemicals. Selecting between polyurethane and chloroprene depends on specific application needs for temperature tolerance and chemical exposure.
Applications in Various Industries
Polyurethane rubber excels in applications requiring high abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for automotive parts, seals, and industrial rollers. Chloroprene rubber, known for its chemical stability and resistance to oil and weathering, is widely used in adhesives, gaskets, and protective clothing across the chemical and construction industries. The choice between polyurethane and chloroprene rubber depends on specific operational demands such as mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and chemical contact.
Advantages of Polyurethane Rubber
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting durability. Its excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals surpasses that of chloroprene rubber, ensuring enhanced performance in harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber also provides greater flexibility and tensile strength, contributing to better shock absorption and wear resistance in industrial uses.
Benefits of Chloroprene Rubber
Chloroprene rubber offers superior weather resistance, maintaining flexibility and durability in extreme temperatures and various environmental conditions compared to polyurethane rubber. Its inherent resistance to oils, chemicals, and ozone contributes to longer service life in industrial and automotive applications. Enhanced fire resistance and excellent tensile strength make chloroprene rubber ideal for heavy-duty uses where safety and durability are critical.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polyurethane rubber typically offers higher cost efficiency due to its durability and resistance to abrasion, resulting in longer service life and reduced replacement frequency. Chloroprene rubber, while generally more affordable upfront, may incur higher maintenance costs because of its moderate wear resistance. Availability of chloroprene rubber tends to be more widespread in global markets, whereas polyurethane rubber is often specialized and may have limited suppliers depending on geographic location.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility such as seals and gaskets. Chloroprene rubber excels in chemical stability and weather resistance, suitable for industrial gloves and automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Selecting the right rubber depends on specific performance criteria, including mechanical strength, environmental conditions, and chemical exposure.
Polyurethane Rubber vs Chloroprene Rubber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com