Compression molding offers precise control over rubber thickness and is ideal for producing large, simple shapes with excellent surface quality. Injection molding enables faster production of complex, detailed rubber parts by injecting material into molds under pressure, improving consistency and reducing waste. Choosing between compression molding and injection molding depends on the required part complexity, production volume, and cost efficiency.
Table of Comparison
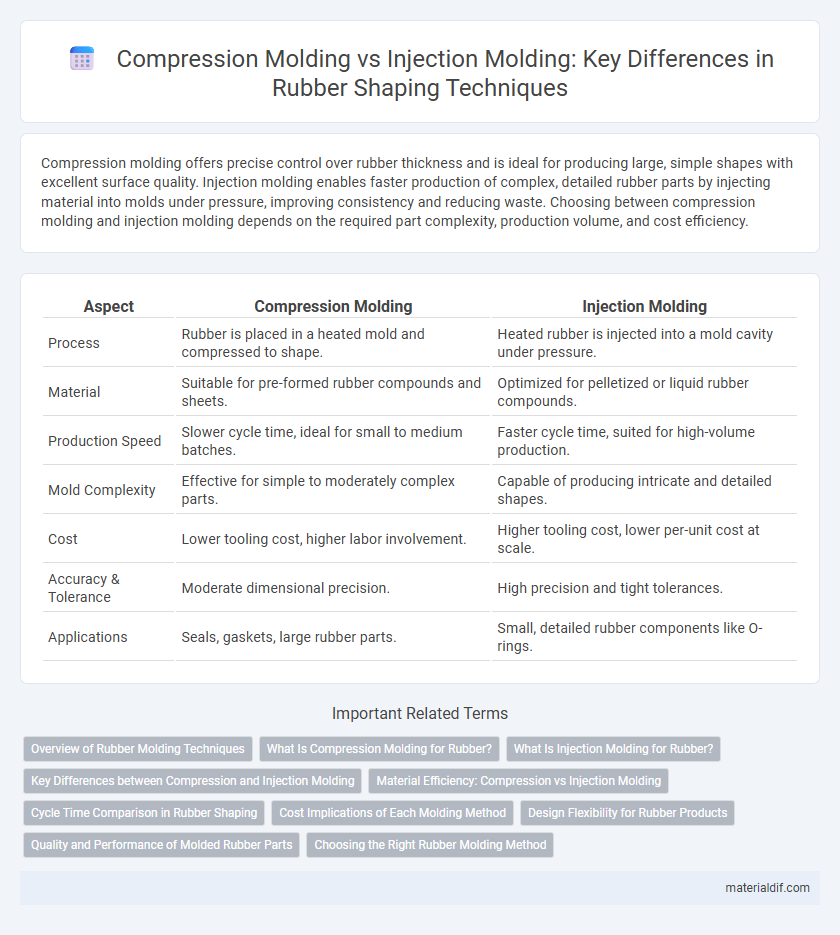
| Aspect | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Rubber is placed in a heated mold and compressed to shape. | Heated rubber is injected into a mold cavity under pressure. |
| Material | Suitable for pre-formed rubber compounds and sheets. | Optimized for pelletized or liquid rubber compounds. |
| Production Speed | Slower cycle time, ideal for small to medium batches. | Faster cycle time, suited for high-volume production. |
| Mold Complexity | Effective for simple to moderately complex parts. | Capable of producing intricate and detailed shapes. |
| Cost | Lower tooling cost, higher labor involvement. | Higher tooling cost, lower per-unit cost at scale. |
| Accuracy & Tolerance | Moderate dimensional precision. | High precision and tight tolerances. |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, large rubber parts. | Small, detailed rubber components like O-rings. |
Overview of Rubber Molding Techniques
Compression molding uses heat and pressure to shape rubber in a heated mold, ideal for large, simple parts with excellent material properties; injection molding injects rubber into a mold cavity, suited for complex, high-volume production with precise detail and minimal finishing. Compression molding offers cost-effective tooling and better control of material flow, while injection molding provides faster cycles and consistent reproducibility. Selecting between these techniques depends on part complexity, production volume, and material specifications in rubber manufacturing.
What Is Compression Molding for Rubber?
Compression molding for rubber is a manufacturing process where pre-measured rubber material, called a preform, is placed into a heated mold cavity and compressed under pressure to form a specific shape. This method is ideal for producing large, durable rubber parts with consistent thickness and excellent mechanical properties. Common applications include seals, gaskets, and automotive components requiring precise elastomeric performance.
What Is Injection Molding for Rubber?
Injection molding for rubber is a precise manufacturing process where heated rubber is injected into a mold cavity to form complex shapes with high accuracy and consistent quality. This method enables rapid production of intricate rubber components, offering superior dimensional control compared to compression molding. Injection molding is ideal for high-volume runs requiring detailed features and minimal finishing.
Key Differences between Compression and Injection Molding
Compression molding uses heat and pressure to shape rubber in a pre-measured mold cavity, ideal for large, simple parts with low tooling costs. Injection molding injects molten rubber into a closed mold via a screw or plunger, offering high precision and faster production for complex, high-volume parts. Key differences include cycle time, with injection molding being faster, and material waste, as compression molding generates less scrap due to its straightforward process.
Material Efficiency: Compression vs Injection Molding
Compression molding offers superior material efficiency for rubber shaping by minimizing waste through precise pre-measured charge placement in the mold cavity. Injection molding requires excess material to compensate for runner systems and potential flash, resulting in slightly higher material consumption. The closed mold process in compression molding reduces scrap rates, making it ideal for high-volume production with consistent material utilization.
Cycle Time Comparison in Rubber Shaping
Compression molding typically involves longer cycle times compared to injection molding due to the slower heating and cooling phases required for curing rubber in molds. Injection molding offers faster cycle times by injecting preheated rubber into molds under pressure, allowing quicker curing and part ejection. For high-volume rubber production, injection molding provides greater efficiency and throughput in cycle time optimization.
Cost Implications of Each Molding Method
Compression molding offers lower initial tooling costs, making it more cost-effective for small to medium production runs, while injection molding requires higher upfront investment in molds but enables faster production cycles and lower per-part costs at high volumes. Material wastage is generally minimized in injection molding due to precise control, potentially reducing raw material expenses over time. Selecting the optimal molding method depends on balancing volume requirements, complexity of the rubber component, and budget constraints related to tooling and production efficiency.
Design Flexibility for Rubber Products
Compression molding offers greater design flexibility for rubber products by accommodating large, complex shapes and varying material thicknesses without extensive tooling changes. Injection molding excels in producing intricate details and high-precision features, making it ideal for parts requiring tight tolerances and consistent quality. Both methods support diverse rubber formulations, but compression molding better suits prototypes and low-volume runs, while injection molding optimizes efficiency for high-volume production.
Quality and Performance of Molded Rubber Parts
Compression molding produces rubber parts with excellent physical properties and high dimensional stability, ensuring consistent quality through uniform heat and pressure application. Injection molding offers superior precision and intricate detail reproduction, resulting in high-performance components with minimal waste and enhanced surface finish. Both methods deliver durable rubber parts, but injection molding typically excels in complex designs requiring tighter tolerances and faster production cycles.
Choosing the Right Rubber Molding Method
Choosing the right rubber molding method depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, and material type. Compression molding excels in producing large, simple shapes with high strength, while injection molding offers faster cycle times and precise detail for complex, high-volume parts. Understanding these differences ensures optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and product quality in rubber manufacturing.
Compression Molding vs Injection Molding (for rubber shaping) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com