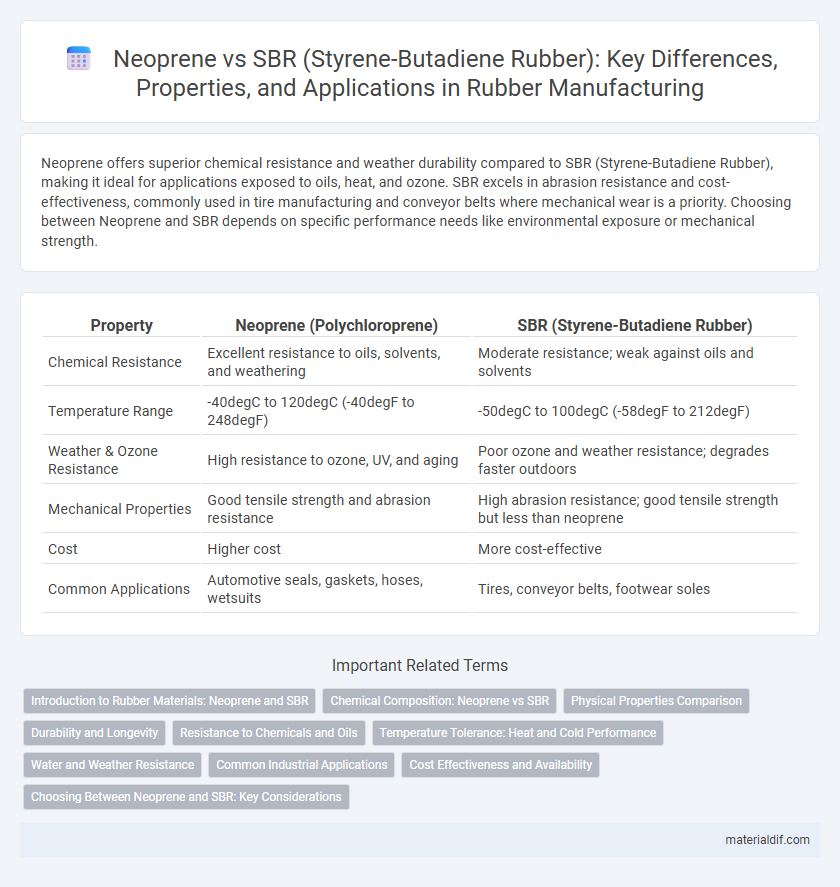
Neoprene offers superior chemical resistance and weather durability compared to SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), making it ideal for applications exposed to oils, heat, and ozone. SBR excels in abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in tire manufacturing and conveyor belts where mechanical wear is a priority. Choosing between Neoprene and SBR depends on specific performance needs like environmental exposure or mechanical strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Neoprene (Polychloroprene) | SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering | Moderate resistance; weak against oils and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) | -50degC to 100degC (-58degF to 212degF) |
| Weather & Ozone Resistance | High resistance to ozone, UV, and aging | Poor ozone and weather resistance; degrades faster outdoors |
| Mechanical Properties | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance; good tensile strength but less than neoprene |
| Cost | Higher cost | More cost-effective |
| Common Applications | Automotive seals, gaskets, hoses, wetsuits | Tires, conveyor belts, footwear soles |
Introduction to Rubber Materials: Neoprene and SBR
Neoprene and SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) are two widely used synthetic rubber materials with distinct properties and applications. Neoprene offers excellent chemical stability, oil resistance, and weather durability, making it ideal for automotive hoses, gaskets, and wetsuits. SBR provides good abrasion resistance and aging stability, commonly utilized in tire manufacturing, footwear, and conveyor belts.
Chemical Composition: Neoprene vs SBR
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber derived from the polymerization of chloroprene, featuring chlorine atoms that enhance its chemical resistance and flexibility. Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of styrene and butadiene, known for its abrasion resistance and good aging stability but lacks the chemical resistance of neoprene. The presence of chlorine in neoprene's chemical structure provides superior resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering compared to the hydrocarbon backbone of SBR.
Physical Properties Comparison
Neoprene exhibits superior oil, chemical, and weather resistance compared to SBR, which makes it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring durability. SBR, known for its excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, is commonly used in tire manufacturing and conveyor belts. Both elastomers offer flexibility and tensile strength, but Neoprene maintains performance under a wider range of temperatures, typically from -40degC to 120degC, whereas SBR operates effectively between -50degC and 100degC.
Durability and Longevity
Neoprene exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to SBR due to its enhanced resistance to weathering, ozone, and chemicals. SBR, while cost-effective and abrasion-resistant, tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and harsh environmental conditions. Industrial applications demanding extended service life often favor neoprene for its robust performance in diverse climates.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Neoprene exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for applications involving exposure to fuels, lubricants, and various industrial chemicals. SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) demonstrates significantly lower resistance to oils and organic solvents, resulting in faster degradation when in contact with such substances. Industrial use favors neoprene for chemical and oil resistance, while SBR is more suited for dry, abrasion-resistant environments.
Temperature Tolerance: Heat and Cold Performance
Neoprene exhibits superior temperature tolerance, maintaining flexibility and performance in a wide range from -40degC to 120degC, making it ideal for both heat and cold environments. SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) generally performs well up to 80degC but becomes stiff and less resilient in temperatures below -20degC. The enhanced heat and cold resistance of Neoprene make it preferable for applications requiring durability under extreme thermal conditions.
Water and Weather Resistance
Neoprene exhibits superior water and weather resistance compared to SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), maintaining flexibility and durability in harsh outdoor environments. Its molecular structure resists ozone, UV radiation, and oxidation, making it ideal for applications exposed to water and varying weather conditions. SBR tends to degrade faster when exposed to prolonged moisture and sunlight, limiting its effectiveness in outdoor settings.
Common Industrial Applications
Neoprene excels in industrial applications requiring excellent chemical, oil, and weather resistance, such as automotive gaskets, hoses, and conveyor belts. SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is widely used for tire treads, footwear, and mechanical goods due to its abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Both materials are essential in manufacturing but are selected based on specific environmental exposure and durability needs.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Neoprene offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to SBR, but it comes at a higher cost, making SBR a more cost-effective option for budget-conscious projects. SBR is widely available due to its extensive industrial production, ensuring easier procurement and lower prices, while Neoprene's specialized uses can lead to limited availability and increased expenses. For applications requiring moderate performance and economic efficiency, SBR remains the preferred choice, whereas Neoprene suits environments demanding enhanced resilience despite the elevated cost.
Choosing Between Neoprene and SBR: Key Considerations
Neoprene offers superior chemical resistance and weather durability, making it ideal for industrial applications exposed to oils, solvents, and UV radiation. SBR provides excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, preferred in automotive tires and footwear manufacturing. When choosing between Neoprene and SBR, prioritize environmental exposure, mechanical performance, and budget constraints to optimize material selection.
Neoprene vs SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com