Food-safe resin is specifically formulated to meet strict safety standards, ensuring it does not leach harmful chemicals into items that come into contact with food or beverages. Industrial grade resin, on the other hand, is designed for durability and chemical resistance in manufacturing processes but may contain additives or compounds unsafe for ingestion or prolonged food contact. Choosing food-safe resin is crucial for applications like kitchenware, utensils, and food packaging to guarantee consumer health and regulatory compliance.
Table of Comparison
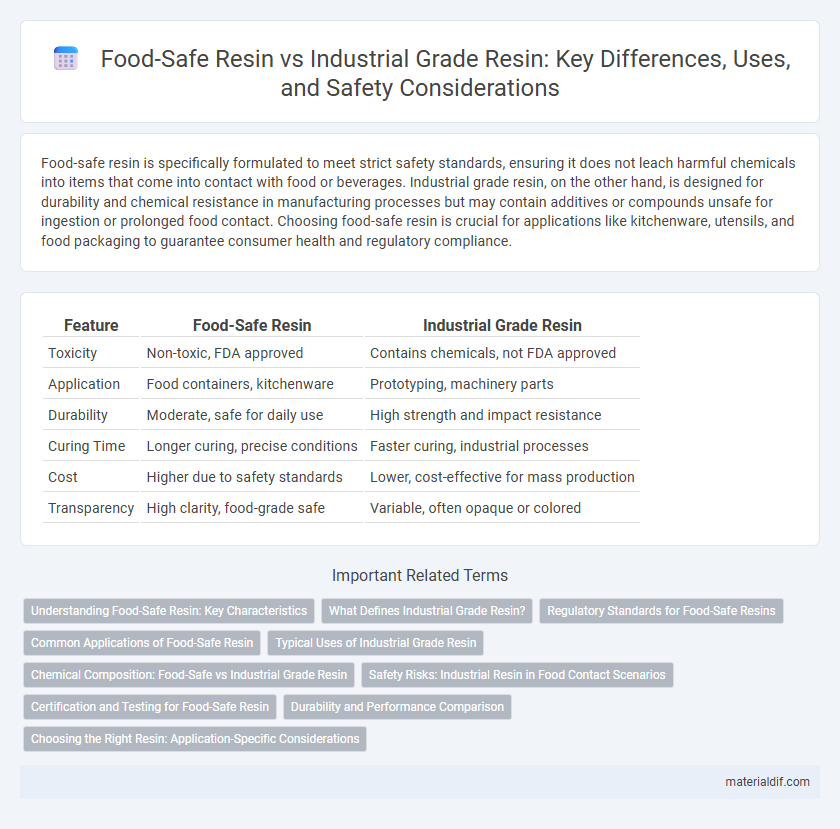
| Feature | Food-Safe Resin | Industrial Grade Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, FDA approved | Contains chemicals, not FDA approved |
| Application | Food containers, kitchenware | Prototyping, machinery parts |
| Durability | Moderate, safe for daily use | High strength and impact resistance |
| Curing Time | Longer curing, precise conditions | Faster curing, industrial processes |
| Cost | Higher due to safety standards | Lower, cost-effective for mass production |
| Transparency | High clarity, food-grade safe | Variable, often opaque or colored |
Understanding Food-Safe Resin: Key Characteristics
Food-safe resin is formulated to meet strict regulatory standards such as FDA and EU food contact approvals, ensuring it is non-toxic and free from harmful chemicals. It exhibits low odor, high chemical resistance, and excellent durability, making it suitable for items like kitchen utensils, food containers, and molds. In contrast, industrial-grade resin often contains additives or solvents that can leach harmful substances, making it unsuitable for direct food contact applications.
What Defines Industrial Grade Resin?
Industrial grade resin is characterized by its robust chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and exceptional mechanical strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty manufacturing and engineering applications. Unlike food-safe resin, which must comply with strict FDA regulations to prevent toxic leaching and ensure safety for consumption, industrial grade resin prioritizes durability and performance over biocompatibility. This type of resin often contains additives and compounds that enhance structural integrity but render it unsuitable for direct food contact.
Regulatory Standards for Food-Safe Resins
Food-safe resin complies with stringent regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR 175.300 and EU Regulation No. 10/2011, ensuring non-toxicity and safety for direct food contact. Industrial grade resin lacks certification for food safety and may contain hazardous substances unsuitable for culinary applications. Manufacturers must verify compliance with migration limits and biocompatibility tests to guarantee resin safety in food-related uses.
Common Applications of Food-Safe Resin
Food-safe resin is primarily used in applications requiring direct contact with consumables, such as creating kitchen utensils, food storage containers, and custom molds for edible products. Its non-toxic composition and FDA compliance make it ideal for producing medical devices, beverage components, and children's toys designed for safety and hygiene. Unlike industrial grade resin, which suits heavy-duty structural parts and automotive components, food-safe resin prioritizes health standards and contamination prevention in everyday food-related products.
Typical Uses of Industrial Grade Resin
Industrial Grade Resin is commonly used in manufacturing applications such as automotive parts, electronic housings, and construction materials due to its high durability and chemical resistance. It is engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions and mechanical stress rather than meet food safety standards. Unlike Food-Safe Resin, which is designed for direct contact with consumables, Industrial Grade Resin focuses on structural strength and long-term performance in industrial settings.
Chemical Composition: Food-Safe vs Industrial Grade Resin
Food-safe resin features a non-toxic chemical composition free from harmful additives like BPA and heavy metals, ensuring it meets FDA and EU standards for direct food contact. Industrial-grade resin contains stronger, more chemically reactive compounds such as styrene and plasticizers, which enhance durability but may release toxins unsuitable for food applications. The molecular structure of food-safe resin prioritizes inertness and biocompatibility, while industrial resin emphasizes mechanical strength and chemical resistance at the expense of food safety.
Safety Risks: Industrial Resin in Food Contact Scenarios
Industrial grade resin contains chemicals and additives not tested or approved for food contact, posing significant health risks such as chemical leaching and contamination. Food-safe resin is specifically formulated to meet FDA or EU food-contact regulations, ensuring it does not release harmful substances when in contact with food. Using industrial resin in food applications can lead to toxicity, allergic reactions, and long-term health hazards.
Certification and Testing for Food-Safe Resin
Food-safe resin undergoes rigorous certification processes such as FDA approval and complies with European Union regulations like EU 10/2011, ensuring it meets standards for non-toxicity and safe contact with food. Industrial grade resin typically lacks these certifications and is primarily tested for mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability rather than food safety. Certification for food-safe resin includes extensive migration testing to evaluate potential chemical leaching, guaranteeing safe usage in applications involving direct food contact.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Food-safe resin is engineered to meet strict health and safety standards, ensuring non-toxicity and resistance to leaching, making it ideal for applications involving direct food contact. Industrial grade resin prioritizes mechanical strength and chemical resistance, offering superior durability for heavy-duty or prolonged exposure environments but may contain additives unsuitable for food safety. Performance-wise, food-safe resin balances moderate durability with biocompatibility, while industrial grade resin excels in robustness but requires careful handling to avoid contamination risks.
Choosing the Right Resin: Application-Specific Considerations
Food-safe resin is formulated to meet strict FDA and EU regulations, ensuring non-toxicity and chemical stability for direct food contact, making it ideal for kitchenware, utensils, and packaging. Industrial grade resin prioritizes durability, chemical resistance, and strength, suited for mechanical parts, prototyping, and industrial manufacturing but often lacks certifications for food safety. Selecting the right resin requires evaluating application-specific factors such as regulatory compliance, mechanical properties, and exposure conditions to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Food-Safe Resin vs Industrial Grade Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com