Unsaturated polyester resin offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and corrosion resistance. Saturated polyester resin provides better flexibility and UV stability, suitable for coatings and applications exposed to sunlight. Choosing between the two depends on the balance between strength and environmental exposure requirements.
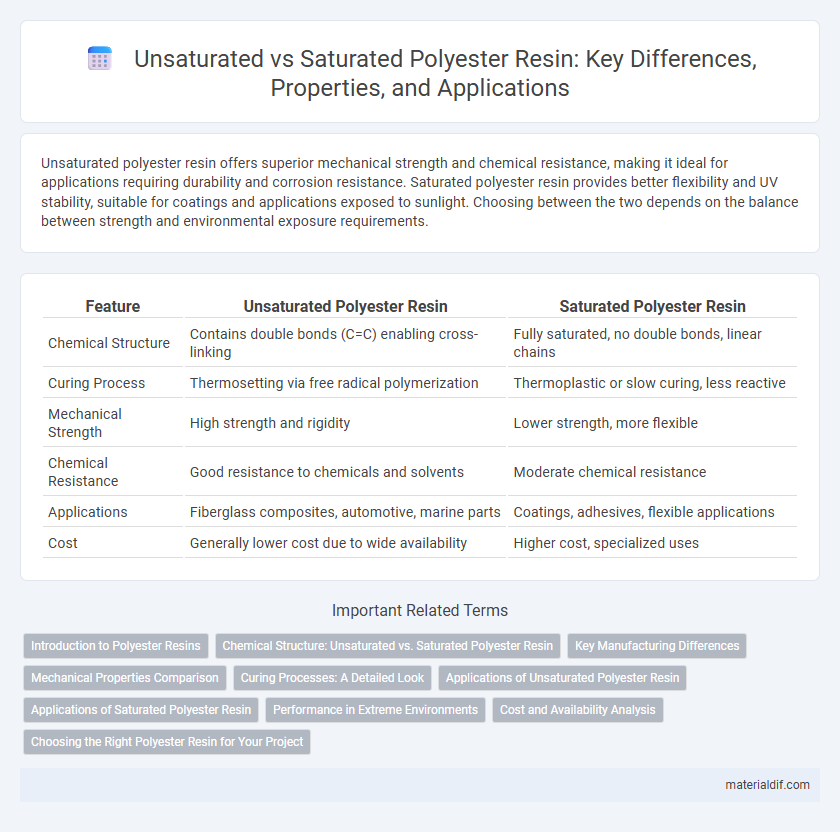
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Unsaturated Polyester Resin | Saturated Polyester Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Contains double bonds (C=C) enabling cross-linking | Fully saturated, no double bonds, linear chains |
| Curing Process | Thermosetting via free radical polymerization | Thermoplastic or slow curing, less reactive |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and rigidity | Lower strength, more flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Applications | Fiberglass composites, automotive, marine parts | Coatings, adhesives, flexible applications |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to wide availability | Higher cost, specialized uses |
Introduction to Polyester Resins
Polyester resins are widely used thermosetting polymers in composites, with unsaturated and saturated types serving different applications. Unsaturated polyester resins contain double bonds in their polymer backbone, enabling cross-linking through copolymerization with styrene, which provides superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Saturated polyester resins lack these double bonds, resulting in a more flexible material often used in coatings, adhesives, and film applications.
Chemical Structure: Unsaturated vs. Saturated Polyester Resin
Unsaturated polyester resin contains carbon-carbon double bonds within its polymer chain, enabling cross-linking through reactive sites that enhance mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Saturated polyester resin lacks these double bonds, resulting in a linear, more stable polymer structure with lower reactivity and improved flexibility. The presence or absence of unsaturation in the chemical structure directly influences curing mechanisms, thermal stability, and end-use performance of the polyesters.
Key Manufacturing Differences
Unsaturated polyester resin is produced by reacting dibasic organic acids with polyhydric alcohols, incorporating unsaturated double bonds that enable cross-linking with styrene, resulting in a thermosetting polymer. Saturated polyester resin, in contrast, is synthesized using saturated acids, which lack double bonds, leading to a thermoplastic material without cross-linking capabilities. Key manufacturing differences include the presence of reactive sites in unsaturated resins for curing and the use of different monomers influencing polymer structure and final resin properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Unsaturated polyester resin offers superior mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength, better impact resistance, and improved flexural modulus compared to saturated polyester resin. Saturated polyester resin typically exhibits lower stiffness and reduced chemical resistance, making it less suitable for high-load or high-stress applications. The enhanced cross-linking in unsaturated polyester resin results in a tougher, more durable composite material favored in structural and automotive industries.
Curing Processes: A Detailed Look
Unsaturated polyester resin cures through a free radical polymerization process initiated by catalysts like methyl ethyl ketone peroxide, requiring precise temperature control to achieve optimal cross-linking and mechanical properties. Saturated polyester resin, on the other hand, typically cures via condensation reactions involving heat or catalysts, resulting in thermoplastic or thermosetting characteristics depending on formulation. Understanding these distinct curing mechanisms is crucial for selecting the right resin type based on application-specific durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance requirements.
Applications of Unsaturated Polyester Resin
Unsaturated polyester resin is widely used in marine, automotive, and construction industries due to its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and versatility in molding processes. It is ideal for producing fiberglass-reinforced composites, boat hulls, automotive body panels, and corrosion-resistant tanks, where durability and lightweight properties are critical. Its ability to cure at room temperature and compatibility with various fillers and reinforcements make it a preferred choice for custom fabrication and industrial applications.
Applications of Saturated Polyester Resin
Saturated polyester resin is widely used in applications requiring excellent chemical resistance and durability, such as automotive coatings, electrical insulation, and packaging films. Its superior resistance to moisture and UV radiation makes it ideal for outdoor and industrial uses, including protective coatings and composite materials. The resin's ability to maintain mechanical properties in harsh environments ensures long-term performance in consumer goods and construction materials.
Performance in Extreme Environments
Unsaturated polyester resin exhibits superior chemical resistance, moisture tolerance, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for extreme environments such as marine and industrial applications. Saturated polyester resin generally offers better heat resistance and dimensional stability but lacks the chemical durability required for highly corrosive or humid conditions. Choosing between the two depends on balancing chemical exposure and temperature fluctuations in the intended application.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Unsaturated polyester resin typically offers lower cost and higher availability compared to saturated polyester resin, making it the preferred choice for mass production and general-purpose applications. Saturated polyester resin, while providing superior chemical resistance and durability, tends to be more expensive and less widely available due to its specialized formulation and limited industrial use. Market demand and raw material sourcing significantly influence the pricing and supply chain dynamics between these two resin types.
Choosing the Right Polyester Resin for Your Project
Unsaturated polyester resin offers superior strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications like fiberglass composites and marine coatings, while saturated polyester resin provides better clarity and UV stability, suited for packaging or electrical insulation. Selecting the right polyester resin depends on factors such as mechanical performance, environmental exposure, and curing requirements to align with project specifications. Balancing durability and aesthetic needs ensures optimized results in construction, automotive, or consumer product applications.
Unsaturated Polyester Resin vs Saturated Polyester Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com