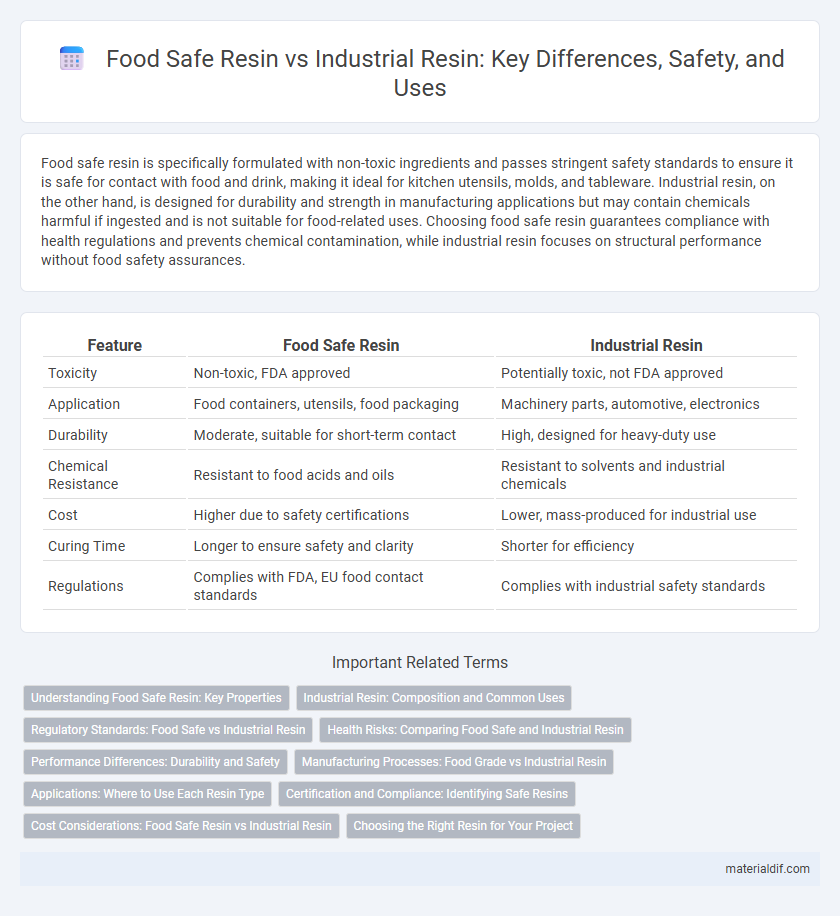
Food safe resin is specifically formulated with non-toxic ingredients and passes stringent safety standards to ensure it is safe for contact with food and drink, making it ideal for kitchen utensils, molds, and tableware. Industrial resin, on the other hand, is designed for durability and strength in manufacturing applications but may contain chemicals harmful if ingested and is not suitable for food-related uses. Choosing food safe resin guarantees compliance with health regulations and prevents chemical contamination, while industrial resin focuses on structural performance without food safety assurances.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Food Safe Resin | Industrial Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, FDA approved | Potentially toxic, not FDA approved |
| Application | Food containers, utensils, food packaging | Machinery parts, automotive, electronics |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for short-term contact | High, designed for heavy-duty use |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to food acids and oils | Resistant to solvents and industrial chemicals |
| Cost | Higher due to safety certifications | Lower, mass-produced for industrial use |
| Curing Time | Longer to ensure safety and clarity | Shorter for efficiency |
| Regulations | Complies with FDA, EU food contact standards | Complies with industrial safety standards |
Understanding Food Safe Resin: Key Properties
Food safe resin is formulated to meet stringent regulatory standards such as FDA and EU regulations, ensuring non-toxic and biocompatible properties suitable for direct food contact. It features low volatile organic compounds (VOCs), high chemical stability, and resistance to leaching harmful substances, making it ideal for kitchenware, food packaging, and utensils. Industrial resin, in contrast, prioritizes mechanical strength and durability over safety certifications, often containing additives that are unsuitable for food applications.
Industrial Resin: Composition and Common Uses
Industrial resin typically consists of epoxy, polyurethane, or polyester compounds formulated for enhanced strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. These resins often contain additives and catalysts that improve durability in harsh environments but render them unsuitable for food contact applications. Common uses of industrial resin include automotive parts, electronic components, coatings, and construction materials where mechanical performance and environmental resistance are critical.
Regulatory Standards: Food Safe vs Industrial Resin
Food safe resin meets stringent regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR 175.300 and EU Regulation No. 10/2011, ensuring non-toxicity and suitability for direct food contact applications. Industrial resin typically complies with standards like ASTM, ISO, or REACH, focusing on mechanical strength and chemical resistance rather than safety for ingestion. Choosing food safe resin is critical for products like kitchenware and packaging to prevent chemical leaching and protect public health.
Health Risks: Comparing Food Safe and Industrial Resin
Food safe resin is specifically formulated to be non-toxic and free from harmful chemicals, making it suitable for items that come into contact with food, whereas industrial resin often contains volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other toxic substances that pose health risks. Exposure to industrial resin can cause respiratory issues, skin irritation, and long-term organ damage due to the release of hazardous fumes and chemicals during curing. Choosing food safe resin minimizes the risk of chemical leaching into consumables, ensuring safer use for kitchenware and food containers compared to industrial-grade alternatives.
Performance Differences: Durability and Safety
Food safe resin is formulated with non-toxic materials that comply with FDA regulations, ensuring it does not leach harmful chemicals into food or beverages. Industrial resin offers superior durability and chemical resistance, designed to withstand harsh environments and mechanical stress but may contain additives that pose health risks if ingested. The key performance difference lies in food safe resin prioritizing safety and compliance for direct food contact, while industrial resin emphasizes structural integrity and resilience for heavy-duty applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Food Grade vs Industrial Resin
Food safe resin undergoes rigorous manufacturing processes that ensure compliance with strict regulatory standards such as FDA and EU food contact regulations, featuring low toxicity and absence of harmful additives. Industrial resin manufacturing prioritizes chemical resistance, durability, and cost-effectiveness, often incorporating additives or fillers that are not suitable for food contact. Advanced curing techniques and stringent quality control distinguish food grade resin production to maintain purity and non-leachability, whereas industrial resin processes optimize performance for mechanical and thermal applications without food safety considerations.
Applications: Where to Use Each Resin Type
Food safe resin is ideal for applications involving direct contact with food or beverages, such as kitchenware, molds for chocolates, and utensils, ensuring non-toxicity and compliance with FDA standards. Industrial resin is suited for manufacturing durable parts, prototypes, and components in automotive, electronics, and construction industries due to its high strength and chemical resistance. Choosing the appropriate resin depends on the end-use requirements, where food safe resin prioritizes safety and regulatory approval, while industrial resin emphasizes performance and durability.
Certification and Compliance: Identifying Safe Resins
Food safe resin typically holds certifications such as FDA approval and complies with strict food-grade regulations, ensuring it does not leach harmful chemicals during contact with food. Industrial resin often lacks these certifications, being formulated for durability and structural applications rather than direct food contact. Identifying safe resins requires verifying third-party certifications and compliance with standards like FDA 21 CFR 175.300 or EU food contact regulations.
Cost Considerations: Food Safe Resin vs Industrial Resin
Food safe resin typically incurs higher costs due to stringent regulatory compliance, non-toxic ingredients, and rigorous testing standards essential for direct food contact applications. Industrial resin, while more affordable, often lacks certification for food safety and is formulated primarily for durability and chemical resistance in manufacturing or construction uses. Budget constraints and the intended use environment heavily influence the cost-effectiveness when choosing between food safe resin and industrial resin.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Food safe resin is formulated to comply with FDA regulations, ensuring it is non-toxic and free from harmful chemicals, making it ideal for projects involving direct food contact such as kitchenware or utensils. Industrial resin offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability, suited for heavy-duty applications like automotive parts or machinery components where safety regulations for food contact are not required. Selecting the right resin depends on the project's end use, prioritizing health safety for food-related items and performance characteristics for industrial applications.
Food Safe Resin vs Industrial Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com