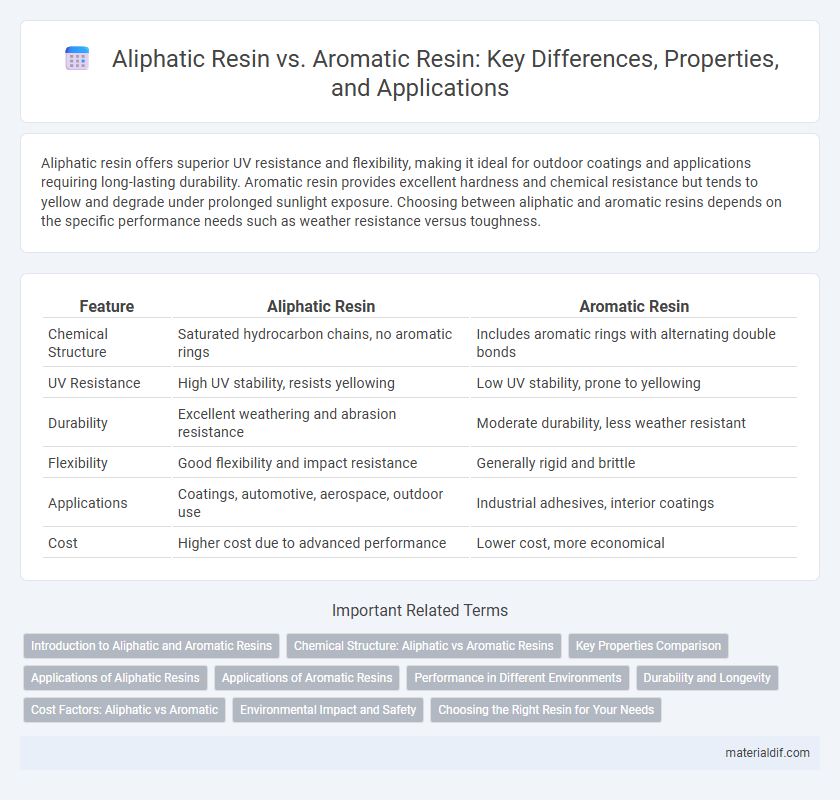
Aliphatic resin offers superior UV resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for outdoor coatings and applications requiring long-lasting durability. Aromatic resin provides excellent hardness and chemical resistance but tends to yellow and degrade under prolonged sunlight exposure. Choosing between aliphatic and aromatic resins depends on the specific performance needs such as weather resistance versus toughness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aliphatic Resin | Aromatic Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Saturated hydrocarbon chains, no aromatic rings | Includes aromatic rings with alternating double bonds |
| UV Resistance | High UV stability, resists yellowing | Low UV stability, prone to yellowing |
| Durability | Excellent weathering and abrasion resistance | Moderate durability, less weather resistant |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility and impact resistance | Generally rigid and brittle |
| Applications | Coatings, automotive, aerospace, outdoor use | Industrial adhesives, interior coatings |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced performance | Lower cost, more economical |
Introduction to Aliphatic and Aromatic Resins
Aliphatic resins are characterized by their straight or branched carbon chains, providing superior UV resistance, color stability, and flexibility which makes them ideal for outdoor coatings and adhesives. Aromatic resins contain benzene ring structures, offering enhanced hardness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability commonly used in industrial coatings and printing inks. The structural differences between aliphatic and aromatic resins directly influence their performance properties and application suitability in various industries.
Chemical Structure: Aliphatic vs Aromatic Resins
Aliphatic resins feature linear or branched hydrocarbon chains with saturated carbon-carbon bonds, providing excellent UV stability and color retention. Aromatic resins contain benzene rings in their molecular structure, resulting in superior adhesive properties and heat resistance but reduced UV durability. The distinct chemical frameworks of aliphatic and aromatic resins determine their suitability for different coatings, inks, and adhesive applications.
Key Properties Comparison
Aliphatic resins offer superior UV resistance, excellent color stability, and higher flexibility, making them ideal for outdoor coatings and high-performance adhesives. Aromatic resins provide greater hardness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, which benefits applications requiring durability and heat resistance. The choice between aliphatic and aromatic resins is determined by the specific performance demands, such as exposure to environmental factors or mechanical stress.
Applications of Aliphatic Resins
Aliphatic resins are widely used in applications requiring excellent UV resistance and color stability, such as automotive clear coats, exterior architectural coatings, and protective finishes for wood. These resins provide superior weather durability and chemical resistance compared to aromatic resins, making them ideal for outdoor use and exposure to harsh environmental conditions. Their high gloss retention and flexibility also support their use in high-performance industrial coatings and adhesives.
Applications of Aromatic Resins
Aromatic resins are widely utilized in adhesives, coatings, and rubber compounding due to their excellent heat resistance and strong adhesive properties. Their compatibility with various polymers enhances durability and weather resistance in automotive and industrial applications. The high thermal stability of aromatic resins also makes them ideal for electrical insulation and high-performance laminates.
Performance in Different Environments
Aliphatic resins offer superior UV resistance and color stability, making them ideal for outdoor applications exposed to sunlight and harsh weather conditions. Aromatic resins, while less UV resistant, provide excellent adhesion and chemical resistance in industrial environments with exposure to solvents and oils. Selecting between aliphatic and aromatic resins depends on the specific environmental stressors, including temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, and chemical contact.
Durability and Longevity
Aliphatic resin offers superior durability and longevity due to its enhanced UV resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for outdoor applications and environments with prolonged sun exposure. Aromatic resin, while cost-effective and easier to process, tends to degrade faster under UV light, resulting in reduced lifespan and increased maintenance requirements. Choosing aliphatic resin ensures longer-lasting performance in demanding conditions where extended durability is critical.
Cost Factors: Aliphatic vs Aromatic
Aliphatic resins generally incur higher production costs due to their complex synthesis processes and superior UV resistance properties, making them ideal for outdoor applications where durability is critical. Aromatic resins are often more cost-effective, benefiting from simpler manufacturing methods and widespread availability, but they may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure. Cost considerations typically weigh aliphatic resins' performance advantages against the economic efficiency of aromatic resins, influencing material selection in industrial and commercial uses.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Aliphatic resins, derived from saturated hydrocarbons, exhibit lower toxicity and reduced emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to aromatic resins, which are based on benzene-ring structures. Aromatic resins often pose higher environmental risks due to their potential for releasing hazardous air pollutants and slower biodegradability. Selecting aliphatic resins enhances workplace safety and aligns with eco-friendly manufacturing practices by minimizing harmful exposure and environmental contamination.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Needs
Aliphatic resin offers superior UV resistance and durability, making it ideal for outdoor applications and coatings exposed to sunlight. Aromatic resin provides excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, suitable for industrial uses where solvent exposure is common. Selecting the right resin depends on balancing environmental factors, performance requirements, and longevity to match specific project needs.
Aliphatic Resin vs Aromatic Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com