Solvent-based resin offers superior adhesion and durability in harsh environments but emits higher volatile organic compounds (VOCs), impacting air quality. Water-based resin provides a safer, environmentally friendly alternative with lower VOC emissions and easier cleanup, though it may have reduced chemical resistance and longer curing times. Choosing between solvent-based and water-based resin depends on application requirements, environmental regulations, and performance needs.
Table of Comparison
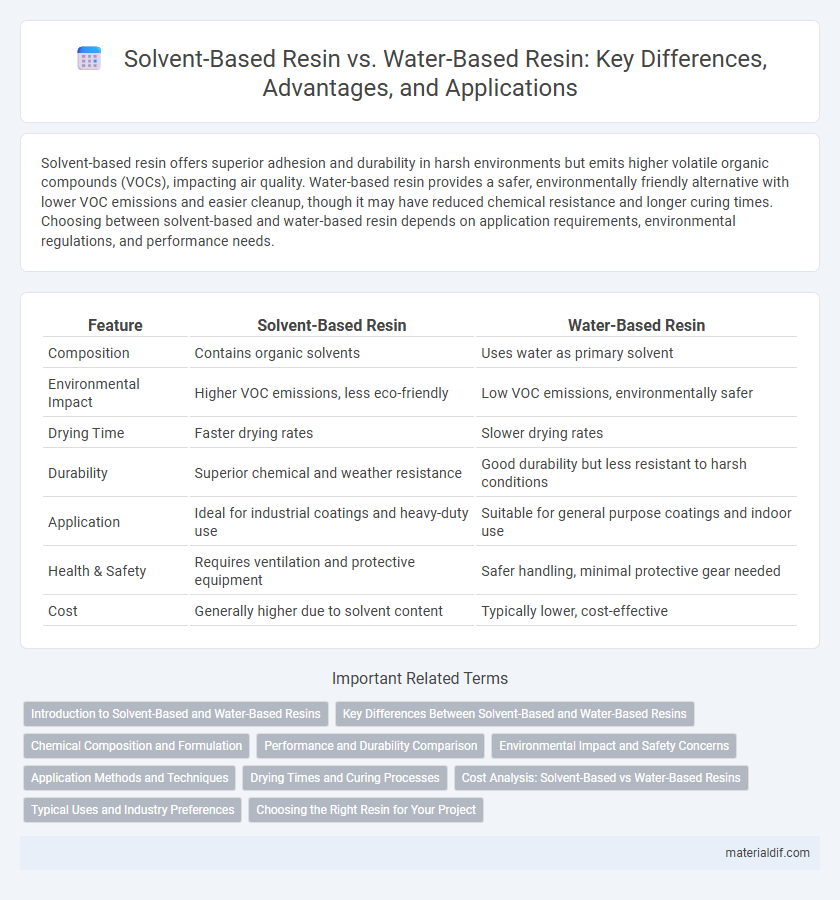
| Feature | Solvent-Based Resin | Water-Based Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains organic solvents | Uses water as primary solvent |
| Environmental Impact | Higher VOC emissions, less eco-friendly | Low VOC emissions, environmentally safer |
| Drying Time | Faster drying rates | Slower drying rates |
| Durability | Superior chemical and weather resistance | Good durability but less resistant to harsh conditions |
| Application | Ideal for industrial coatings and heavy-duty use | Suitable for general purpose coatings and indoor use |
| Health & Safety | Requires ventilation and protective equipment | Safer handling, minimal protective gear needed |
| Cost | Generally higher due to solvent content | Typically lower, cost-effective |
Introduction to Solvent-Based and Water-Based Resins
Solvent-based resins consist of synthetic polymers dissolved in organic solvents, offering strong adhesion and excellent durability for industrial coatings and adhesives. Water-based resins use water as the primary solvent, promoting environmentally friendly solutions with reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and easier cleanup. Both types serve crucial roles in manufacturing, with solvent-based resins favored for heavy-duty applications and water-based resins preferred for eco-conscious and indoor uses.
Key Differences Between Solvent-Based and Water-Based Resins
Solvent-based resins contain organic solvents, offering superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and faster drying times compared to water-based resins, which use water as the primary solvent and are environmentally friendly with lower VOC emissions. Water-based resins prioritize sustainability and safety, making them suitable for indoor applications, while solvent-based resins are preferred for industrial uses due to their durability and performance in harsh conditions. The choice between solvent-based and water-based resins depends on factors such as environmental regulations, application requirements, and desired finish quality.
Chemical Composition and Formulation
Solvent-based resins primarily consist of synthetic polymers dissolved in organic solvents such as toluene or xylene, which enhance film formation and durability in coatings and adhesives. Water-based resins utilize emulsified or dispersed polymers in aqueous media, relying on coalescing agents and surfactants to achieve stable formulations with reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. The chemical composition of solvent-based resins typically offers superior chemical resistance and adhesion, while water-based resins prioritize environmental safety and ease of cleanup.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Solvent-based resins typically exhibit superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability in harsh environments, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring long-lasting performance. Water-based resins offer improved environmental safety and ease of cleanup but may have lower resistance to moisture and chemicals, resulting in reduced durability over time. Factors such as exposure conditions and specific use cases influence the performance gap between solvent-based and water-based resins.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Solvent-based resins emit higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing significantly to air pollution and posing health risks such as respiratory irritation and dizziness during application. Water-based resins contain fewer VOCs, making them safer for indoor use and reducing environmental harm through lower emissions. Despite slower drying times, water-based resins offer a more eco-friendly option with improved safety profiles for both users and the environment.
Application Methods and Techniques
Solvent-based resin requires application techniques emphasizing proper ventilation and solvent evaporation, often using spray guns or brushes for smooth, durable finishes in industrial settings. Water-based resin favors air-drying methods, allowing easier cleanup with water, and is commonly applied with rollers or brushes for eco-friendly coatings and flexible surfaces. Both resins demand surface preparation but differ in drying times and environmental impact, influencing the choice of application tools and handling practices.
Drying Times and Curing Processes
Solvent-based resins typically exhibit faster drying times due to the rapid evaporation of organic solvents, enabling quicker handling and application in industrial settings. Water-based resins rely on the evaporation of water, resulting in slower drying and extended curing processes that can enhance environmental safety by reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. The curing process for solvent-based resins often involves chemical cross-linking accelerated by solvent evaporation, whereas water-based resins cure through coalescence and film formation that depend on temperature and humidity levels.
Cost Analysis: Solvent-Based vs Water-Based Resins
Solvent-based resins typically incur higher raw material and disposal costs due to the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and stringent environmental regulations. Water-based resins offer lower upfront expenses and reduced hazardous waste treatment, resulting in overall cost savings in manufacturing and compliance. Industrial applications often find water-based resins more economical, balancing performance requirements with regulatory and operational cost-efficiency.
Typical Uses and Industry Preferences
Solvent-based resins are preferred in automotive coatings and industrial applications due to their superior durability, chemical resistance, and gloss retention, making them ideal for heavy-duty environments. Water-based resins are favored in furniture finishes, packaging, and consumer goods for their low VOC emissions and environmental compliance, aligning with increasing regulatory standards. Industry preference shifts towards water-based resins in sectors prioritizing sustainability, while solvent-based resins dominate where performance under harsh conditions is critical.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Solvent-based resin offers superior adhesion and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring chemical resistance and strong bonding on non-porous surfaces. Water-based resin provides an eco-friendly, low-VOC alternative with easier cleanup and faster drying times, suited for indoor projects and surfaces sensitive to harsh chemicals. Selecting the right resin depends on project requirements like environmental impact, surface type, and performance needs to ensure optimal results.
Solvent-Based Resin vs Water-Based Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com