UV resin cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, offering a smooth finish ideal for small crafts and jewelry, while polyurethane resin cures through a chemical reaction, providing greater durability and flexibility for larger projects. UV resin typically requires less ventilation and produces minimal odor, making it suitable for indoor use, whereas polyurethane resin often emits stronger fumes and demands a well-ventilated workspace. Both resins have distinct thermal and mechanical properties, with polyurethane resin excelling in impact resistance and UV resin favored for its fast curing time and ease of use.
Table of Comparison
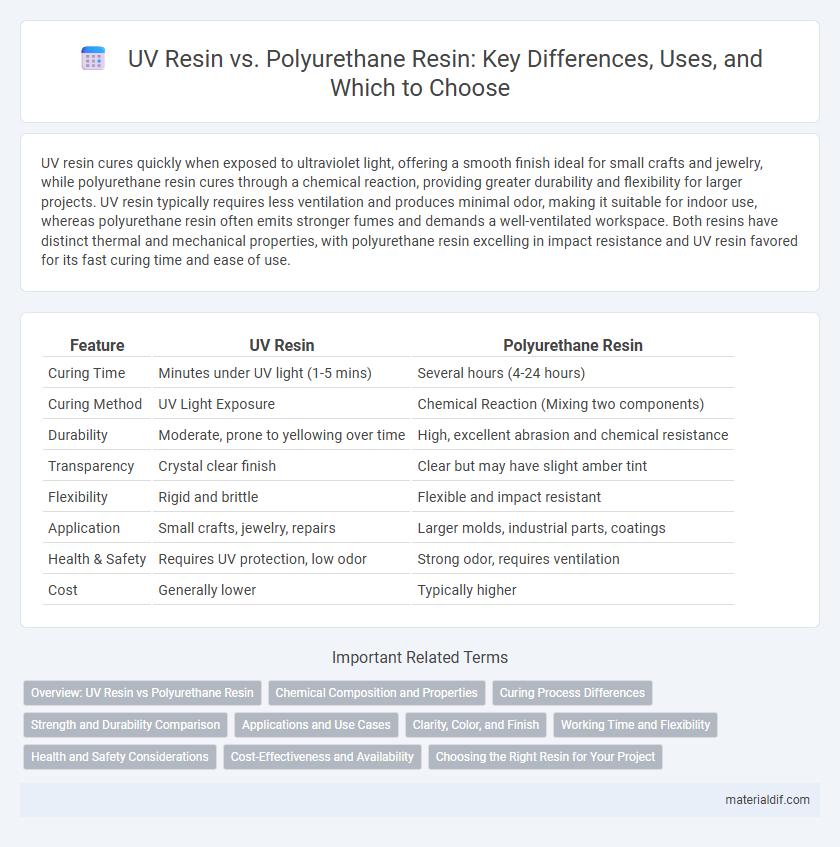
| Feature | UV Resin | Polyurethane Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Time | Minutes under UV light (1-5 mins) | Several hours (4-24 hours) |
| Curing Method | UV Light Exposure | Chemical Reaction (Mixing two components) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to yellowing over time | High, excellent abrasion and chemical resistance |
| Transparency | Crystal clear finish | Clear but may have slight amber tint |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and impact resistant |
| Application | Small crafts, jewelry, repairs | Larger molds, industrial parts, coatings |
| Health & Safety | Requires UV protection, low odor | Strong odor, requires ventilation |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
Overview: UV Resin vs Polyurethane Resin
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small, detailed projects requiring fast setting times, while polyurethane resin cures through a chemical reaction and offers greater durability and flexibility for casting larger or more complex items. UV resin generally provides a clearer finish and is more resistant to yellowing, whereas polyurethane resin is more suitable for applications needing impact resistance and toughness. Both resins have specific optimal uses, with UV resin favored in jewelry and small crafts, and polyurethane resin preferred in industrial molds and outdoor applications.
Chemical Composition and Properties
UV resin is composed primarily of acrylate or methacrylate monomers that polymerize quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, resulting in a hard, clear, and durable finish with rapid curing times. Polyurethane resin consists of urethane linkages formed from the reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, offering superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and impact strength compared to UV resin. The chemical composition of UV resin favors fast curing with limited yellowing, while polyurethane resin provides enhanced mechanical resilience and longer curing periods.
Curing Process Differences
UV resin cures rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light, enabling precise control over the curing time and resulting in a hard, glossy finish within minutes. Polyurethane resin undergoes a chemical curing process that involves mixing two components, which then harden through a polymerization reaction over several hours to days, depending on the formulation and environmental conditions. The UV resin's curing process allows for immediate handling and layering, while polyurethane resin requires careful temperature and humidity control during its longer curing phase to achieve optimal strength and durability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, producing a hard, glossy finish with moderate strength ideal for small crafts and jewelry. Polyurethane resin offers superior strength and durability, resisting impact, abrasion, and chemicals, making it optimal for industrial applications and high-stress environments. The long-term resilience of polyurethane resin exceeds that of UV resin, which can become brittle and yellow with prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Applications and Use Cases
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small-scale crafts, jewelry making, and detailed prototypes where fast turnaround is essential. Polyurethane resin offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, preferred for industrial parts, automotive components, and durable casting applications. Both resins excel in distinct use cases, with UV resin favored for precision and speed, while polyurethane resin supports heavy-duty, long-lasting projects.
Clarity, Color, and Finish
UV resin offers superior clarity and a glass-like finish compared to polyurethane resin, making it ideal for projects requiring high transparency. Polyurethane resin tends to have a slightly amber tint and a softer, more flexible finish, which can affect the vibrancy of embedded colors. The choice between UV and polyurethane resin depends on whether crystal-clear color representation or durability and flexibility in the finish are the priorities.
Working Time and Flexibility
UV resin offers a significantly shorter working time due to its rapid curing under ultraviolet light, typically solidifying within minutes, whereas polyurethane resin requires longer curing periods ranging from several hours to days. In terms of flexibility, polyurethane resin provides superior elasticity and durability, making it ideal for applications needing impact resistance and bending, while UV resin tends to be more rigid and brittle after curing. Choosing between UV and polyurethane resin depends on the balance needed between quick setting times and material flexibility for specific project requirements.
Health and Safety Considerations
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, reducing exposure to uncured chemicals but may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that require adequate ventilation. Polyurethane resin involves mixing two components that can release isocyanates, substances linked to respiratory issues and skin sensitization, necessitating the use of gloves, masks, and work in well-ventilated areas. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and adherence to safety guidelines are critical when handling both UV and polyurethane resins to minimize health risks.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
UV resin offers faster curing times and requires less energy, making it cost-effective for small-scale projects, while polyurethane resin is generally more affordable per volume and widely available in bulk for industrial uses. Polyurethane resin's diverse formulations cater to various durability needs, often justifying its slightly higher upfront cost with long-term performance benefits. Availability varies by region, but polyurethane resins tend to be easier to source from industrial suppliers, whereas UV resin is popular in specialty craft stores and online markets.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small crafts, jewelry, and projects requiring fast turnaround. Polyurethane resin offers superior durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat and chemicals, suited for larger molds, mechanical parts, and prototypes. Consider project size, curing time, and environmental exposure when choosing between UV resin and polyurethane resin to ensure optimal performance and finish.
UV Resin vs Polyurethane Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com