Bisphenol-A epoxy resins offer excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance, making them ideal for general-purpose coatings and adhesives. Novolac epoxy resins provide superior thermal stability and higher chemical resistance, suitable for demanding industrial applications and high-temperature environments. Selecting between the two depends on the required performance criteria, especially in terms of heat resistance and chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
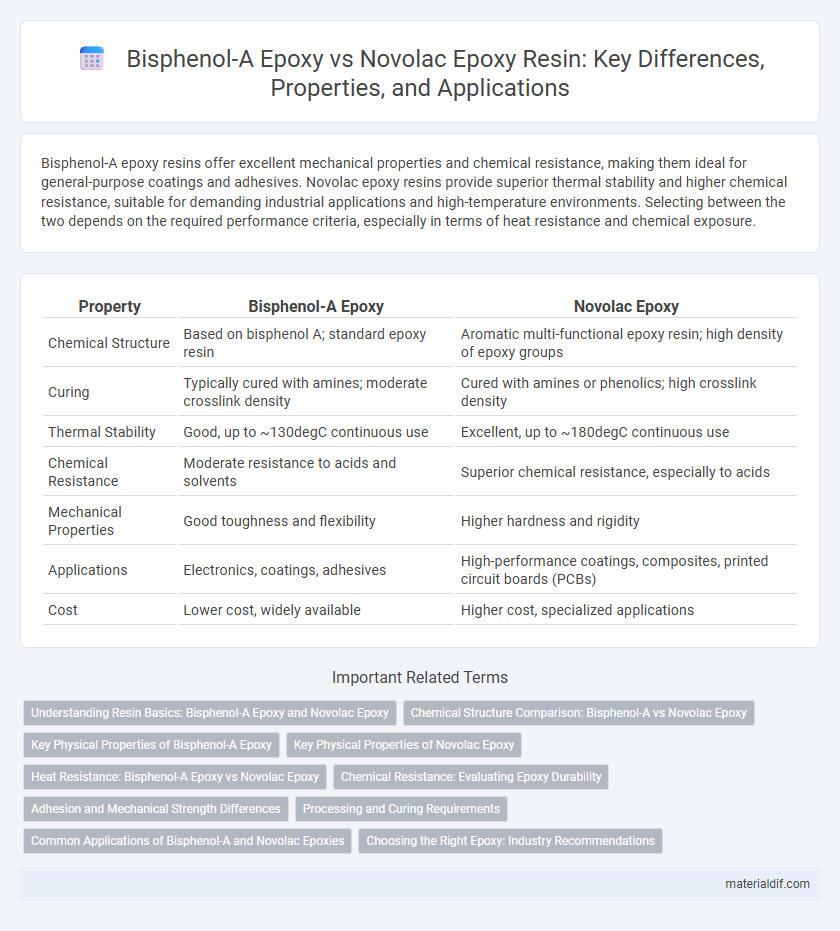
| Property | Bisphenol-A Epoxy | Novolac Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Based on bisphenol A; standard epoxy resin | Aromatic multi-functional epoxy resin; high density of epoxy groups |
| Curing | Typically cured with amines; moderate crosslink density | Cured with amines or phenolics; high crosslink density |
| Thermal Stability | Good, up to ~130degC continuous use | Excellent, up to ~180degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to acids and solvents | Superior chemical resistance, especially to acids |
| Mechanical Properties | Good toughness and flexibility | Higher hardness and rigidity |
| Applications | Electronics, coatings, adhesives | High-performance coatings, composites, printed circuit boards (PCBs) |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized applications |
Understanding Resin Basics: Bisphenol-A Epoxy and Novolac Epoxy
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins are widely used for their excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and ease of processing, making them ideal for coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. Novolac epoxy resins, derived from phenol-formaldehyde novolac, offer superior thermal stability, higher chemical resistance, and improved cross-link density, which makes them suitable for demanding applications such as printed circuit boards and aerospace components. Understanding the fundamental differences in molecular structure and curing behavior between Bisphenol-A and Novolac epoxies enables optimized resin selection for specific industrial requirements.
Chemical Structure Comparison: Bisphenol-A vs Novolac Epoxy
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins feature a rigid structure characterized by two phenol groups connected via a propane bridge, offering high mechanical strength and thermal stability. Novolac epoxy resins contain multiple phenol units linked through methylene bridges, resulting in a higher epoxy equivalent weight and enhanced chemical resistance. The structural difference in the aromatic frameworks significantly influences curing behavior, crosslink density, and resulting thermal and chemical properties of the epoxy systems.
Key Physical Properties of Bisphenol-A Epoxy
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins exhibit excellent mechanical strength, high chemical resistance, and a glass transition temperature (Tg) typically ranging from 120degC to 150degC, making them suitable for general-purpose coatings and adhesives. Their viscosity is moderate, ensuring easy processing and good flow properties compared to Novolac epoxy resins, which have higher crosslink density and thermal stability. Bisphenol-A epoxy also demonstrates good electrical insulation properties and low moisture absorption, contributing to reliable performance in electronic encapsulation and laminates.
Key Physical Properties of Novolac Epoxy
Novolac epoxy resin exhibits superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to Bisphenol-A epoxy, making it ideal for high-performance applications. It typically has a higher glass transition temperature (Tg), often exceeding 150degC, which enhances its durability under thermal stress. The curing process of Novolac epoxy produces a highly cross-linked network, resulting in improved mechanical strength and improved resistance to solvents and corrosive environments.
Heat Resistance: Bisphenol-A Epoxy vs Novolac Epoxy
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins typically exhibit moderate heat resistance with thermal stability up to approximately 120-150degC. Novolac epoxy resins outperform Bisphenol-A types by offering superior heat resistance, often withstanding temperatures exceeding 200degC due to their highly cross-linked aromatic structure. This elevated thermal stability makes Novolac epoxy ideal for high-temperature applications in electronics and industrial coatings.
Chemical Resistance: Evaluating Epoxy Durability
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins exhibit moderate chemical resistance, performing well against acids, alkalis, and solvents but showing susceptibility to prolonged exposure to strong chemicals. Novolac epoxy resins, derived from phenol-formaldehyde novolac, offer superior chemical resistance, especially to aggressive acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. The enhanced cross-link density in novolac epoxy contributes to its exceptional durability and resistance to chemical degradation compared to Bisphenol-A epoxy.
Adhesion and Mechanical Strength Differences
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins exhibit strong adhesion due to their balanced molecular structure, providing excellent bonding to metal and composite surfaces, but their mechanical strength is moderate under high thermal stress. Novolac epoxy resins offer superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for demanding environments, though their adhesion properties can be less effective without proper surface preparation. The choice between Bisphenol-A and Novolac epoxy depends on the trade-off between adhesion performance and mechanical durability needed for specific industrial applications.
Processing and Curing Requirements
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins typically require moderate curing temperatures between 100-150degC and standard curing agents like amines, allowing for flexible processing conditions and shorter cycle times. Novolac epoxy resins demand higher curing temperatures above 150degC due to their multi-functional epoxy groups, resulting in a more complex cross-linking network and enhanced thermal and chemical resistance. The increased curing temperature and extended curing time for novolac epoxies necessitate specialized equipment and precise process control to achieve optimal mechanical properties.
Common Applications of Bisphenol-A and Novolac Epoxies
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins are widely used in coatings, adhesives, and electrical laminates due to their excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Novolac epoxies, characterized by higher thermal stability and superior chemical resistance, are commonly found in industrial flooring, high-performance composites, and corrosion-resistant coatings. Both epoxies serve critical roles in electronics, but Novolac formulations are preferred for harsh environments requiring enhanced durability.
Choosing the Right Epoxy: Industry Recommendations
Bisphenol-A epoxy resins exhibit excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making them suitable for general-purpose coatings and adhesives, while Novolac epoxy resins offer superior thermal stability and enhanced resistance to harsh chemicals, ideal for high-temperature applications and aggressive environments. Industry recommendations highlight selecting Bisphenol-A epoxy for structural bonding and electrical insulation, whereas Novolac epoxy is preferred in aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors requiring high-performance durability. Understanding application conditions and required performance metrics is essential for choosing the right epoxy resin type to ensure optimal product lifespan and reliability.
Bisphenol-A Epoxy vs Novolac Epoxy Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com