Two-part epoxy consists of a resin and a hardener that must be mixed prior to use, providing a stronger, more durable bond ideal for resin pet projects requiring high strength and chemical resistance. One-part epoxy is pre-mixed and cures with the application of heat, offering convenience and faster application but generally less mechanical strength compared to two-part systems. Choosing between two-part and one-part epoxy depends on the complexity of the project, desired bond strength, and application conditions for resin pet crafting.
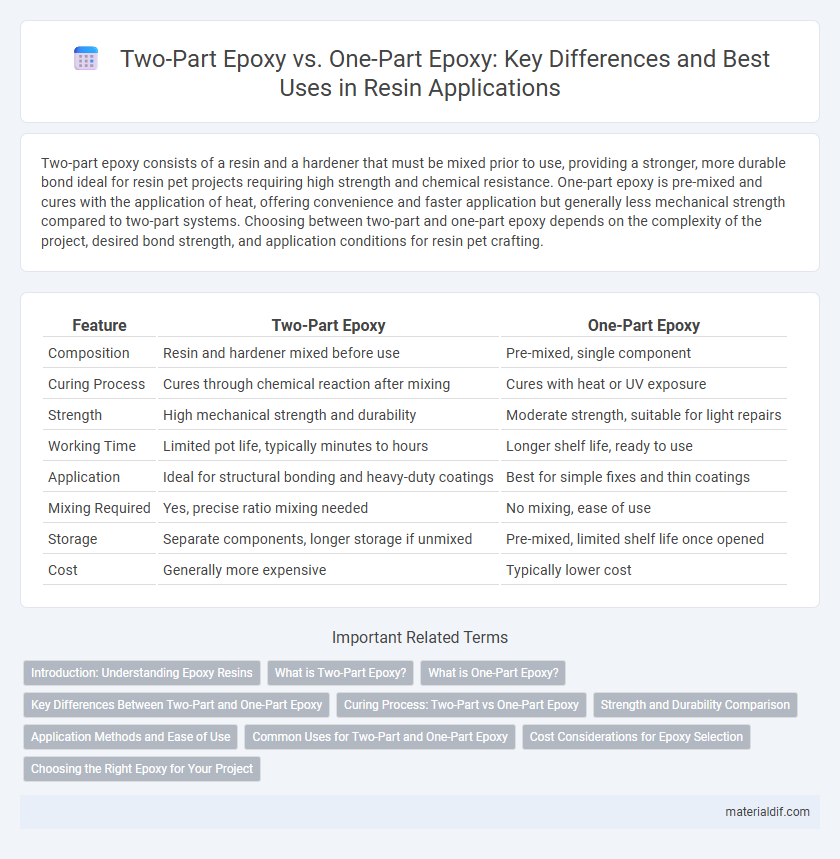
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Two-Part Epoxy | One-Part Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Resin and hardener mixed before use | Pre-mixed, single component |
| Curing Process | Cures through chemical reaction after mixing | Cures with heat or UV exposure |
| Strength | High mechanical strength and durability | Moderate strength, suitable for light repairs |
| Working Time | Limited pot life, typically minutes to hours | Longer shelf life, ready to use |
| Application | Ideal for structural bonding and heavy-duty coatings | Best for simple fixes and thin coatings |
| Mixing Required | Yes, precise ratio mixing needed | No mixing, ease of use |
| Storage | Separate components, longer storage if unmixed | Pre-mixed, limited shelf life once opened |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically lower cost |
Introduction: Understanding Epoxy Resins
Two-part epoxy consists of a resin and a hardener that chemically react when mixed, creating a strong, durable bond ideal for industrial and DIY applications. One-part epoxy is pre-mixed and cures with heat, offering convenience but generally less strength and chemical resistance compared to two-part formulas. Understanding the differences in composition and curing methods helps in selecting the right epoxy resin for specific bonding, coating, or sealing needs.
What is Two-Part Epoxy?
Two-part epoxy consists of a resin and a hardener that chemically react when mixed, creating a strong, durable bond used in various applications from construction to crafting. This type of epoxy provides superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties compared to one-part epoxy, making it ideal for heavy-duty repairs and industrial use. The mixing ratio and curing time are critical factors that influence the final strength and performance of two-part epoxy systems.
What is One-Part Epoxy?
One-part epoxy is a resin system that cures upon exposure to specific environmental conditions such as heat or moisture, eliminating the need for mixing separate components. This type of epoxy offers convenience and ease of use compared to two-part epoxies, which require precise mixing of resin and hardener to initiate the chemical reaction. Common applications of one-part epoxy include coatings, adhesives, and repairs where controlled curing and simplicity are preferred.
Key Differences Between Two-Part and One-Part Epoxy
Two-part epoxy consists of a resin and a hardener that must be mixed in precise proportions to initiate the chemical curing process, offering superior strength and durability compared to one-part epoxy, which cures through exposure to moisture or heat. Two-part epoxy provides enhanced adhesion and chemical resistance, making it ideal for structural repairs and industrial applications, whereas one-part epoxy is easier to apply and suitable for minor repairs or coatings. The curing time of two-part epoxy is generally faster and more controllable, while one-part epoxy offers convenience but often sacrifices performance in demanding environments.
Curing Process: Two-Part vs One-Part Epoxy
Two-part epoxy consists of resin and hardener components that chemically react during mixing to initiate a curing process, resulting in a strong, durable bond with controlled working time. One-part epoxy cures through exposure to heat or moisture, simplifying application but often requiring elevated temperatures or longer curing durations. The two-part system offers greater versatility and faster cure times, while the one-part epoxy provides convenience for specific industrial or repair applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Two-part epoxy offers superior strength and durability compared to one-part epoxy due to its chemical curing process that creates a robust molecular bond. The dual components--a resin and a hardener--react to form a solid, resilient material ideal for heavy-duty applications and structural repairs. One-part epoxies, while easier to use, generally provide less resistance to impact, heat, and chemicals, making them better suited for lighter or temporary fixes.
Application Methods and Ease of Use
Two-part epoxy requires mixing resin and hardener before application, offering precise control over curing time and strength, making it ideal for complex repairs and bonding tasks. One-part epoxy comes pre-mixed and cures upon exposure to heat or air, simplifying application with minimal preparation, which suits quick fixes and surface coatings. The two-part system demands more effort but provides greater versatility, while the one-part system excels in convenience and speed.
Common Uses for Two-Part and One-Part Epoxy
Two-part epoxy is commonly used for structural repairs, bonding metals, laminates, and in automotive and marine applications due to its superior strength and chemical resistance. One-part epoxy is typically applied as a coating or adhesive in easier, less demanding tasks such as household repairs, wood finishing, and electrical insulation because it cures with heat or moisture exposure. The choice between two-part and one-part epoxy depends on the required durability, curing conditions, and application complexity.
Cost Considerations for Epoxy Selection
Two-part epoxy typically involves higher upfront costs due to the need for separate resin and hardener components, offering superior strength and durability for demanding applications. One-part epoxy, often available as pre-mixed or heat-curable formulations, provides cost savings in ease of use and reduced waste, making it ideal for smaller repair projects or less critical bonding. Evaluating total project expenses, including labor, curing time, and material performance, is crucial when selecting between two-part and one-part epoxy systems.
Choosing the Right Epoxy for Your Project
Two-part epoxy consists of resin and hardener components that chemically react to form a strong, durable bond, making it ideal for structural repairs and industrial applications. One-part epoxy cures by exposure to heat or moisture, providing convenience for minor fixes and surface coatings without mixing requirements. Selecting the right epoxy depends on factors like project scale, curing conditions, and desired strength, with two-part epoxy offering higher performance for demanding tasks and one-part epoxy suited for simpler, faster applications.
Two-Part Epoxy vs One-Part Epoxy Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com