Phenolic resin is known for its exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and high heat tolerance, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring strong bonding and insulation. Melamine resin offers superior hardness, scratch resistance, and a glossy finish, often used in laminates and decorative surfaces. While phenolic resin excels in structural strength, melamine resin is preferred for aesthetic and surface protection purposes.
Table of Comparison
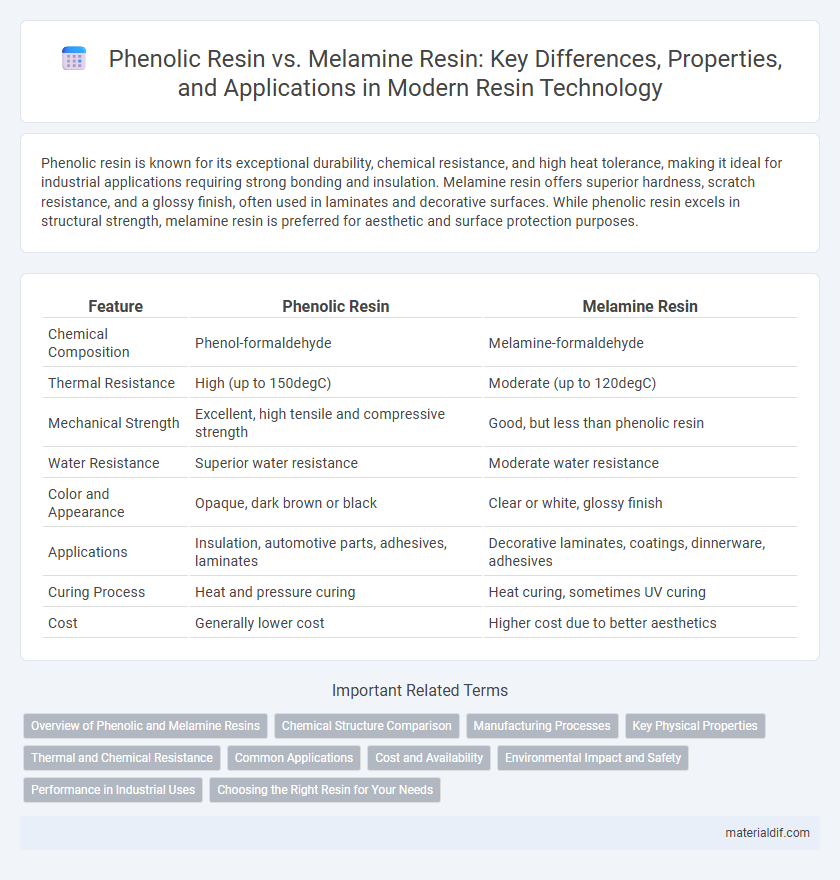
| Feature | Phenolic Resin | Melamine Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Phenol-formaldehyde | Melamine-formaldehyde |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 120degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent, high tensile and compressive strength | Good, but less than phenolic resin |
| Water Resistance | Superior water resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Color and Appearance | Opaque, dark brown or black | Clear or white, glossy finish |
| Applications | Insulation, automotive parts, adhesives, laminates | Decorative laminates, coatings, dinnerware, adhesives |
| Curing Process | Heat and pressure curing | Heat curing, sometimes UV curing |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to better aesthetics |
Overview of Phenolic and Melamine Resins
Phenolic resin is a thermosetting polymer known for its high mechanical strength, heat resistance, and excellent insulating properties, commonly used in adhesives, laminates, and molding compounds. Melamine resin, also a thermosetting polymer, is prized for its hardness, chemical resistance, and glossy finish, making it ideal for decorative laminates, dinnerware, and coatings. Both resins exhibit strong thermal stability and durability, but phenolic resin excels in fire resistance while melamine resin offers superior surface hardness and aesthetic appeal.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Phenolic resin consists of phenol and formaldehyde molecules linked by methylene bridges, creating a highly cross-linked, aromatic polymer structure renowned for heat resistance and mechanical strength. Melamine resin is formed from melamine and formaldehyde, featuring triazine rings that provide enhanced hardness, transparency, and chemical resistance compared to phenolic resin. The key structural difference lies in phenolic resin's phenol-based network versus melamine resin's nitrogen-rich triazine ring system, influencing their distinct thermal and physical properties.
Manufacturing Processes
Phenolic resin manufacturing involves the condensation reaction of phenol and formaldehyde under either acidic or alkaline conditions, forming a thermosetting polymer with high heat resistance and mechanical strength. Melamine resin production is based on the reaction between melamine and formaldehyde, producing a highly cross-linked network polymer known for its superior hardness, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy. The curing process of phenolic resins typically requires longer times and higher temperatures compared to melamine resins, which cure faster and allow for more precise molding applications.
Key Physical Properties
Phenolic resin exhibits high thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Melamine resin offers outstanding hardness, low moisture absorption, and superior surface finish, which are preferred in laminates and coatings. Both resins provide good electrical insulation, but phenolic resins typically outperform melamine in heat endurance and chemical inertness.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Phenolic resin demonstrates superior thermal resistance, maintaining stability at temperatures up to 150degC to 180degC, making it ideal for heat-resistant applications. Melamine resin offers excellent chemical resistance, particularly against acids and alkalis, but typically withstands temperatures only up to around 120degC. In environments requiring high thermal endurance combined with moderate chemical resistance, phenolic resin is preferred, while melamine resin suits applications demanding robust chemical stability under lower temperature conditions.
Common Applications
Phenolic resin is commonly used in the production of circuit boards, automotive parts, and molded products due to its high mechanical strength and thermal stability. Melamine resin is widely applied in laminates, adhesives, and kitchenware, valued for its hardness, scratch resistance, and glossy finish. Both resins serve critical roles in manufacturing, with phenolic preferred for heat-resistant and structural uses, while melamine is favored for decorative and surface applications.
Cost and Availability
Phenolic resin typically offers a lower cost and greater availability due to its widespread industrial use and simpler manufacturing process. Melamine resin, while more expensive, provides superior hardness and resistance properties but is less commonly produced, affecting its market availability. The cost difference makes phenolic resin a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications where high mechanical strength is required.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Phenolic resins release lower levels of formaldehyde compared to melamine resins, contributing to improved indoor air quality and reduced health risks during use. Melamine resins, while offering higher water resistance and durability, may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that pose greater environmental concerns. Phenolic resins also tend to be more biodegradable, making them a safer choice in applications prioritizing environmental sustainability and human safety.
Performance in Industrial Uses
Phenolic resin offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as automotive parts and electrical insulation. Melamine resin provides excellent hardness, scratch resistance, and chemical stability, often used in laminates, coatings, and molding compounds. Both resins exhibit strong adhesive properties, but phenolic resin dominates in durability under extreme conditions, while melamine resin excels in aesthetic and surface performance.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Needs
Phenolic resin offers exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for industrial applications such as automotive parts and electrical insulators. Melamine resin excels in providing superior hardness, scratch resistance, and glossy finishes, often used in laminates, kitchenware, and decorative surfaces. Selecting the right resin depends on factors like durability requirements, exposure conditions, and aesthetic preferences to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Phenolic resin vs Melamine resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com