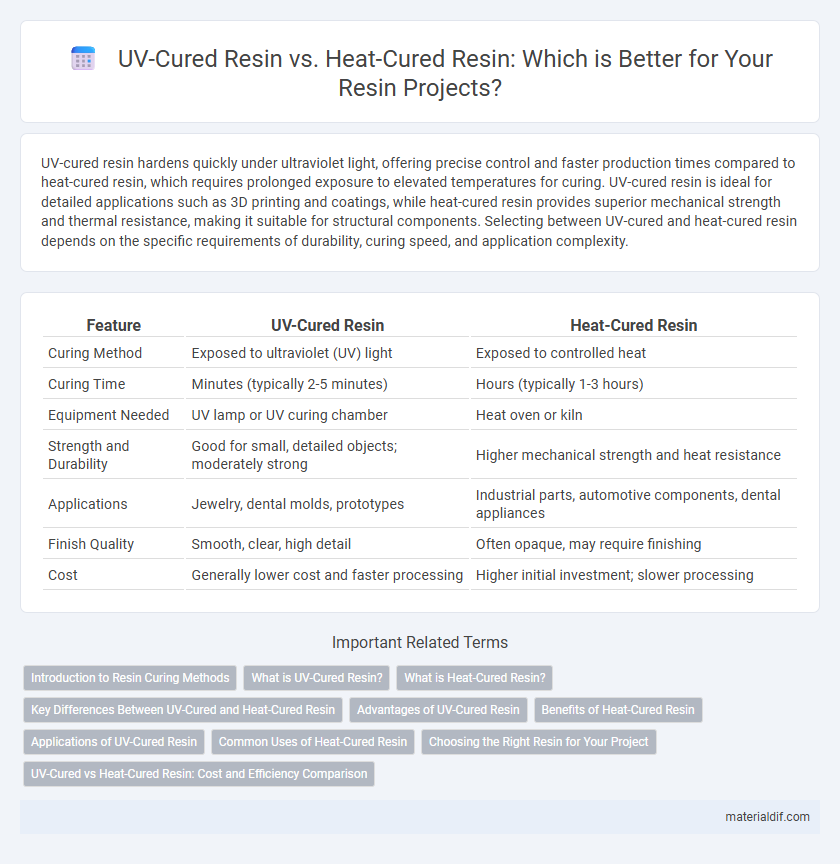
UV-cured resin hardens quickly under ultraviolet light, offering precise control and faster production times compared to heat-cured resin, which requires prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures for curing. UV-cured resin is ideal for detailed applications such as 3D printing and coatings, while heat-cured resin provides superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making it suitable for structural components. Selecting between UV-cured and heat-cured resin depends on the specific requirements of durability, curing speed, and application complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UV-Cured Resin | Heat-Cured Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Method | Exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light | Exposed to controlled heat |
| Curing Time | Minutes (typically 2-5 minutes) | Hours (typically 1-3 hours) |
| Equipment Needed | UV lamp or UV curing chamber | Heat oven or kiln |
| Strength and Durability | Good for small, detailed objects; moderately strong | Higher mechanical strength and heat resistance |
| Applications | Jewelry, dental molds, prototypes | Industrial parts, automotive components, dental appliances |
| Finish Quality | Smooth, clear, high detail | Often opaque, may require finishing |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and faster processing | Higher initial investment; slower processing |
Introduction to Resin Curing Methods
UV-cured resin utilizes ultraviolet light to initiate a rapid polymerization process, resulting in faster curing times and high precision in applications such as 3D printing and coatings. Heat-cured resin requires elevated temperatures over extended periods to trigger chemical cross-linking, offering superior mechanical strength and thermal stability ideal for industrial and aerospace uses. Both curing methods influence the resin's physical properties, processing speed, and end-use performance, making selection dependent on specific application requirements and environmental conditions.
What is UV-Cured Resin?
UV-cured resin is a type of polymer that hardens or cures when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, enabling rapid and precise solidification. This resin is commonly used in applications like 3D printing, coatings, and adhesives due to its fast curing time and ability to produce high-resolution details. The curing process involves photoinitiators within the resin that react to UV wavelengths, triggering polymerization and transforming the liquid resin into a durable solid.
What is Heat-Cured Resin?
Heat-cured resin is a polymer that hardens through a thermal curing process, requiring elevated temperatures to initiate chemical reactions that form a durable, solid material. This type of resin is commonly used in dental applications, composite manufacturing, and coatings due to its superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Unlike UV-cured resin, which hardens quickly under ultraviolet light, heat-cured resin typically needs a controlled oven environment to achieve full polymerization and optimal performance.
Key Differences Between UV-Cured and Heat-Cured Resin
UV-cured resin solidifies rapidly when exposed to specific ultraviolet light wavelengths, enabling faster production cycles and precise curing control. Heat-cured resin requires elevated temperatures for extended periods to achieve full polymerization, resulting in increased mechanical strength and enhanced thermal resistance. Differences in curing methods impact application suitability, with UV-cured resin favored for quick prototyping and heat-cured resin preferred for durable, high-performance components.
Advantages of UV-Cured Resin
UV-cured resin offers rapid curing times, typically seconds to minutes, significantly enhancing production efficiency compared to heat-cured resin, which often requires hours of baking. This resin type provides superior precision and detail in applications such as 3D printing and coatings due to its controlled UV light exposure. UV-cured resin also exhibits lower energy consumption and reduced thermal stress on substrates, improving material compatibility and durability.
Benefits of Heat-Cured Resin
Heat-cured resin offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to UV-cured resin, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term stability. It provides enhanced resistance to heat and chemicals, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments. The controlled curing process allows for uniform polymerization, reducing the risk of incomplete curing and improving overall material consistency.
Applications of UV-Cured Resin
UV-cured resin is widely used in applications requiring fast curing times and high precision, such as 3D printing, dental restorations, and electronics encapsulation. Its ability to rapidly harden under UV light makes it ideal for intricate designs and fine detail work in industries including jewelry making and optical lens manufacturing. The superior adhesion and durability of UV-cured resin enhance its performance in coatings, adhesives, and protective layers for various commercial and industrial purposes.
Common Uses of Heat-Cured Resin
Heat-cured resin is widely utilized in dental applications, particularly for fabricating durable dentures, orthodontic appliances, and dental bases due to its superior mechanical strength and biocompatibility. It is also common in industrial and craft settings for producing robust molds, prosthetics, and custom tools, benefiting from its ability to withstand higher temperatures and stress. The heat-curing process ensures enhanced adhesion and longevity, making heat-cured resin the preferred choice where structural integrity and wear resistance are essential.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
UV-cured resin offers rapid curing times and high detail precision, making it ideal for intricate 3D prints and small-scale projects requiring fine resolution. Heat-cured resin provides superior durability and chemical resistance, suitable for automotive parts, dental applications, and industrial prototypes that must endure harsh conditions. Selecting the right resin depends on balancing project requirements such as curing speed, mechanical properties, and environmental resistance.
UV-Cured vs Heat-Cured Resin: Cost and Efficiency Comparison
UV-cured resin typically offers faster curing times, often curing within minutes under UV light, resulting in higher production efficiency compared to heat-cured resin which may require hours at elevated temperatures. While UV-cured resin systems tend to have higher initial costs due to specialized UV lamps and equipment, their lower energy consumption and quicker turnaround can reduce overall operational expenses. Heat-cured resins generally have lower upfront equipment costs but incur higher energy expenses and longer cycle times, impacting total manufacturing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
UV-Cured Resin vs Heat-Cured Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com