Fast-cure resin offers rapid setting times, enabling quicker project completion and reducing downtime. Slow-cure resin provides extended working time, allowing for detailed adjustments and minimizing the risk of air bubbles or imperfections. Selecting between fast-cure and slow-cure resin depends on the specific application requirements, balancing speed with precision.
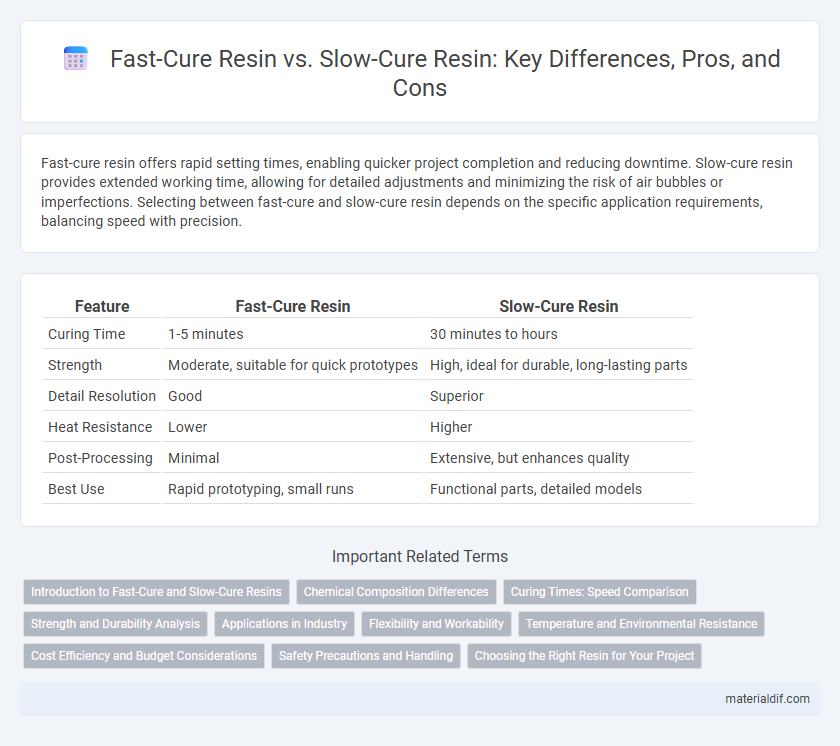
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fast-Cure Resin | Slow-Cure Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Time | 1-5 minutes | 30 minutes to hours |
| Strength | Moderate, suitable for quick prototypes | High, ideal for durable, long-lasting parts |
| Detail Resolution | Good | Superior |
| Heat Resistance | Lower | Higher |
| Post-Processing | Minimal | Extensive, but enhances quality |
| Best Use | Rapid prototyping, small runs | Functional parts, detailed models |
Introduction to Fast-Cure and Slow-Cure Resins
Fast-cure resin rapidly polymerizes, enabling quicker production cycles and early demolding, which is ideal for urgent prototyping and small-batch manufacturing. Slow-cure resin offers extended working time and improved mechanical properties, making it suitable for complex molds and high-strength applications. Understanding the balance between curing speed and resin performance aids in selecting the right resin for specific industrial or artistic needs.
Chemical Composition Differences
Fast-cure resin typically contains higher concentrations of reactive monomers and accelerators, enabling rapid polymerization through enhanced free-radical activity. Slow-cure resin formulations incorporate stabilizers and lower cross-linker content, which prolong the curing process by controlling the rate of polymer chain growth. These chemical composition differences significantly affect the resin's viscosity, thermal stability, and mechanical properties during and after curing.
Curing Times: Speed Comparison
Fast-cure resin typically hardens within minutes to an hour, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and quick repairs, while slow-cure resin can take several hours to fully cure, providing more working time for detailed applications and large projects. The shorter curing time of fast-cure resin accelerates production cycles but may result in increased brittleness, whereas slow-cure resin offers greater structural integrity and reduced stress in the final product due to its gradual polymerization. Choosing between fast-cure and slow-cure resin depends on balancing the need for speed against the desired mechanical properties and project complexity.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Fast-cure resin typically achieves initial hardness quickly but may exhibit lower ultimate strength and reduced long-term durability compared to slow-cure resin. Slow-cure resin allows more complete polymer cross-linking, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength and increased resistance to environmental stressors. Selecting slow-cure resin is often preferable for applications requiring superior toughness and prolonged lifespan.
Applications in Industry
Fast-cure resin is ideal for high-speed manufacturing processes such as automotive parts and rapid prototyping due to its shorter setting time and enhanced productivity. Slow-cure resin is preferred in aerospace and marine industries where superior mechanical strength and reduced internal stress are critical for long-term durability. Selecting the appropriate resin curing time impacts production efficiency, product performance, and material stability across industrial applications.
Flexibility and Workability
Fast-cure resin offers increased flexibility due to its rapid polymerization, making it ideal for projects requiring quick setting and easy manipulation. Slow-cure resin provides superior workability, allowing extended shaping and smoothing time before hardening, which benefits detailed or complex applications. Choosing between fast-cure and slow-cure resins depends on balancing the need for flexibility during initial handling and the desired working time for precision finishes.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance
Fast-cure resin typically cures at lower temperatures, making it ideal for applications requiring quick turnaround times, but it often exhibits reduced resistance to high heat and harsh environmental conditions. Slow-cure resin generally requires higher curing temperatures, allowing for a more controlled polymerization process that enhances thermal stability and long-term environmental resistance. Choosing between fast-cure and slow-cure resin depends on balancing the need for rapid curing with desired performance in elevated temperatures and exposure to elements such as moisture and UV radiation.
Cost Efficiency and Budget Considerations
Fast-cure resin offers significant cost efficiency by reducing production time and energy consumption, making it ideal for tight budgets and quick project turnarounds. Slow-cure resin, while typically more expensive due to longer curing durations and increased labor costs, provides enhanced durability and finish quality that may justify the higher initial investment in long-term applications. Choosing between fast-cure and slow-cure resin depends on balancing immediate budget constraints with the desired performance and lifecycle costs of the final product.
Safety Precautions and Handling
Fast-cure resin requires strict safety precautions due to its rapid chemical reaction, which can generate heat and increase the risk of burns or toxic fume exposure, making it essential to use gloves, protective eyewear, and work in a well-ventilated area. Slow-cure resin allows more working time and generally produces fewer fumes, reducing immediate hazards, but still demands careful handling to avoid skin contact and inhalation of styrene vapors. Proper storage and disposal guidelines must be followed for both resins to prevent environmental contamination and health risks.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Fast-cure resin offers rapid setting times ideal for quick turnarounds or small-scale projects requiring immediate handling strength. Slow-cure resin provides enhanced clarity and reduced stress development, making it suitable for large casts and intricate molds where durability and finish quality are paramount. Selecting the right resin depends on balancing project size, detail requirements, and working time to achieve optimal results.
Fast-Cure Resin vs Slow-Cure Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com