Flame retardant resin offers enhanced fire resistance compared to standard resin, significantly reducing the risk of ignition and slowing the spread of flames. This specialized resin contains additives that improve safety in applications requiring strict fire safety standards. Standard resin, while versatile and durable, lacks these fire-retardant properties, making it less suitable for environments with high fire hazards.
Table of Comparison
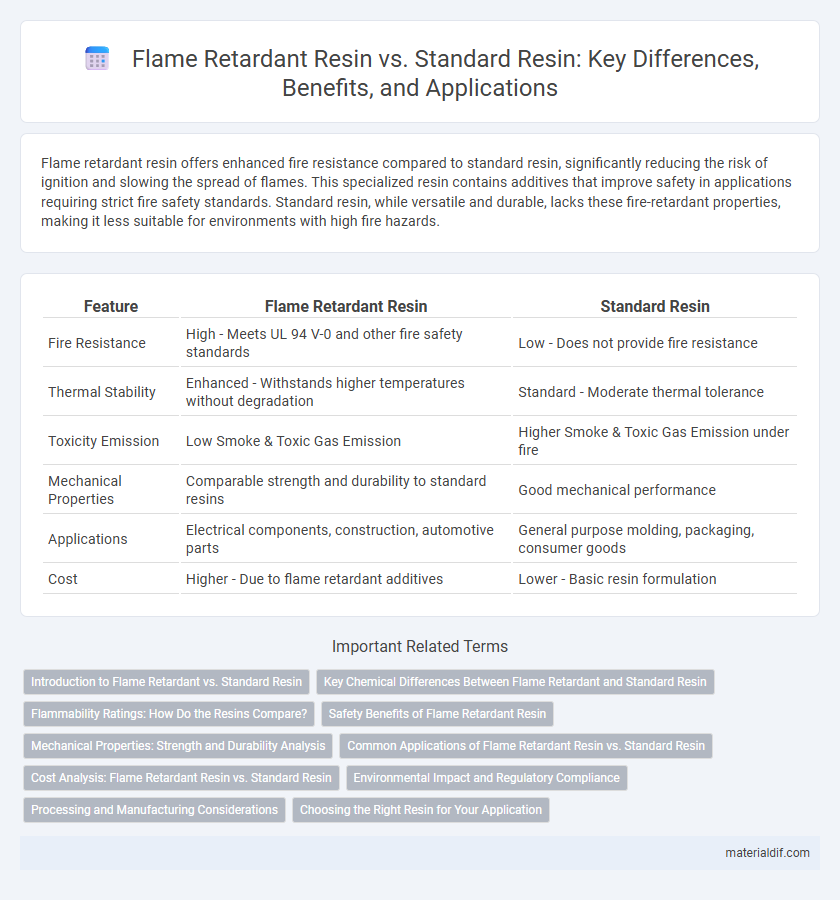
| Feature | Flame Retardant Resin | Standard Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High - Meets UL 94 V-0 and other fire safety standards | Low - Does not provide fire resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced - Withstands higher temperatures without degradation | Standard - Moderate thermal tolerance |
| Toxicity Emission | Low Smoke & Toxic Gas Emission | Higher Smoke & Toxic Gas Emission under fire |
| Mechanical Properties | Comparable strength and durability to standard resins | Good mechanical performance |
| Applications | Electrical components, construction, automotive parts | General purpose molding, packaging, consumer goods |
| Cost | Higher - Due to flame retardant additives | Lower - Basic resin formulation |
Introduction to Flame Retardant vs. Standard Resin
Flame retardant resin is engineered by incorporating chemical additives that significantly reduce flammability and slow combustion compared to standard resin, which lacks these fire-resistant properties. This specialized resin is crucial in industries requiring stringent fire safety standards, such as electronics, automotive, and construction. Standard resin offers flexibility and general durability but does not provide the enhanced fire protection essential for applications exposed to high heat or potential ignition sources.
Key Chemical Differences Between Flame Retardant and Standard Resin
Flame retardant resin contains chemically integrated additives such as halogens, phosphorus, or nitrogen compounds that inhibit combustion, unlike standard resin which lacks these fire-resistant components. The molecular structure of flame retardant resin promotes char formation and reduces flammable gas release, significantly enhancing fire resistance. Standard resins typically consist of hydrocarbons prone to ignition and faster flame propagation due to the absence of specialized retardant chemicals.
Flammability Ratings: How Do the Resins Compare?
Flame retardant resins have significantly lower flammability ratings compared to standard resins, often meeting UL 94 V-0 standards, which indicates high resistance to ignition and slow burning rates. Standard resins typically exhibit higher flammability with classifications like UL 94 HB or higher, making them less suitable for applications requiring stringent fire safety. The enhanced fire retardant properties of specialized resins result from additives that promote char formation and inhibit flame propagation, thus improving overall fire performance.
Safety Benefits of Flame Retardant Resin
Flame retardant resin significantly enhances safety by inhibiting the ignition and slowing the spread of fire, reducing the risk of fire-related damage and injury. Its chemical additives form a protective char layer that acts as a barrier against heat and flames, making it ideal for applications demanding high fire resistance. Compared to standard resin, flame retardant resin complies with stringent fire safety standards, ensuring better protection in construction, electronics, and transportation industries.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability Analysis
Flame retardant resin exhibits enhanced mechanical properties compared to standard resin, with superior tensile strength and improved impact resistance due to the incorporation of flame-resistant additives. The durability of flame retardant resin is increased, offering better resistance to thermal degradation and prolonged service life in high-temperature environments. These improvements make flame retardant resin suitable for applications requiring both fire safety and mechanical reliability.
Common Applications of Flame Retardant Resin vs. Standard Resin
Flame retardant resin is widely used in electronics, automotive components, and construction materials where enhanced fire safety is critical. Standard resin is typically employed in packaging, consumer goods, and general molding applications where fire resistance is not a primary concern. The key distinction lies in flame retardant resin's ability to self-extinguish, making it essential for industries requiring strict compliance with fire safety regulations.
Cost Analysis: Flame Retardant Resin vs. Standard Resin
Flame retardant resin typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to standard resin due to specialized additives and processing requirements that enhance fire resistance. Despite the initial expense, flame retardant resin can reduce overall lifecycle costs by minimizing fire damage, lowering insurance premiums, and meeting stringent safety regulations. Standard resin offers a cost-effective solution for non-critical applications but may expose projects to higher risk and compliance costs in fire-sensitive environments.
Environmental Impact and Regulatory Compliance
Flame retardant resin incorporates specialized additives to reduce flammability, which often involve halogenated compounds that can release toxic byproducts during degradation, posing greater environmental risks compared to standard resin. Regulatory compliance for flame retardant resins is stringent, with mandates such as REACH in Europe and EPA TSCA in the United States requiring rigorous testing to limit the use of hazardous substances and ensure safe disposal. Conversely, standard resin typically has fewer regulatory constraints but lacks the fire safety benefits, making it less suitable for applications with strict fire performance and environmental standards.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Flame retardant resin requires specialized processing conditions due to its higher thermal stability and often increased viscosity compared to standard resin, which can affect mold filling and cycle times. Manufacturing with flame retardant resin demands careful selection of additives and precise temperature control to maintain flame retardancy without compromising mechanical properties. Equipment wear and compatibility with common manufacturing methods such as injection molding or extrusion must also be evaluated to ensure consistent product quality and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Application
Flame retardant resin incorporates chemical additives that significantly enhance fire resistance by inhibiting ignition and slowing combustion, making it ideal for applications in electronics, construction, and automotive industries where safety regulations are stringent. Standard resin, while offering excellent mechanical strength and durability, lacks specialized fire resistance properties and is better suited for applications where fire risk is minimal. Selecting the right resin involves assessing environmental exposure, compliance standards, and performance requirements to ensure optimal safety and functionality for your specific project.
Flame Retardant Resin vs Standard Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com