Synthetic resin offers enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and faster curing times compared to natural resin. Natural resin, derived from plant secretions, provides biodegradability and is favored for traditional applications requiring minimal environmental impact. Choosing between synthetic and natural resin depends on the specific requirements of strength, environmental sustainability, and application method.
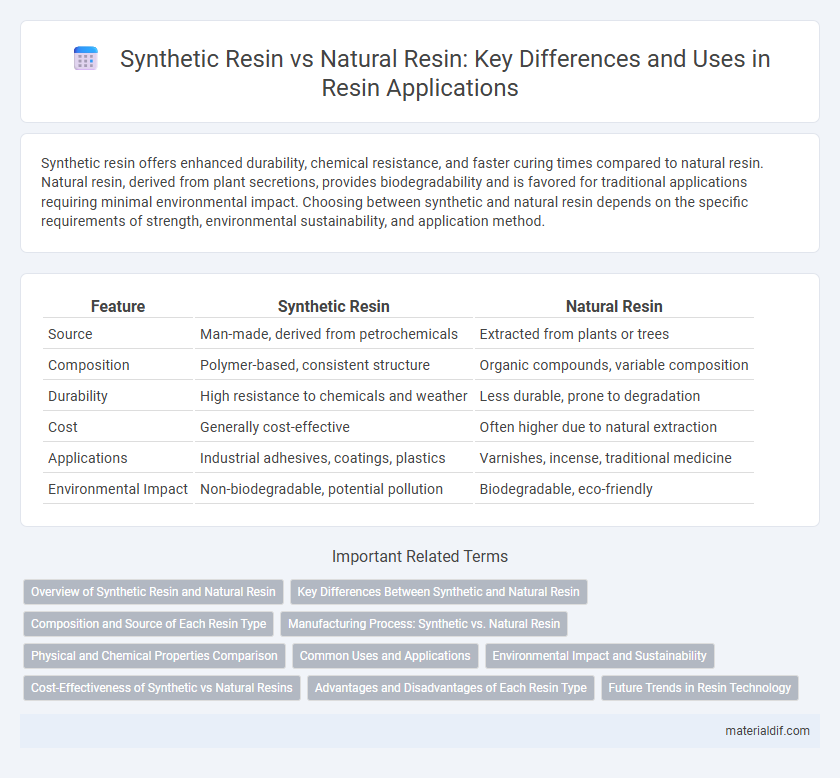
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Resin | Natural Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made, derived from petrochemicals | Extracted from plants or trees |
| Composition | Polymer-based, consistent structure | Organic compounds, variable composition |
| Durability | High resistance to chemicals and weather | Less durable, prone to degradation |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective | Often higher due to natural extraction |
| Applications | Industrial adhesives, coatings, plastics | Varnishes, incense, traditional medicine |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, potential pollution | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
Overview of Synthetic Resin and Natural Resin
Synthetic resins are man-made polymers derived from petrochemicals, designed for consistent quality, enhanced durability, and precise application in industries like adhesives, coatings, and plastics. Natural resins, secreted by plants such as pine trees, consist of organic compounds like terpenes and exhibit biodegradability, traditional uses in varnishes, and medicinal properties. While synthetic resins offer superior resistance to heat and chemicals, natural resins provide eco-friendly alternatives with renewable sourcing and unique aromatic characteristics.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Natural Resin
Synthetic resin is chemically engineered from petrochemicals, offering consistent quality and customizable properties for industrial applications, whereas natural resin is exuded from plants and trees, primarily composed of organic compounds like terpenes. Synthetic resin typically exhibits higher durability, resistance to environmental factors, and ease of processing, making it suitable for plastic manufacturing and coatings, while natural resin is valued for its biodegradability, aroma, and traditional uses in varnishes and adhesives. Cost-effectiveness and scalability favor synthetic resin production, contrasting with the limited availability and seasonal variability inherent to natural resin extraction.
Composition and Source of Each Resin Type
Synthetic resin is primarily composed of polymerized hydrocarbons derived from petrochemical sources, offering uniform molecular structure and customizable properties. Natural resin originates from plant exudates or fossilized organic materials like amber, consisting mainly of complex mixtures of terpenes and other organic compounds. The source difference influences their chemical composition, with synthetic resins enabling precise industrial applications while natural resins provide biodegradable and bio-based options.
Manufacturing Process: Synthetic vs. Natural Resin
Synthetic resin manufacturing involves polymerization of monomers derived from petrochemicals, enabling precise control over molecular weight and properties through processes like addition or condensation polymerization. Natural resin extraction is a raw material-driven process, obtained from plant secretions such as pine trees, and involves solvent extraction or tapping methods without chemical alteration. The synthetic process offers scalability and consistency, while natural resin production depends on environmental factors and seasonal availability.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Synthetic resin exhibits uniform molecular structure, enhanced thermal stability, and superior mechanical strength compared to natural resin, which is characterized by variable composition and lower melting points. Natural resin is primarily composed of complex organic compounds like terpenes and phenolic substances, while synthetic resin consists of polymerized monomers such as epoxy or polyester. Chemical resistance and curing time are significantly improved in synthetic resin, making it more versatile for industrial applications.
Common Uses and Applications
Synthetic resin is widely used in industrial applications such as adhesives, coatings, plastics manufacturing, and electronics due to its customizable properties and consistency. Natural resin, derived from plants, finds common use in varnishes, incense, traditional medicine, and as a raw material for certain adhesives and perfumes. Both types of resin play essential roles in manufacturing and consumer products, with synthetic resin favored for mass production and natural resin valued for specialty and eco-friendly uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic resin, derived primarily from petrochemical sources, often results in higher carbon emissions and poses challenges in biodegradability, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Natural resin, harvested from plants or insects, offers renewable sourcing and greater biodegradability, reducing ecological footprint and enhancing sustainability in applications. The environmental impact of synthetic versus natural resin highlights the need for innovations in eco-friendly production and efficient recycling methods to minimize carbon footprint and resource depletion.
Cost-Effectiveness of Synthetic vs Natural Resins
Synthetic resins offer greater cost-effectiveness compared to natural resins due to their consistent production processes and scalable manufacturing, which reduce variability and lower overall expenses. Natural resins often require labor-intensive extraction from plants, leading to higher costs and limited supply availability. The affordability of synthetic resins makes them preferred in industrial applications where large volumes are needed at predictable prices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Resin Type
Synthetic resin offers superior consistency, durability, and resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for industrial applications, but its production often involves non-renewable resources and environmental concerns. Natural resin, derived from plant secretions, is biodegradable and eco-friendly, yet it generally has lower mechanical strength and limited resistance to heat and chemicals compared to synthetic resin. Choosing between synthetic and natural resin depends on the specific requirements for performance, sustainability, and environmental impact.
Future Trends in Resin Technology
Future trends in resin technology emphasize the development of bio-based synthetic resins that mimic the properties of natural resins while offering enhanced durability and environmental sustainability. Advances in polymer science enable the creation of resins with improved thermal resistance, biodegradability, and compatibility with renewable feedstocks. Innovations in nanotechnology and green chemistry are driving the evolution of resins toward more efficient production processes and reduced carbon footprints.
Synthetic Resin vs Natural Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com