UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small projects and rapid prototyping, while two-part resin requires mixing resin and hardener, providing stronger, more durable results suited for casting and thicker applications. UV resin offers ease of use and minimal mess but may yellow over time, whereas two-part resin requires precise measurements and longer curing time but yields superior mechanical properties and less vulnerability to UV damage. Choosing between UV resin and two-part resin depends on the project's complexity, desired finish, and durability requirements.
Table of Comparison
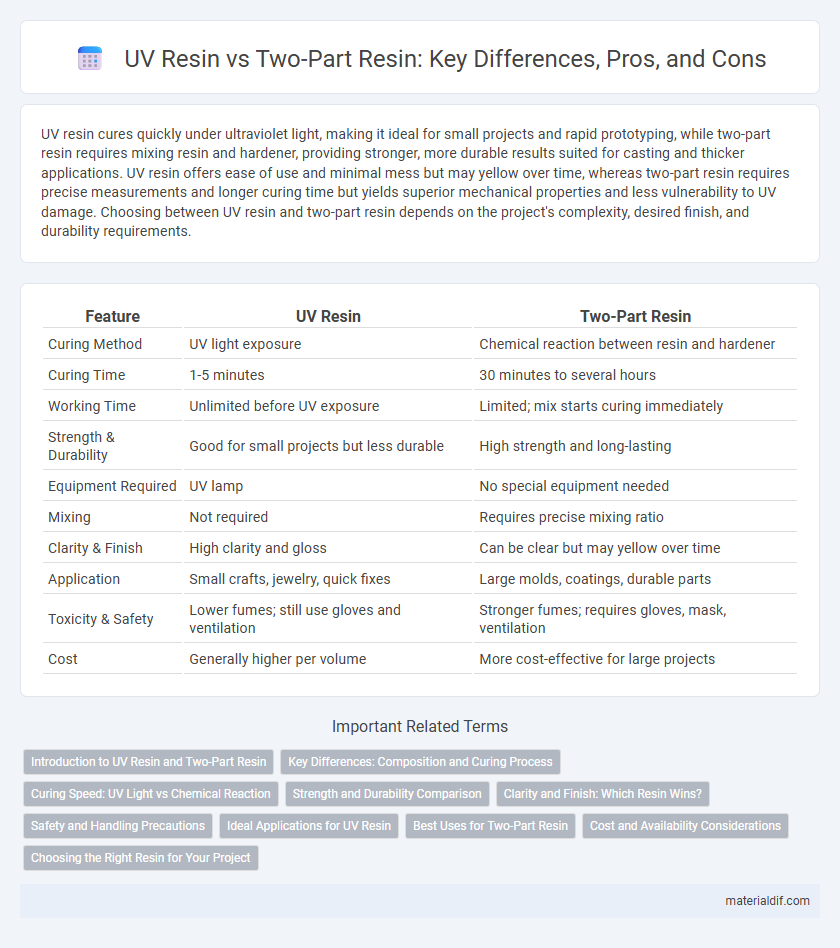
| Feature | UV Resin | Two-Part Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Method | UV light exposure | Chemical reaction between resin and hardener |
| Curing Time | 1-5 minutes | 30 minutes to several hours |
| Working Time | Unlimited before UV exposure | Limited; mix starts curing immediately |
| Strength & Durability | Good for small projects but less durable | High strength and long-lasting |
| Equipment Required | UV lamp | No special equipment needed |
| Mixing | Not required | Requires precise mixing ratio |
| Clarity & Finish | High clarity and gloss | Can be clear but may yellow over time |
| Application | Small crafts, jewelry, quick fixes | Large molds, coatings, durable parts |
| Toxicity & Safety | Lower fumes; still use gloves and ventilation | Stronger fumes; requires gloves, mask, ventilation |
| Cost | Generally higher per volume | More cost-effective for large projects |
Introduction to UV Resin and Two-Part Resin
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small, detailed projects and rapid prototyping. Two-part resin consists of a resin and hardener that chemically react when mixed, providing a durable and strong finish suitable for casting and large molds. Both resins differ in curing time, application techniques, and final hardness, catering to specific crafting and industrial needs.
Key Differences: Composition and Curing Process
UV resin cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, using photoinitiators that trigger polymerization, resulting in a fast, convenient process ideal for small projects. Two-part resin consists of a resin and hardener mixed in precise ratios, initiating a chemical reaction that cures over several hours, producing a stronger, more durable finish suitable for larger or structural applications. The composition difference lies in UV resin's single-component formula versus two-part resin's dual-component system, influencing curing time, strength, and usage versatility.
Curing Speed: UV Light vs Chemical Reaction
UV resin cures rapidly within minutes when exposed to specific wavelengths of UV light, offering precise control over curing time and reducing project duration. Two-part resin undergoes a slower chemical reaction involving mixing resin and hardener, typically requiring hours to fully cure and limiting immediate work continuation. Choosing UV resin is ideal for quick, detailed applications, while two-part resin suits projects needing stronger, long-lasting durability despite slower curing speeds.
Strength and Durability Comparison
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, resulting in a hard and glossy finish ideal for small, detailed projects but tends to be less durable under heavy stress or impact. Two-part resin, composed of resin and hardener mixed in precise ratios, cures through a chemical reaction that produces a stronger, more flexible, and more impact-resistant material suitable for larger, load-bearing applications. The choice between UV resin and two-part resin depends on the required strength and durability, with two-part resin generally providing superior mechanical properties and longevity.
Clarity and Finish: Which Resin Wins?
UV resin offers superior clarity with a crystal-clear finish due to its fast curing under ultraviolet light, minimizing yellowing and maintaining brilliance over time. Two-part resin, while durable and versatile, often results in a slightly hazier finish and requires longer curing, which can affect overall transparency. For projects demanding sharp, glossy, and vibrant clarity, UV resin typically outperforms two-part resin in delivering a flawless finish.
Safety and Handling Precautions
UV resin cures quickly under UV light, reducing exposure to uncured chemicals, but requires careful handling to avoid skin contact and inhalation of fumes. Two-part resin involves mixing resin and hardener, which can emit stronger fumes and requires proper ventilation and protective gloves to prevent skin irritation. Both types demand the use of nitrile gloves, safety goggles, and work in well-ventilated areas to minimize health risks during curing and handling.
Ideal Applications for UV Resin
UV resin cures rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small, detailed projects such as jewelry, nail art, and miniature crafting. Its quick curing time allows for efficient layering and fine precision in applications requiring intricate designs. Due to its single-component nature, UV resin is highly convenient for hobbyists and professionals who need fast results without mixing.
Best Uses for Two-Part Resin
Two-part resin is ideal for applications requiring high durability, chemical resistance, and heat tolerance, such as automotive parts, industrial coatings, and jewelry making. Its ability to cure at room temperature and form rigid, impact-resistant objects makes it preferred for functional prototypes and detailed molds. Unlike UV resin, two-part resin excels in thicker pours and larger casts where uniform curing is essential.
Cost and Availability Considerations
UV resin offers affordability and easy availability, with lower upfront costs and widespread retail presence, making it suitable for small-scale projects and beginners. Two-part resin, while more expensive and sometimes harder to find, provides superior durability and versatility, often justified in professional or large-scale applications. Cost-efficiency and accessibility make UV resin ideal for quick crafts, whereas two-part resin suits requirements demanding structural strength despite higher investment.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small, detailed projects and rapid prototyping, while two-part resin offers greater durability and chemical resistance, suitable for larger castings and industrial applications. Consider project size, curing time, and mechanical properties when choosing; UV resin provides ease of use and speed, whereas two-part resin requires precise mixing but yields stronger, more versatile results. Select UV resin for quick, lightweight crafts and two-part resin for heavy-duty, high-strength items to optimize project outcomes.
UV Resin vs Two-Part Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com