Injection molding resin offers precise, high-volume production with consistent quality and faster cycle times, ideal for complex and detailed parts. Hand lamination resin provides greater flexibility and control for custom shapes and repairs, emphasizing strength and durability in low-volume or intricate projects. Choosing between these resins depends on project scale, detail requirements, and production speed.
Table of Comparison
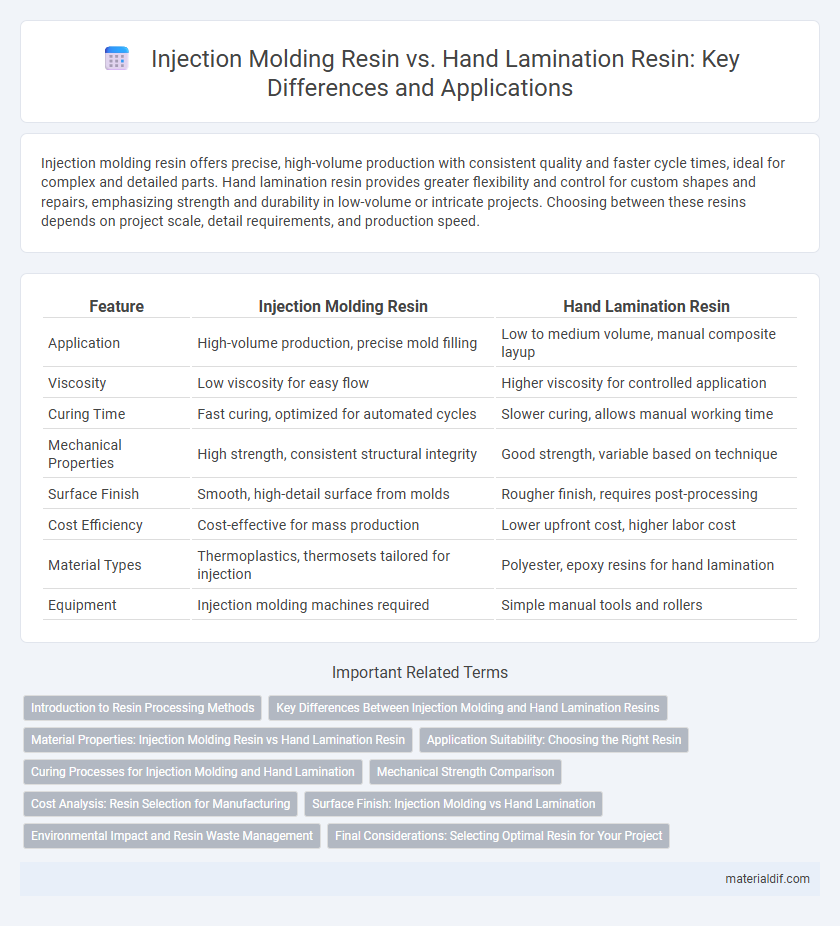
| Feature | Injection Molding Resin | Hand Lamination Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Application | High-volume production, precise mold filling | Low to medium volume, manual composite layup |
| Viscosity | Low viscosity for easy flow | Higher viscosity for controlled application |
| Curing Time | Fast curing, optimized for automated cycles | Slower curing, allows manual working time |
| Mechanical Properties | High strength, consistent structural integrity | Good strength, variable based on technique |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, high-detail surface from molds | Rougher finish, requires post-processing |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for mass production | Lower upfront cost, higher labor cost |
| Material Types | Thermoplastics, thermosets tailored for injection | Polyester, epoxy resins for hand lamination |
| Equipment | Injection molding machines required | Simple manual tools and rollers |
Introduction to Resin Processing Methods
Injection molding resin offers precise control and rapid production by injecting molten material into molds, ideal for mass manufacturing complex parts with consistent quality. Hand lamination resin, typically polyester or epoxy, allows for manual layering of fibers and resin, providing flexibility for custom shapes and repair work but with slower curing times. Understanding these resin processing methods highlights the trade-offs between automation efficiency and manual craftsmanship in composite fabrication.
Key Differences Between Injection Molding and Hand Lamination Resins
Injection molding resins are engineered for high precision and rapid production, featuring low viscosity to ensure easy flow into molds and uniform curing, which contrasts with hand lamination resins that have higher viscosity tailored for manual application and enhanced structural adhesion. Injection molding resins utilize thermoplastic or thermosetting polymers optimized for automated processes, while hand lamination resins, typically polyester or epoxy-based, prioritize flexibility and gap-filling properties for composite fabrication. Furthermore, injection molding resins shrink minimally during curing to maintain dimensional accuracy, whereas hand lamination resins allow more tolerance for shrinkage and air entrapment due to their manual application nature.
Material Properties: Injection Molding Resin vs Hand Lamination Resin
Injection molding resin exhibits high viscosity, excellent flow characteristics, and superior dimensional stability, making it ideal for producing complex, precise parts. Hand lamination resin generally has lower viscosity, allowing for easier manual application and better air release during curing, but it offers less mechanical strength compared to injection molding resin. The thermal resistance and impact toughness of injection molding resins typically surpass those of hand lamination resins, which are better suited for larger, less detailed fiberglass structures.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Resin
Injection molding resin offers precise flow control and rapid curing, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing of complex, detailed parts with consistent quality. Hand lamination resin provides superior flexibility and strength, suitable for custom or large-scale composite structures where manual application ensures better adhesion and layering. Selecting the right resin depends on production scale, part complexity, and performance requirements in automotive, aerospace, or marine industries.
Curing Processes for Injection Molding and Hand Lamination
Injection molding resin cures through a controlled thermal process where heat and pressure initiate polymerization within a closed mold, ensuring precise shaping and rapid solidification. Hand lamination resin undergoes a chemical curing process at room temperature or with minimal heat, relying on resin and hardener mixing to gradually harden and form a strong composite layer. The injection molding curing process offers superior dimensional accuracy and faster cycle times, while hand lamination curing provides flexibility for complex shapes and larger surface areas without specialized equipment.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Injection molding resin typically exhibits higher mechanical strength due to its uniform molecular structure and ability to withstand greater stress and impact, making it ideal for precision-engineered components. Hand lamination resin, often polyester or epoxy-based, offers good strength but tends to have lower tensile and flexural strength compared to injection molding resin because of manual application inconsistencies and air entrapment. For applications requiring superior durability and consistent mechanical properties, injection molding resin is generally preferred.
Cost Analysis: Resin Selection for Manufacturing
Injection molding resin typically involves higher upfront costs due to mold design and fabrication but offers lower per-part costs and faster production cycles, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing. Hand lamination resin has lower initial expenses and greater flexibility for customization but results in higher labor costs and longer production times, increasing per-unit expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires balancing volume demands and production speed against material and labor costs to select the optimal resin for manufacturing efficiency.
Surface Finish: Injection Molding vs Hand Lamination
Injection molding resin delivers a consistently smooth surface finish with high precision, ideal for mass production of complex shapes. Hand lamination resin often results in a more textured and less uniform surface, which may require additional sanding or finishing for aesthetic purposes. The controlled curing environment of injection molding enhances surface quality compared to the manual variability in hand lamination processes.
Environmental Impact and Resin Waste Management
Injection molding resin typically generates less waste due to precise material usage and automated processes, reducing environmental impact compared to hand lamination resin, which often results in higher resin off-cuts and excess material. Hand lamination resins, frequently based on polyester or vinyl ester, can release more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during curing, posing greater environmental hazards. Effective resin waste management strategies, such as recycling cured resin scrap and optimizing mold design, are essential to minimize ecological footprint in both injection molding and hand lamination applications.
Final Considerations: Selecting Optimal Resin for Your Project
Injection molding resin offers superior precision and consistency ideal for high-volume production, while hand lamination resin provides greater flexibility and ease of use for custom, low-volume projects. Consider mechanical properties, curing time, and surface finish requirements when selecting the resin to ensure optimal performance and durability. Cost efficiency and project scale play crucial roles in determining whether injection molding or hand lamination resin is the best fit for your application.
Injection Molding Resin vs Hand Lamination Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com