BPA-free resin is preferred for pet products due to its non-toxic and safer chemical composition, reducing health risks associated with Bisphenol A exposure. BPA-containing resin can leach harmful substances, potentially causing hormonal disruptions and adverse effects in pets over time. Choosing BPA-free resin ensures durability and safety, promoting well-being for pets and peace of mind for owners.
Table of Comparison
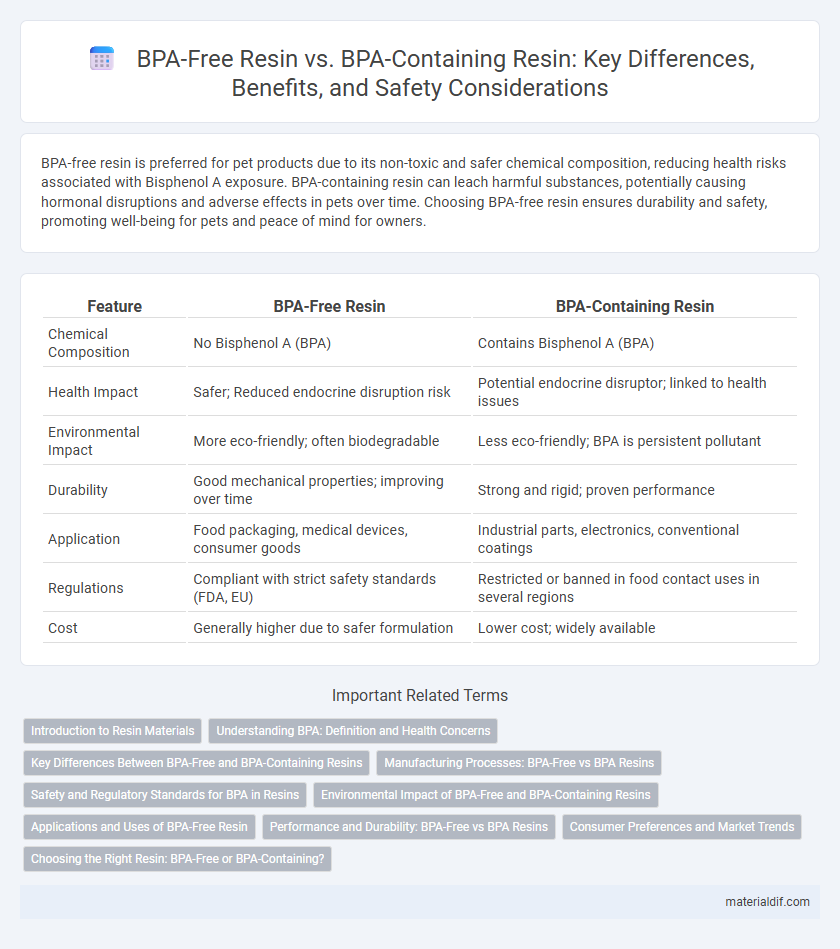
| Feature | BPA-Free Resin | BPA-Containing Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | No Bisphenol A (BPA) | Contains Bisphenol A (BPA) |
| Health Impact | Safer; Reduced endocrine disruption risk | Potential endocrine disruptor; linked to health issues |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly; often biodegradable | Less eco-friendly; BPA is persistent pollutant |
| Durability | Good mechanical properties; improving over time | Strong and rigid; proven performance |
| Application | Food packaging, medical devices, consumer goods | Industrial parts, electronics, conventional coatings |
| Regulations | Compliant with strict safety standards (FDA, EU) | Restricted or banned in food contact uses in several regions |
| Cost | Generally higher due to safer formulation | Lower cost; widely available |
Introduction to Resin Materials
BPA-free resin materials offer safer alternatives to BPA-containing resins by eliminating bisphenol A, a chemical linked to health risks such as hormonal disruption. These BPA-free resins maintain essential properties like durability, clarity, and heat resistance, making them suitable for food packaging, medical devices, and consumer products. Advances in BPA-free resin formulations prioritize environmental safety and regulatory compliance while preserving performance standards important in industrial and commercial applications.
Understanding BPA: Definition and Health Concerns
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an industrial chemical commonly used in producing certain resins and plastics, known for its role in polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. BPA-containing resins can pose health risks due to BPA's endocrine-disrupting properties, which may interfere with hormone function and increase the risk of reproductive and developmental issues. BPA-free resins are formulated without this chemical, offering safer alternatives that reduce exposure to potential toxic effects linked to BPA.
Key Differences Between BPA-Free and BPA-Containing Resins
BPA-free resin eliminates bisphenol A, a chemical linked to health risks such as hormone disruption, offering safer alternatives for food packaging and consumer products. BPA-containing resin maintains structural strength and clarity but poses potential leaching hazards under heat or wear, raising safety concerns. The key differences center on health safety, regulatory approvals, and environmental impact, making BPA-free resins preferable in health-sensitive applications.
Manufacturing Processes: BPA-Free vs BPA Resins
BPA-free resin manufacturing utilizes alternative monomers such as bisphenol S or bio-based materials to eliminate bisphenol A, reducing endocrine disruption risks. In contrast, BPA-containing resin production involves polymerization of BPA-derived compounds, known for their rigidity and thermal stability but linked to health concerns. The shift to BPA-free manufacturing often requires modification of curing agents and catalysts to maintain performance standards while ensuring safer chemical composition.
Safety and Regulatory Standards for BPA in Resins
BPA-free resins are formulated to eliminate bisphenol A, a chemical linked to health risks such as endocrine disruption, ensuring safer alternatives for consumer products. Regulatory standards, including FDA and EU regulations, strictly limit or ban BPA in food-contact resins to reduce exposure and protect public health. Compliance with these safety standards drives the adoption of BPA-free resins in manufacturing, promoting safer materials in packaging, coatings, and other resin applications.
Environmental Impact of BPA-Free and BPA-Containing Resins
BPA-free resin significantly reduces environmental contamination as it eliminates the release of bisphenol A, a toxic compound linked to water and soil pollution. In contrast, BPA-containing resin contributes to endocrine disruptors leaching into ecosystems, harming wildlife and disrupting reproductive systems. Choosing BPA-free resin supports sustainable manufacturing by minimizing hazardous waste and lowering ecological risk.
Applications and Uses of BPA-Free Resin
BPA-free resin is widely used in food packaging, medical devices, and consumer goods due to its safety and non-toxicity, reducing the risk of endocrine disruption associated with BPA-containing resins. It is favored in applications requiring high durability and heat resistance without compromising health, such as baby bottles, water containers, and kitchenware. The growing demand for eco-friendly and health-conscious materials drives the preference for BPA-free resin in packaging, automotive parts, and electronics housings.
Performance and Durability: BPA-Free vs BPA Resins
BPA-free resin offers competitive performance and enhanced durability compared to BPA-containing resin, as it resists yellowing and maintains mechanical strength over time. BPA-containing resin, while traditionally praised for its rigidity and thermal stability, may degrade faster under UV exposure and cause potential health risks. Advances in BPA-free resin formulations have significantly improved impact resistance and chemical stability, making them ideal for long-term applications in food packaging and medical devices.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly prefer BPA-free resin due to health concerns linked to bisphenol A, driving manufacturers to develop safer, non-toxic alternatives. Market trends demonstrate a significant rise in demand for BPA-free resin products, reflecting growing awareness and regulatory pressures globally. This shift influences packaging, automotive, and consumer goods sectors to prioritize BPA-free materials for enhanced market competitiveness.
Choosing the Right Resin: BPA-Free or BPA-Containing?
Choosing the right resin involves understanding the health and environmental impacts of BPA-free resin versus BPA-containing resin. BPA-free resin eliminates risks associated with bisphenol A exposure, such as hormonal disruptions and potential carcinogenic effects, making it a safer option for food containers and children's products. BPA-containing resin, while often more affordable and structurally robust, carries concerns about leaching toxic chemicals, prompting many manufacturers to shift towards BPA-free alternatives for safer consumer use.
BPA-free resin vs BPA-containing resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com