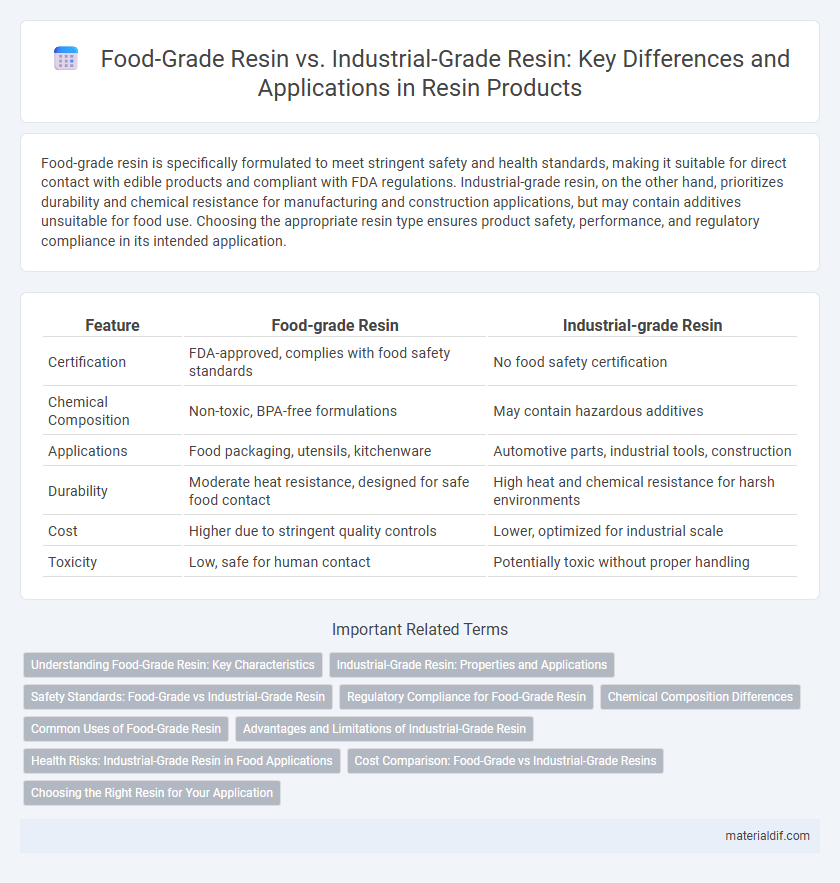
Food-grade resin is specifically formulated to meet stringent safety and health standards, making it suitable for direct contact with edible products and compliant with FDA regulations. Industrial-grade resin, on the other hand, prioritizes durability and chemical resistance for manufacturing and construction applications, but may contain additives unsuitable for food use. Choosing the appropriate resin type ensures product safety, performance, and regulatory compliance in its intended application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Food-grade Resin | Industrial-grade Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | FDA-approved, complies with food safety standards | No food safety certification |
| Chemical Composition | Non-toxic, BPA-free formulations | May contain hazardous additives |
| Applications | Food packaging, utensils, kitchenware | Automotive parts, industrial tools, construction |
| Durability | Moderate heat resistance, designed for safe food contact | High heat and chemical resistance for harsh environments |
| Cost | Higher due to stringent quality controls | Lower, optimized for industrial scale |
| Toxicity | Low, safe for human contact | Potentially toxic without proper handling |
Understanding Food-Grade Resin: Key Characteristics
Food-grade resin is specifically formulated to meet strict safety standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, ensuring it is non-toxic and safe for direct contact with food and beverages. Key characteristics include high chemical resistance, durability at varying temperatures, and the absence of harmful additives like BPA or phthalates, which are commonly restricted in food packaging materials. Industrial-grade resin, in contrast, lacks these stringent requirements and may contain additives unsuitable for food contact, limiting its application to manufacturing or structural uses where food safety is not a concern.
Industrial-Grade Resin: Properties and Applications
Industrial-grade resin exhibits superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent mechanical strength compared to food-grade resin, making it ideal for demanding manufacturing environments. This resin type is commonly used in automotive components, electrical insulation, and construction materials due to its durability and ability to withstand harsh conditions. Its formulation often includes additives that enhance performance characteristics such as flame retardancy and UV resistance, expanding its application range in industrial settings.
Safety Standards: Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade Resin
Food-grade resin adheres to stringent FDA and EU safety standards, ensuring non-toxic properties suitable for direct contact with food and beverages, whereas industrial-grade resin is formulated for durability and chemical resistance without guarantees for human safety. The rigorous testing of food-grade resin includes compliance with migration limits and absence of harmful contaminants, making it ideal for packaging, kitchenware, and medical applications. In contrast, industrial-grade resin often contains additives and fillers that may pose health risks if ingested or used in food-related contexts.
Regulatory Compliance for Food-Grade Resin
Food-grade resin strictly adheres to regulatory standards such as FDA 21 CFR 175.300 and EU Regulation No. 10/2011 to ensure safety for direct food contact applications. These resins undergo rigorous testing for chemical migration, toxicity, and contamination to prevent harmful substances from leaching into food products. Industrial-grade resin lacks these certifications and is not suitable for applications requiring stringent compliance with food safety regulations.
Chemical Composition Differences
Food-grade resin contains non-toxic, BPA-free polymers specifically formulated to meet FDA and EFSA safety standards, ensuring no harmful chemicals leach into consumables. Industrial-grade resin often includes additives like heavy metals, plasticizers, and stabilizers that enhance durability but pose toxicity risks if used in food applications. The distinct chemical compositions reflect their intended uses, with food-grade resins prioritizing biocompatibility and industrial resins emphasizing physical robustness.
Common Uses of Food-Grade Resin
Food-grade resin is primarily used in applications that require direct contact with consumables, such as packaging materials, food containers, and kitchenware, ensuring safety and compliance with FDA regulations. It is often employed in the production of bottle caps, food storage bins, and sealants for food processing equipment to prevent contamination. Compared to industrial-grade resin, which is designed for durability and chemical resistance in manufacturing or automotive parts, food-grade resin prioritizes non-toxicity and hygienic properties.
Advantages and Limitations of Industrial-Grade Resin
Industrial-grade resin offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to food-grade resin, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications in manufacturing and construction. However, its lack of compliance with food safety standards limits its use in products that come into direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade resin may also contain additives or contaminants that are unsuitable for ingestion, restricting its application in food packaging and kitchenware.
Health Risks: Industrial-Grade Resin in Food Applications
Industrial-grade resin used in food applications poses significant health risks due to potential contamination with harmful chemicals such as heavy metals, residual solvents, and unreacted monomers. Food-grade resin undergoes rigorous testing and certification to ensure compliance with FDA and EFSA standards, minimizing toxic leaching and ensuring safety for direct food contact. Using industrial-grade resin in food containers or packaging can lead to chemical migration, increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses and long-term health complications.
Cost Comparison: Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade Resins
Food-grade resin typically costs 20-40% more than industrial-grade resin due to stricter safety standards and certification processes required for contact with consumables. Industrial-grade resin, suitable for non-food applications, offers a more economical option but lacks the regulatory approvals necessary for food safety compliance. The price difference reflects the additional testing, purity requirements, and compliance with FDA or EFSA regulations inherent to food-grade materials.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Application
Food-grade resin ensures compliance with FDA regulations for safety and non-toxicity, making it ideal for packaging, utensils, and containers that come into direct contact with food. Industrial-grade resin offers enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance, suitable for heavy-duty manufacturing, automotive parts, and construction materials. Selecting the appropriate resin depends on application requirements like safety standards, durability, and exposure conditions to achieve optimal performance and regulatory compliance.
Food-grade Resin vs Industrial-grade Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com