UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, offering faster project completion and a smoother finish compared to standard resin, which requires hours to days for curing. Standard resin provides greater depth and durability, making it ideal for larger or thicker castings, while UV resin is best suited for small, detailed items. Both types have unique benefits, but choice depends on specific project requirements and desired results.
Table of Comparison
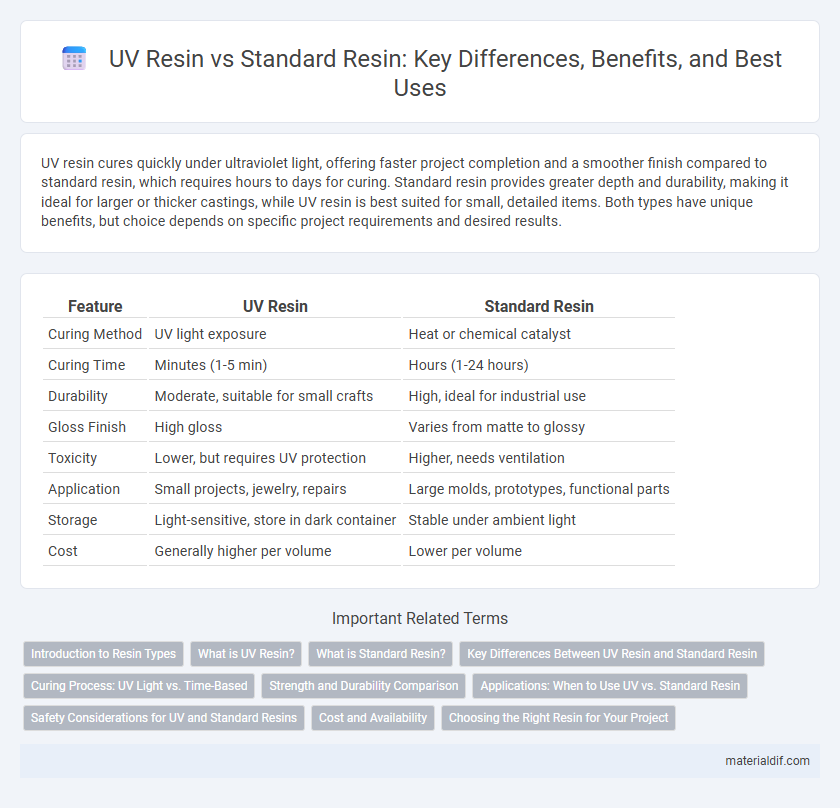
| Feature | UV Resin | Standard Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Method | UV light exposure | Heat or chemical catalyst |
| Curing Time | Minutes (1-5 min) | Hours (1-24 hours) |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for small crafts | High, ideal for industrial use |
| Gloss Finish | High gloss | Varies from matte to glossy |
| Toxicity | Lower, but requires UV protection | Higher, needs ventilation |
| Application | Small projects, jewelry, repairs | Large molds, prototypes, functional parts |
| Storage | Light-sensitive, store in dark container | Stable under ambient light |
| Cost | Generally higher per volume | Lower per volume |
Introduction to Resin Types
UV resin cures rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet light, enabling quick project completion and fine detail precision. Standard resin, often epoxy-based, requires a chemical hardener and longer curing times, providing durability and versatility for various applications. The choice between UV resin and standard resin depends on project needs, curing preferences, and desired finish quality.
What is UV Resin?
UV resin is a type of photopolymer that cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, enabling fast and precise hardening for detailed projects. Unlike standard resin, which typically requires hours or days to fully cure through a chemical reaction, UV resin solidifies within minutes, making it ideal for small-scale crafts, jewelry, and prototyping. Its composition includes photoinitiators that trigger polymerization under UV exposure, resulting in a durable, glossy finish with minimal shrinkage.
What is Standard Resin?
Standard resin is a type of thermosetting polymer commonly used in 3D printing and casting that cures through heat or chemically without exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. It typically requires longer curing times and may involve additional equipment like heat ovens to harden properly compared to UV resin. Standard resin offers durable and strong end products, suitable for applications needing high mechanical strength and thermal resistance.
Key Differences Between UV Resin and Standard Resin
UV resin cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, offering rapid hardening and precise control over the curing process. Standard resin requires mixing a resin with a hardener, which triggers a chemical reaction and results in a longer curing time, often several hours to days. UV resin is ideal for small projects needing fast results, while standard resin is preferred for larger casts due to its longer working time and greater durability.
Curing Process: UV Light vs. Time-Based
UV resin cures rapidly when exposed to specific UV light wavelengths, typically solidifying within minutes due to photoinitiators reacting to ultraviolet radiation. Standard resin relies on a chemical curing process based on time and temperature, often requiring several hours to days to fully harden through polymerization. The UV resin's fast curing process offers precise control and minimal waiting, while standard resin provides deeper curing for thicker applications but with longer drying times.
Strength and Durability Comparison
UV resin cures faster through exposure to ultraviolet light, resulting in a hard, durable finish ideal for small, detailed projects, while standard resin requires mixing and longer curing times but generally offers greater overall strength and resistance to impact. Standard resin exhibits superior mechanical properties, making it more suitable for large-scale or load-bearing applications where long-term durability is critical. UV resin tends to be more brittle under stress compared to standard resin, which maintains better flexibility and toughness.
Applications: When to Use UV vs. Standard Resin
UV resin is ideal for small-scale projects requiring quick curing times, such as jewelry making, nail art, and detailed miniatures due to its fast exposure to ultraviolet light. Standard resin is better suited for larger casts, molds, and industrial applications where longer working time and deeper curing are necessary, such as in furniture, automotive parts, and prototyping. Choosing between UV and standard resin depends on project size, curing speed, and required durability.
Safety Considerations for UV and Standard Resins
UV resin offers faster curing times and lower odor emissions compared to standard resin, reducing inhalation risks during use. Standard resin typically contains higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and requires prolonged exposure to solvents, increasing potential skin irritation and respiratory hazards. Proper ventilation, use of nitrile gloves, and eye protection are essential safety measures for handling both UV and standard resins to minimize allergic reactions and chemical exposure.
Cost and Availability
UV resin generally costs more per ounce than standard resin due to its specialized curing process and formulation. While UV resin offers rapid curing with exposure to ultraviolet light, standard resin is more widely available and often sold in larger quantities, making it more cost-effective for extensive projects. The accessibility of standard resin in various retail and online outlets enhances its affordability compared to the relatively niche market for UV resin.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
UV resin cures quickly under UV light, making it ideal for small, detailed projects or rapid prototyping, while standard resin requires longer curing times and is better suited for larger molds or items needing a tougher finish. UV resin offers convenience and precision but may lack the durability and heat resistance of standard epoxy resins. Selecting the right resin depends on project size, required strength, curing time, and desired finish quality.
UV Resin vs Standard Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com