Alkyd resin offers excellent flexibility and is commonly used in coatings and paints due to its superior adhesion and gloss properties. Phenolic resin provides exceptional heat resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and electrical insulation. Choosing between alkyd and phenolic resins depends on the specific requirements for durability, thermal resistance, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
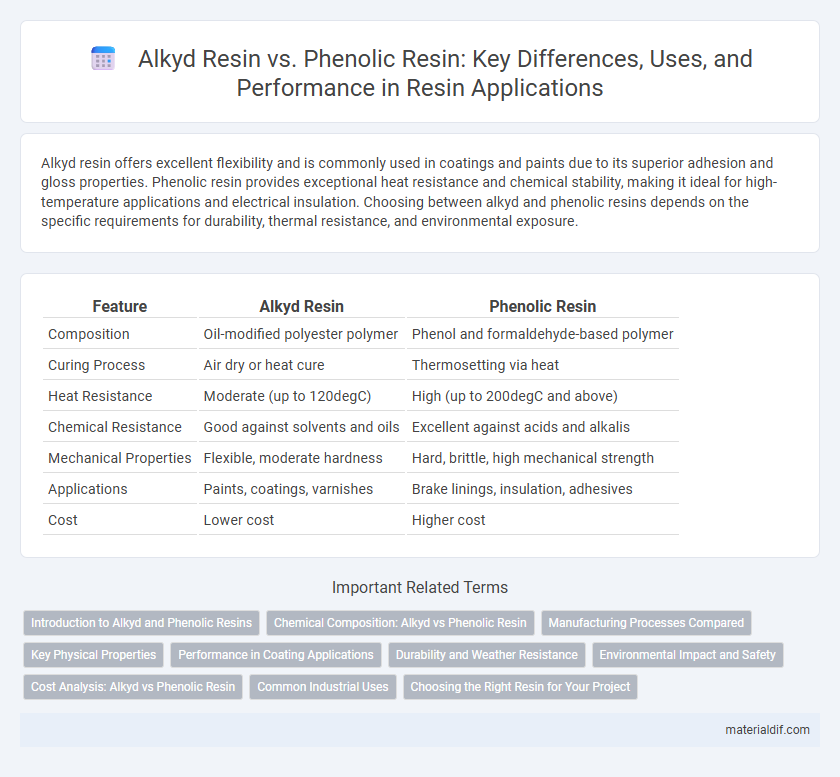
| Feature | Alkyd Resin | Phenolic Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Oil-modified polyester polymer | Phenol and formaldehyde-based polymer |
| Curing Process | Air dry or heat cure | Thermosetting via heat |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 120degC) | High (up to 200degC and above) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against solvents and oils | Excellent against acids and alkalis |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible, moderate hardness | Hard, brittle, high mechanical strength |
| Applications | Paints, coatings, varnishes | Brake linings, insulation, adhesives |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Alkyd and Phenolic Resins
Alkyd resin, a polyester modified with fatty acids and polyols, is widely used in coatings and paints due to its excellent adhesion, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. Phenolic resin, derived from phenol and formaldehyde, offers high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulating properties, making it ideal for industrial applications like molding and laminates. Both resins serve distinct roles in manufacturing, with alkyd resins favored in decorative finishes and phenolic resins preferred for heat-resistant and durable components.
Chemical Composition: Alkyd vs Phenolic Resin
Alkyd resin is a polyester modified with fatty acids and glycerol, forming a complex network of ester bonds that provide flexibility and durability in coatings and paints. Phenolic resin consists of phenol and formaldehyde, producing a thermosetting polymer with high thermal stability and chemical resistance due to its rigid aromatic structure. The distinct chemical compositions result in alkyd resins offering better elasticity, whereas phenolic resins excel in heat resistance and structural strength.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Alkyd resin manufacturing involves the polycondensation of polyols with dibasic acids or their anhydrides, followed by modification with fatty acids or oils to achieve desired flexibility and gloss. Phenolic resin synthesis typically occurs through the acid- or base-catalyzed reaction of phenol with formaldehyde, resulting in either novolac or resol types that differ in curing mechanism and molecular structure. The alkyd resin process emphasizes esterification and incorporation of natural oils, whereas phenolic resin production centers on the formation of methylene bridges, impacting their respective thermal stability and application scopes.
Key Physical Properties
Alkyd resin exhibits excellent flexibility, moderate hardness, and good adhesion, making it ideal for coatings and paints with moisture resistance around 10-15%. Phenolic resin is characterized by high thermal stability, exceptional chemical resistance, and superior hardness, typically used in high-temperature applications with moisture resistance below 5%. The tensile strength of alkyd resins ranges from 20-40 MPa, whereas phenolic resins can reach up to 70 MPa, highlighting their structural robustness.
Performance in Coating Applications
Alkyd resins offer excellent flexibility, UV resistance, and gloss retention, making them ideal for decorative coatings and industrial applications requiring aesthetic appeal and moderate durability. Phenolic resins provide superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and corrosion protection, making them suitable for heavy-duty coatings exposed to harsh environments and high temperatures. Performance-wise, alkyd resins excel in outdoor decorative finishes, while phenolic resins dominate in protective coatings for metals and industrial equipment.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Alkyd resin offers moderate durability and weather resistance, making it suitable for paints and coatings exposed to mild environmental conditions. Phenolic resin exhibits superior durability and outstanding weather resistance due to its high thermal stability and chemical inertness, ideal for harsh outdoor and industrial applications. The enhanced cross-linking structure in phenolic resin ensures prolonged lifespan and resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations compared to alkyd resin.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Alkyd resin, derived from natural oils and polyols, generally has lower toxicity and is more biodegradable compared to phenolic resin, which is petroleum-based and releases formaldehyde during curing, posing higher environmental and health risks. Phenolic resins exhibit greater resistance to heat and chemicals but contribute to air pollution and occupational hazards due to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted during manufacturing. Choosing alkyd resin over phenolic resin can reduce harmful emissions and improve workplace safety, aligning with green manufacturing practices.
Cost Analysis: Alkyd vs Phenolic Resin
Alkyd resin typically offers a lower initial cost compared to phenolic resin, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications with budget constraints. Phenolic resin, while more expensive upfront, provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. The overall cost analysis favors alkyd resin for short-term projects, whereas phenolic resin delivers better value in demanding environments with higher performance requirements.
Common Industrial Uses
Alkyd resins are widely used in coatings, paints, and varnishes due to their excellent adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for automotive, architectural, and wood finishing applications. Phenolic resins are preferred in high-temperature and electrical insulation industries, commonly found in molded parts, laminates, and brake linings, offering superior thermal stability and mechanical strength. Both resins play critical roles in manufacturing, but alkyds excel in surface coatings while phenolics dominate in structural and heat-resistant components.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Alkyd resin offers excellent flexibility, weather resistance, and glossy finishes, making it ideal for outdoor paints and coatings, while phenolic resin provides superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength, suitable for industrial applications like laminates and brakes. Selecting the right resin depends on project requirements such as exposure conditions, durability needs, and thermal or chemical resistance. Evaluating factors like curing time, adhesion properties, and cost-effectiveness ensures optimal resin performance in your application.
Alkyd Resin vs Phenolic Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com