UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, offering superior clarity and flexibility, making it ideal for detailed crafts and jewelry. UV epoxy combines the properties of epoxy with UV curing, providing increased hardness and chemical resistance for durable coatings and repairs. Choosing between UV resin and UV epoxy depends on the desired balance of cure time, strength, and finish quality for your specific project.
Table of Comparison
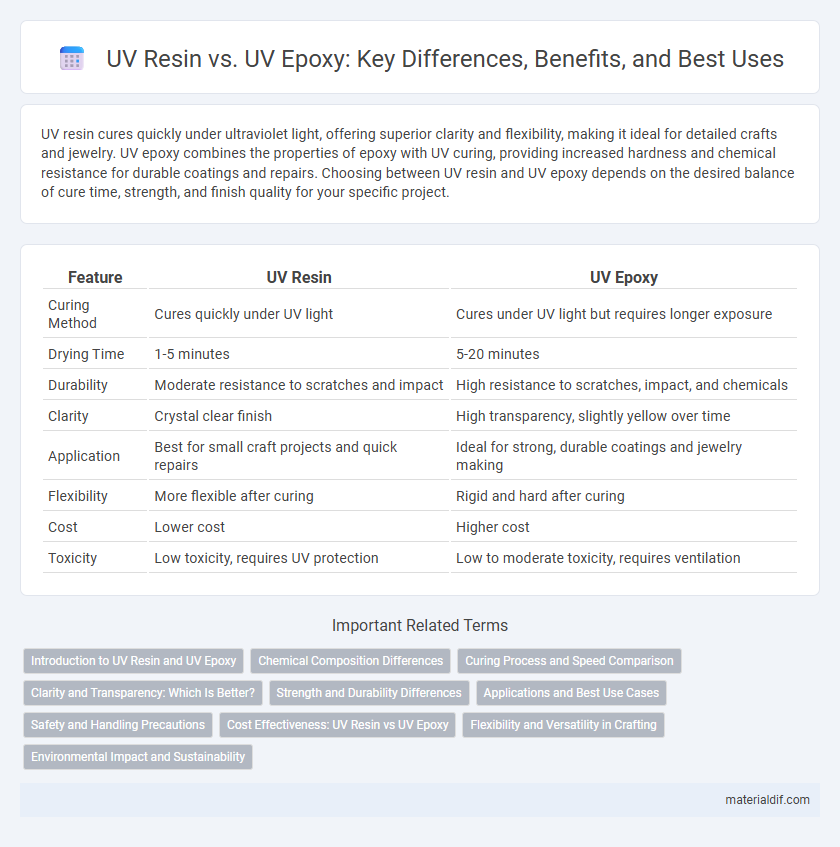
| Feature | UV Resin | UV Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Method | Cures quickly under UV light | Cures under UV light but requires longer exposure |
| Drying Time | 1-5 minutes | 5-20 minutes |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to scratches and impact | High resistance to scratches, impact, and chemicals |
| Clarity | Crystal clear finish | High transparency, slightly yellow over time |
| Application | Best for small craft projects and quick repairs | Ideal for strong, durable coatings and jewelry making |
| Flexibility | More flexible after curing | Rigid and hard after curing |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity, requires UV protection | Low to moderate toxicity, requires ventilation |
Introduction to UV Resin and UV Epoxy
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, offering a clear, flexible finish ideal for small crafts and jewelry. UV epoxy combines ultraviolet curing with epoxy's strong bonding properties, resulting in a tougher, more durable coating suitable for industrial applications. Both materials require UV light for curing but differ in viscosity, hardness, and chemical resistance.
Chemical Composition Differences
UV resin consists primarily of acrylate monomers and oligomers that polymerize rapidly under ultraviolet light, resulting in a flexible and quick-curing material. UV epoxy combines epoxy resin compounds with photoinitiators, curing into a harder and more durable finish but generally requiring longer exposure to UV light. Differences in chemical composition influence their mechanical properties, with UV resin offering greater elasticity and UV epoxy providing enhanced chemical resistance and strength.
Curing Process and Speed Comparison
UV resin cures quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light, typically hardening within 2 to 5 minutes, making it ideal for rapid projects. UV epoxy requires a similar exposure but often demands a longer curing time, generally between 5 and 30 minutes, due to its denser chemical composition. The curing speed of UV resin is faster, but UV epoxy offers greater durability and chemical resistance once fully cured.
Clarity and Transparency: Which Is Better?
UV resin offers superior clarity and transparency compared to UV epoxy, making it ideal for projects requiring a glass-like finish and vibrant color brilliance. UV resin cures quickly under UV light, maintaining a crystal-clear appearance without yellowing over time, while UV epoxy tends to have a slight amber tint and can yellow with prolonged exposure to sunlight. For applications demanding maximum visual purity, UV resin is generally the better choice.
Strength and Durability Differences
UV resin cures faster but tends to be less durable and more brittle compared to UV epoxy, which offers superior strength and impact resistance due to its denser molecular structure. UV epoxy's enhanced durability makes it ideal for applications requiring long-term wear and structural integrity, such as jewelry or coatings subject to frequent handling. The rigidity of UV epoxy also reduces the risk of cracking, whereas UV resin may yellow or degrade more quickly when exposed to prolonged UV light.
Applications and Best Use Cases
UV Resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, making it ideal for small craft projects, jewelry making, and detailed art pieces requiring fast turnaround times. UV Epoxy, while also cured by UV light, offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it better suited for industrial applications, coatings, and protective layers on electronics. For precise, decorative items, UV Resin is preferred, whereas UV Epoxy excels in functional parts and heavy-duty usage.
Safety and Handling Precautions
UV resin cures quickly under ultraviolet light, releasing minimal harmful fumes, making it safer for indoor use when handled in well-ventilated areas. UV epoxy requires longer curing times and may emit stronger odors, necessitating gloves and protective masks to prevent skin irritation and respiratory issues. Both resins should be stored away from direct sunlight and used with proper personal protective equipment to avoid contact with uncured material.
Cost Effectiveness: UV Resin vs UV Epoxy
UV resin typically offers greater cost effectiveness due to faster curing times and lower material costs compared to UV epoxy, making it ideal for smaller projects and rapid production. UV epoxy generally requires higher initial investment and longer curing with UV light, but its enhanced durability and chemical resistance justify the expense for heavy-duty applications. Evaluating project scale and performance needs helps determine the best balance between upfront costs and long-term value when choosing between UV resin and UV epoxy.
Flexibility and Versatility in Crafting
UV resin offers superior flexibility and faster curing times, making it ideal for intricate craft projects requiring detailed molding and quick setting. UV epoxy, while less flexible, provides greater durability and chemical resistance, suitable for applications demanding long-lasting strength and a harder finish. Both materials enable versatile crafting options, but UV resin excels in projects prioritizing elasticity and rapid curing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
UV resin generally has a lower environmental impact than UV epoxy due to its formulation without bisphenol A (BPA) and fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a more sustainable choice. UV epoxy often contains BPA and releases higher levels of VOCs during curing, which contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. Choosing UV resin enhances sustainability by reducing toxic emissions and promoting safer disposal methods in resin crafting.
UV Resin vs UV Epoxy Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com