Phenolic resin offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength compared to urea resin, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and structural components. Urea resin is favored for its excellent clarity and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in adhesives and laminates where aesthetic appeal is important. While phenolic resin excels in durability, urea resin provides better resistance to moisture and is easier to process in molding operations.
Table of Comparison
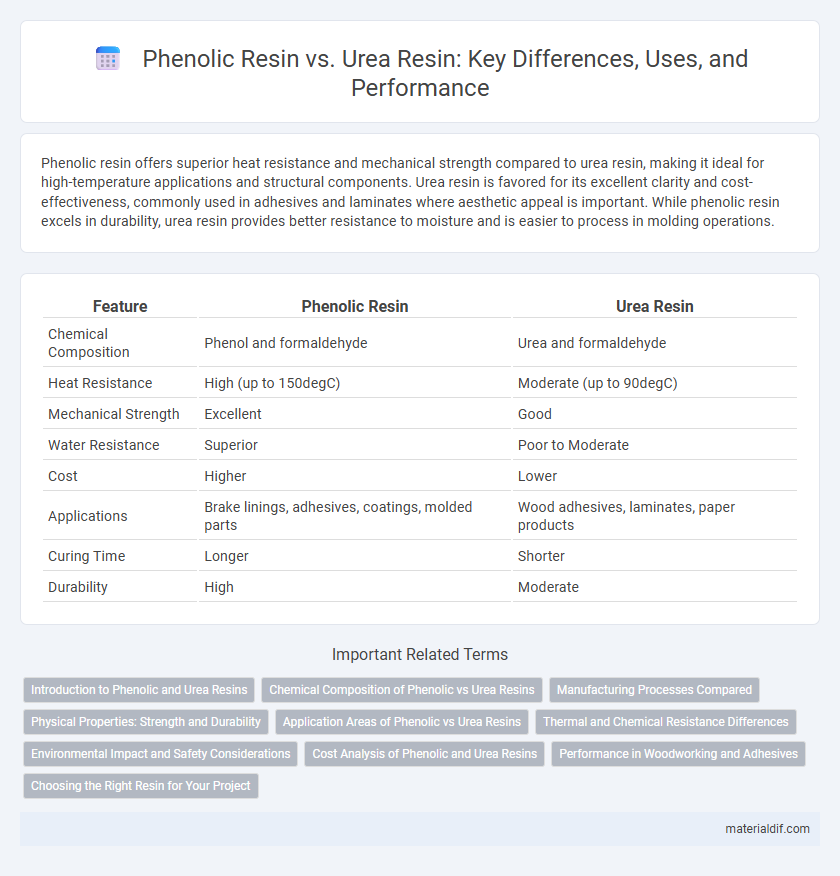
| Feature | Phenolic Resin | Urea Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Phenol and formaldehyde | Urea and formaldehyde |
| Heat Resistance | High (up to 150degC) | Moderate (up to 90degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent | Good |
| Water Resistance | Superior | Poor to Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Brake linings, adhesives, coatings, molded parts | Wood adhesives, laminates, paper products |
| Curing Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
Introduction to Phenolic and Urea Resins
Phenolic resins, derived from phenol and formaldehyde, exhibit excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as laminates and adhesives. Urea resins, synthesized from urea and formaldehyde, offer superior clarity, fast curing times, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in woodworking adhesives and molded objects. Both resins belong to the thermosetting polymer family, with phenolic resins favoring durability and heat resistance, while urea resins prioritize ease of processing and economic efficiency.
Chemical Composition of Phenolic vs Urea Resins
Phenolic resins are thermosetting polymers formed by the reaction of phenol with formaldehyde, resulting in a network of methylene bridges linking aromatic phenol units. Urea resins, on the other hand, are synthesized from urea and formaldehyde, producing linear or branched chains with methylene and methylol (-CH2OH) groups. The aromatic structure of phenolic resins provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to the aliphatic framework of urea resins, which are more susceptible to hydrolysis and have lower heat resistance.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Phenolic resin manufacturing involves the condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde under acidic or basic conditions, producing a thermosetting polymer with high heat resistance and mechanical strength. Urea resin is created through the polymerization of urea and formaldehyde, resulting in a thermosetting resin that cures faster but has lower heat tolerance compared to phenolic resin. The phenolic resin process often requires longer curing times and higher temperatures, while urea resin manufacturing is typically faster and used for applications demanding cost efficiency and quick setting.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Phenolic resin exhibits superior strength and durability compared to urea resin, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Its exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture extends the lifespan of finished products. Urea resin, while offering good rigidity and cost-effectiveness, is more prone to brittleness and lower resistance to environmental factors.
Application Areas of Phenolic vs Urea Resins
Phenolic resins are widely used in high-performance applications such as automotive brake linings, circuit boards, and aerospace components due to their excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength. Urea resins find primary application in the production of wood-based panels, laminates, and adhesives for furniture manufacturing because of their strong bonding properties and cost-effectiveness. Phenolic resins dominate in industrial molding and insulation, while urea resins are preferred in interior applications where moisture resistance is less critical.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance Differences
Phenolic resin exhibits superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to 150-200degC compared to urea resin, which typically degrades above 100degC. Chemical resistance in phenolic resin is also higher, showing excellent resistance to solvents, acids, and alkalis, whereas urea resin is more susceptible to chemical attack and moisture degradation. These properties make phenolic resin preferred for high-temperature and harsh chemical environments, while urea resin suits applications requiring lower thermal and chemical resilience.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Phenolic resin offers superior environmental benefits due to its lower formaldehyde emissions and higher thermal stability, reducing hazardous exposure risks compared to urea resin. Urea resin, while cost-effective and commonly used in wood adhesives, releases more formaldehyde, posing significant indoor air quality and health concerns. Safety considerations favor phenolic resin in applications requiring durable, flame-retardant materials with minimized toxic emissions.
Cost Analysis of Phenolic and Urea Resins
Phenolic resins generally incur higher production costs due to their complex synthesis process involving phenol and formaldehyde, but they offer superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them cost-effective for high-performance applications. Urea resins are less expensive to manufacture, primarily derived from urea and formaldehyde, and their faster curing times reduce processing expenses, suitable for cost-sensitive projects with moderate performance needs. Evaluating total cost involves balancing phenolic resin's durability and longevity against urea resin's lower initial expenditure and faster production cycle.
Performance in Woodworking and Adhesives
Phenolic resin offers superior water resistance, heat stability, and mechanical strength compared to urea resin, making it ideal for exterior wood applications and high-performance adhesives. Urea resin, while more cost-effective and easier to process, provides lower durability and moisture resistance, limiting its use primarily to interior woodworking products. Performance differences in bonding strength and resistance to environmental factors largely determine the selection between phenolic and urea resins in the woodworking and adhesive industries.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Phenolic resin offers superior heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance applications like automotive parts and electrical components. Urea resin, known for its cost-effectiveness and ease of molding, is preferred in decorative laminates, adhesives, and wood products where affordability and fast curing are priorities. Selecting the right resin depends on project requirements such as durability, budget constraints, and environmental resistance to maximize efficiency and product quality.
Phenolic Resin vs Urea Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com