Polyurethane resin offers superior flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion compared to polyethylene resin, making it ideal for applications requiring elasticity and toughness. Polyethylene resin, known for its excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, excels in lightweight, cost-effective solutions with good impact strength. Choosing between polyurethane and polyethylene resin depends on the specific performance requirements, such as flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance needed for the project.
Table of Comparison
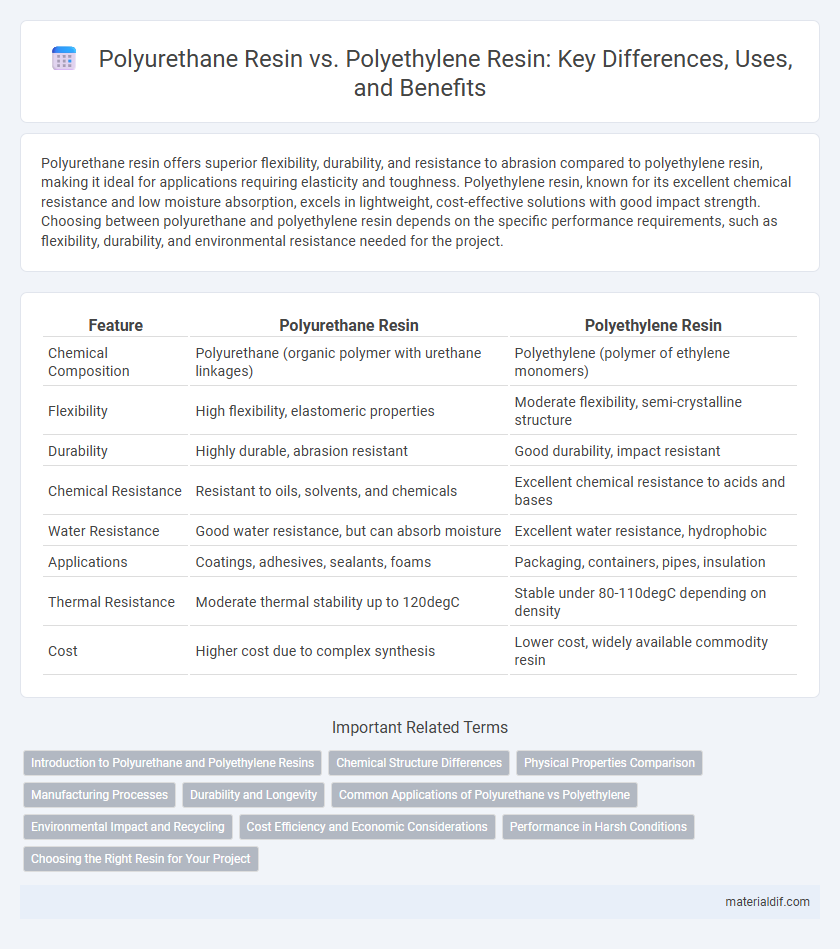
| Feature | Polyurethane Resin | Polyethylene Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Polyurethane (organic polymer with urethane linkages) | Polyethylene (polymer of ethylene monomers) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, elastomeric properties | Moderate flexibility, semi-crystalline structure |
| Durability | Highly durable, abrasion resistant | Good durability, impact resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance to acids and bases |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance, but can absorb moisture | Excellent water resistance, hydrophobic |
| Applications | Coatings, adhesives, sealants, foams | Packaging, containers, pipes, insulation |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate thermal stability up to 120degC | Stable under 80-110degC depending on density |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex synthesis | Lower cost, widely available commodity resin |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyethylene Resins
Polyurethane resin is a versatile polymer known for its flexibility, toughness, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals, widely used in coatings, adhesives, and foams. Polyethylene resin, a common thermoplastic, offers excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and high impact strength, making it ideal for packaging, containers, and plastic films. Both resins differ significantly in molecular structure, with polyurethane formed by reacting diisocyanates and polyols, while polyethylene results from polymerizing ethylene monomers.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polyurethane resin is formed through the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, creating urethane linkages with alternating soft and hard segments that offer flexibility and durability. Polyethylene resin, on the other hand, consists of long chains of repeating ethylene monomers forming a simple hydrocarbon structure with strong C-C and C-H bonds, resulting in high chemical resistance and rigidity. The presence of polar urethane groups in polyurethane contrasts sharply with the nonpolar, saturated carbon backbone of polyethylene, influencing their mechanical properties and applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane resin offers superior elasticity and impact resistance compared to polyethylene resin, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability. Polyethylene resin exhibits higher chemical resistance and better moisture barrier properties, suitable for packaging and containers. The tensile strength of polyurethane typically ranges from 20 to 50 MPa, while polyethylene varies between 10 to 30 MPa, influencing their performance under stress.
Manufacturing Processes
Polyurethane resin is produced through a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, often involving a controlled polymerization process that allows for customization in rigidity and elasticity, essential in flexible foam and coatings manufacturing. Polyethylene resin is typically synthesized via polymerization of ethylene gas using high-pressure or catalytic processes like Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, resulting in a thermoplastic material widely used in packaging and molded products. The manufacturing process of polyurethane resin offers greater versatility in physical properties compared to polyethylene resin, which is valued for its high chemical resistance and ease of processing.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane resin offers superior durability compared to polyethylene resin due to its resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and UV exposure, making it ideal for high-stress applications. Polyethylene resin provides good flexibility and moisture resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged environmental stress. The longevity of polyurethane resin typically exceeds polyethylene resin by several years in demanding industrial and outdoor environments.
Common Applications of Polyurethane vs Polyethylene
Polyurethane resin is widely used in coatings, adhesives, and flexible foam applications due to its excellent durability and elasticity. Polyethylene resin is primarily utilized in packaging materials such as plastic bags, containers, and films, benefiting from its chemical resistance and strength. Common applications highlight polyurethane's role in automotive parts and furniture, while polyethylene dominates in consumer goods and industrial packaging.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polyurethane resin typically exhibits lower recyclability compared to polyethylene resin due to its thermosetting nature, which complicates reuse and promotes longer environmental persistence. Polyethylene resin, being a thermoplastic, is more easily recycled through mechanical processes, reducing landfill accumulation and environmental pollution. Environmentally, polyethylene production generates fewer hazardous byproducts than polyurethane, making it a more sustainable choice in terms of lifecycle emissions and end-of-life disposal.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Polyurethane resin typically offers superior durability and flexibility but comes at a higher cost compared to polyethylene resin, making cost efficiency a critical factor in material selection. Polyethylene resin stands out for its lower price and ease of processing, appealing to budget-conscious projects with less demanding mechanical requirements. Economic considerations often prioritize polyethylene in large-scale applications due to its cost-effectiveness and availability, whereas polyurethane is chosen for specialized uses where performance justifies the premium.
Performance in Harsh Conditions
Polyurethane resin exhibits superior abrasion resistance and flexibility under extreme temperatures, making it ideal for harsh chemical or mechanical environments. Polyethylene resin offers excellent moisture resistance and impact strength but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure or aggressive solvents. Selecting polyurethane resin ensures enhanced durability and longevity in demanding industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Polyurethane resin offers superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and complex molding. Polyethylene resin provides excellent moisture resistance and impact strength, suited for lightweight, high-volume production with cost efficiency. Selecting the right resin depends on your project's specific mechanical, thermal, and environmental demands to ensure optimal performance.
Polyurethane Resin vs Polyethylene Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com