Acrylic resin offers excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications and displays requiring high transparency. Polycarbonate resin provides superior impact resistance and heat tolerance, suitable for engineering parts and protective gear. Both resins serve distinct purposes based on durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure requirements.
Table of Comparison
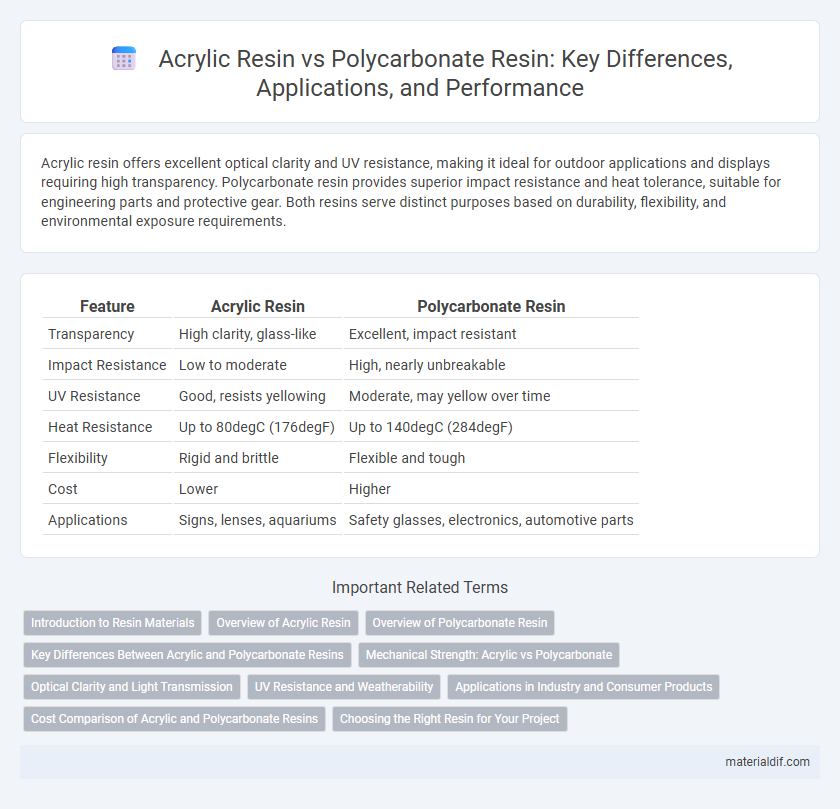
| Feature | Acrylic Resin | Polycarbonate Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High clarity, glass-like | Excellent, impact resistant |
| Impact Resistance | Low to moderate | High, nearly unbreakable |
| UV Resistance | Good, resists yellowing | Moderate, may yellow over time |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC (176degF) | Up to 140degC (284degF) |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and tough |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Signs, lenses, aquariums | Safety glasses, electronics, automotive parts |
Introduction to Resin Materials
Acrylic resin and polycarbonate resin are two widely used thermoplastic materials known for their clarity and durability in various applications. Acrylic resin offers excellent optical clarity, weather resistance, and is commonly used in signage, displays, and automotive parts. Polycarbonate resin provides superior impact resistance, high heat resistance, and is often utilized in electronic components, eyewear lenses, and protective gear.
Overview of Acrylic Resin
Acrylic resin, a transparent thermoplastic polymer, is widely used for its excellent clarity, weather resistance, and UV stability, making it ideal for outdoor applications and displays. It offers high hardness and scratch resistance but is more brittle compared to polycarbonate resin, which provides superior impact resistance and flexibility. Acrylic resin serves as a cost-effective choice in fields such as automotive lighting, signage, and optical devices where optical clarity is paramount.
Overview of Polycarbonate Resin
Polycarbonate resin is a highly durable thermoplastic known for its exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for applications like eyewear lenses, automotive components, and electronic housings. Unlike acrylic resin, polycarbonate exhibits superior heat resistance and toughness, allowing it to withstand demanding environments without cracking or deforming. Its versatility in molding and ability to maintain dimensional stability under stress further distinguish polycarbonate from other resins.
Key Differences Between Acrylic and Polycarbonate Resins
Acrylic resin offers superior clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications and optical uses. Polycarbonate resin provides better impact resistance and higher heat tolerance, suitable for safety equipment and automotive parts. The choice depends on whether transparency or durability is the primary requirement in the application.
Mechanical Strength: Acrylic vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate resin exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to acrylic resin, with impact resistance up to 250 times greater, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and toughness. Acrylic resin offers good tensile strength and rigidity but is more prone to cracking under stress or impact, limiting its use in high-strength environments. Polycarbonate's enhanced mechanical properties make it suitable for automotive parts, safety equipment, and electronic housings where resistance to mechanical deformation is critical.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Acrylic resin offers superior optical clarity with light transmission rates up to 92%, making it ideal for applications requiring high transparency and minimal distortion. Polycarbonate resin provides excellent impact resistance but has slightly lower optical clarity with light transmission around 88%. Both resins are used in lenses and protective covers, but acrylic is preferred when maximum clarity and light transmittance are crucial.
UV Resistance and Weatherability
Acrylic resin exhibits superior UV resistance and weatherability compared to polycarbonate resin, maintaining clarity and color stability under prolonged sun exposure. Polycarbonate resin is more prone to yellowing and surface degradation when subjected to UV radiation without protective coatings. This makes acrylic resin the preferred choice for outdoor applications requiring long-term durability and aesthetic retention.
Applications in Industry and Consumer Products
Acrylic resin is widely used in applications requiring clarity and weather resistance, such as automotive parts, signage, and optical lenses, due to its excellent transparency and UV stability. Polycarbonate resin offers superior impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for safety helmets, electronic components, and bulletproof glass in both industrial and consumer products. Both resins serve crucial roles in manufacturing, with acrylic favored for aesthetic and clarity-driven uses while polycarbonate excels in durability and protection.
Cost Comparison of Acrylic and Polycarbonate Resins
Acrylic resin typically costs less than polycarbonate resin, making it a more budget-friendly option for applications where high impact resistance is not critical. Polycarbonate resin, while more expensive, provides superior durability and impact strength, justifying its higher price in safety and high-performance uses. Price variations depend on factors such as grade, supply chain, and volume purchased, but acrylic resin generally remains the more cost-effective choice for clear plastic applications.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Acrylic resin offers excellent clarity, UV resistance, and is ideal for applications requiring a lightweight, transparent material, such as display cases or acrylic sheets. Polycarbonate resin provides superior impact strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for high-performance applications like safety glasses and automotive parts. Selecting the right resin depends on balancing factors like optical clarity, durability, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Acrylic Resin vs Polycarbonate Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com