UV stabilized polymer PET resists degradation from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light, maintaining its strength, clarity, and color over time. Non-UV stabilized PET can become brittle, discolored, and weakened when exposed to sunlight, limiting its outdoor durability. Choosing UV stabilized PET ensures enhanced longevity and performance in applications with frequent UV exposure.
Table of Comparison
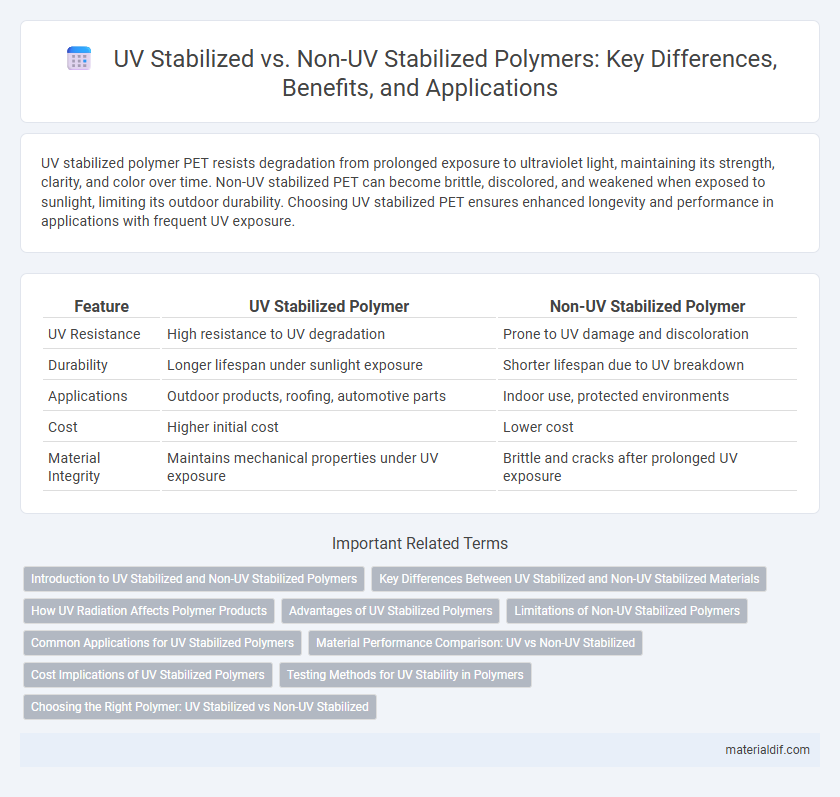
| Feature | UV Stabilized Polymer | Non-UV Stabilized Polymer |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | High resistance to UV degradation | Prone to UV damage and discoloration |
| Durability | Longer lifespan under sunlight exposure | Shorter lifespan due to UV breakdown |
| Applications | Outdoor products, roofing, automotive parts | Indoor use, protected environments |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Material Integrity | Maintains mechanical properties under UV exposure | Brittle and cracks after prolonged UV exposure |
Introduction to UV Stabilized and Non-UV Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers contain additives that protect the material from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, extending the polymer's lifespan and maintaining mechanical properties under sunlight exposure. Non-UV stabilized polymers lack these protective additives, making them susceptible to UV-induced discoloration, brittleness, and loss of strength when exposed to outdoor environments. The selection between UV stabilized and non-UV stabilized polymers depends on the application's exposure to sunlight and desired durability requirements.
Key Differences Between UV Stabilized and Non-UV Stabilized Materials
UV stabilized polymers contain additives that absorb or block ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing their resistance to photo-degradation and prolonging their service life in outdoor applications. Non-UV stabilized materials lack these protective compounds, making them more susceptible to discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical properties when exposed to sunlight. The presence of UV stabilizers is crucial for materials used in construction, automotive, and packaging industries where durability under UV exposure is essential.
How UV Radiation Affects Polymer Products
UV radiation causes photodegradation in polymer products, leading to molecular chain scission, discoloration, loss of mechanical strength, and surface cracking. UV stabilized polymers incorporate additives like UV absorbers or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) to absorb or neutralize harmful UV energy, significantly extending the material's lifespan and maintaining its structural integrity. Non-UV stabilized polymers degrade rapidly under sunlight exposure, resulting in brittleness, reduced performance, and premature failure in outdoor applications.
Advantages of UV Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers offer enhanced durability and prolonged lifespan by resisting degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation exposure. These polymers maintain mechanical strength, color fastness, and structural integrity in outdoor applications, reducing maintenance costs and material replacement frequency. Incorporating UV stabilizers improves performance in automotive components, construction materials, and packaging products exposed to sunlight.
Limitations of Non-UV Stabilized Polymers
Non-UV stabilized polymers degrade rapidly when exposed to sunlight, leading to discoloration, loss of mechanical strength, and surface cracking. Their limited resistance to ultraviolet radiation shortens the lifespan of products in outdoor applications. This vulnerability results in increased maintenance costs and environmental waste due to frequent replacement.
Common Applications for UV Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers are commonly used in outdoor applications such as roofing materials, automotive parts, and agricultural films where prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause degradation. These polymers incorporate UV absorbers or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) to enhance durability and prevent color fading, cracking, or brittleness. Their resistance to ultraviolet radiation makes them ideal for building facades, greenhouse panels, and outdoor furniture, ensuring extended service life in harsh environmental conditions.
Material Performance Comparison: UV vs Non-UV Stabilized
UV stabilized polymers incorporate additives that absorb or screen ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing material durability by preventing chain scission and discoloration caused by prolonged sun exposure. Non-UV stabilized polymers degrade faster under UV radiation, leading to reduced mechanical strength, increased brittleness, and surface cracking. Performance metrics such as tensile strength retention and color stability over time consistently favor UV stabilized materials in outdoor and high-UV environments.
Cost Implications of UV Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers incorporate additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation, significantly extending the material's lifespan in outdoor applications. These additives increase the production cost by 10-30% compared to non-UV stabilized polymers, impacting the overall budget for large-scale manufacturing or construction projects. However, the enhanced durability and reduced maintenance expenses associated with UV stabilized polymers often justify the upfront investment through long-term cost savings.
Testing Methods for UV Stability in Polymers
Testing methods for UV stability in polymers primarily include accelerated weathering tests such as xenon arc and UV fluorescent lamp exposure, which simulate natural sunlight to evaluate polymer degradation. Spectroscopic analysis techniques like UV-Vis and FTIR spectroscopy detect chemical changes, while mechanical testing assesses retention of tensile strength and elasticity after UV exposure. These methods help differentiate UV stabilized polymers, which contain additives to absorb or block harmful UV radiation, from non-UV stabilized variants that degrade more rapidly under sunlight.
Choosing the Right Polymer: UV Stabilized vs Non-UV Stabilized
UV stabilized polymers contain additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer degradation and extending the material's lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV stabilized polymers lack these protective additives, making them more susceptible to fading, brittleness, and structural failure when exposed to sunlight over time. Selecting the right polymer involves evaluating environmental UV exposure, desired durability, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
UV Stabilized vs Non-UV Stabilized Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com