Impact modified polymer PET enhances toughness and resistance to cracking compared to unmodified PET, making it suitable for applications requiring greater durability. Unmodified PET offers higher rigidity and clarity but is more brittle under stress, limiting its use in impact-sensitive environments. Choosing between impact modified and unmodified PET depends on the specific performance needs, balancing strength and aesthetic requirements.
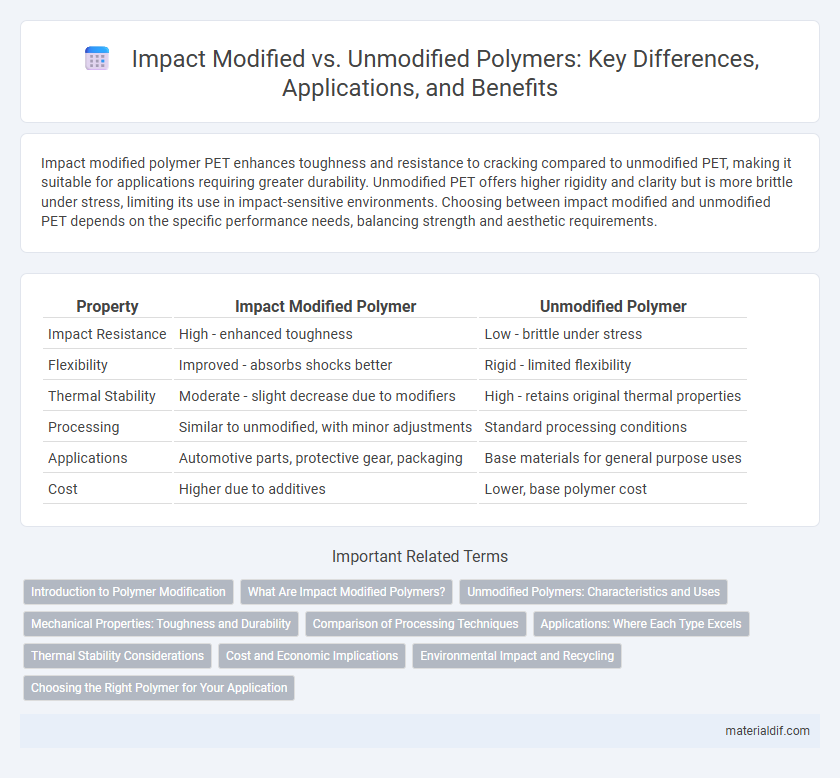
Table of Comparison
| Property | Impact Modified Polymer | Unmodified Polymer |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High - enhanced toughness | Low - brittle under stress |
| Flexibility | Improved - absorbs shocks better | Rigid - limited flexibility |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate - slight decrease due to modifiers | High - retains original thermal properties |
| Processing | Similar to unmodified, with minor adjustments | Standard processing conditions |
| Applications | Automotive parts, protective gear, packaging | Base materials for general purpose uses |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Lower, base polymer cost |
Introduction to Polymer Modification
Impact modified polymers exhibit enhanced toughness and resistance to fracture compared to unmodified polymers, achieved through the incorporation of rubber particles or elastomers into the polymer matrix. Unmodified polymers typically have higher stiffness and strength but are more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. Polymer modification techniques, such as impact modification, improve performance in applications requiring durability and impact resistance without compromising essential mechanical properties.
What Are Impact Modified Polymers?
Impact modified polymers are engineered by incorporating rubber particles or elastomers into a rigid polymer matrix to enhance toughness and resistance to impact forces. These modifications improve the polymer's ability to absorb energy without fracturing, making them ideal for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Unmodified polymers typically exhibit higher brittleness and lower impact resistance compared to their impact modified counterparts.
Unmodified Polymers: Characteristics and Uses
Unmodified polymers exhibit a rigid molecular structure, resulting in high tensile strength and chemical resistance but limited impact resistance. Commonly utilized in applications such as packaging, automotive components, and consumer goods, these polymers maintain dimensional stability under stress. Their inherent stiffness and clarity make them ideal for products requiring durability without the need for enhanced toughness.
Mechanical Properties: Toughness and Durability
Impact modified polymers exhibit enhanced toughness and durability by incorporating rubber particles or elastomers that absorb and dissipate energy during impact, reducing brittleness and preventing crack propagation. Unmodified polymers typically show higher stiffness but lower impact resistance, making them more prone to fracture under dynamic loading conditions. The choice between impact modified and unmodified polymers depends on specific application demands for mechanical resilience and long-term durability.
Comparison of Processing Techniques
Impact modified polymers require specialized processing techniques such as dynamic vulcanization or reactive extrusion to integrate elastomeric phases, enhancing toughness without compromising processability. Unmodified polymers often utilize conventional methods like injection molding or extrusion, benefiting from simpler thermal and mechanical stability during fabrication. The choice of technique directly influences the polymer's morphology and final mechanical properties, dictating performance in end-use applications.
Applications: Where Each Type Excels
Impact modified polymers excel in automotive components, protective gear, and packaging applications due to their enhanced toughness and resistance to sudden forces. Unmodified polymers are preferred in applications requiring rigidity and chemical resistance, such as in medical devices and structural parts. The choice depends on balancing flexibility and strength requirements for specific industrial uses.
Thermal Stability Considerations
Impact modified polymers exhibit enhanced toughness and resistance to crack propagation but often demonstrate slightly reduced thermal stability compared to their unmodified counterparts due to the presence of elastomeric modifiers. Unmodified polymers maintain higher thermal degradation thresholds and better retention of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making them preferable in applications demanding superior heat resistance. Thermal stability considerations must balance the improved impact performance against potential compromises in operating temperature ranges.
Cost and Economic Implications
Impact modified polymers typically incur higher production costs due to the incorporation of rubber-like additives that enhance toughness and durability. Unmodified polymers, while generally less expensive, may result in higher long-term costs owing to increased susceptibility to impact damage and reduced lifespan in demanding applications. Economic implications favor impact modified polymers for products requiring extended durability, balancing upfront expenditures with reduced maintenance and replacement expenses.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Impact modified polymers contain additives that enhance toughness but can complicate recycling processes by reducing material homogeneity. Unmodified polymers offer simpler recycling with lower environmental impact due to the absence of blending agents that can contaminate recycling streams. Selecting unmodified polymers supports improved recyclability and reduces ecological footprint in polymer lifecycle management.
Choosing the Right Polymer for Your Application
Impact modified polymers exhibit enhanced toughness and resistance to cracking, making them ideal for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Unmodified polymers offer superior stiffness and clarity but may be more brittle, suitable for applications prioritizing aesthetic and structural rigidity. Selecting the right polymer depends on balancing impact resistance with mechanical properties specific to the application's performance requirements.
Impact Modified vs Unmodified Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com