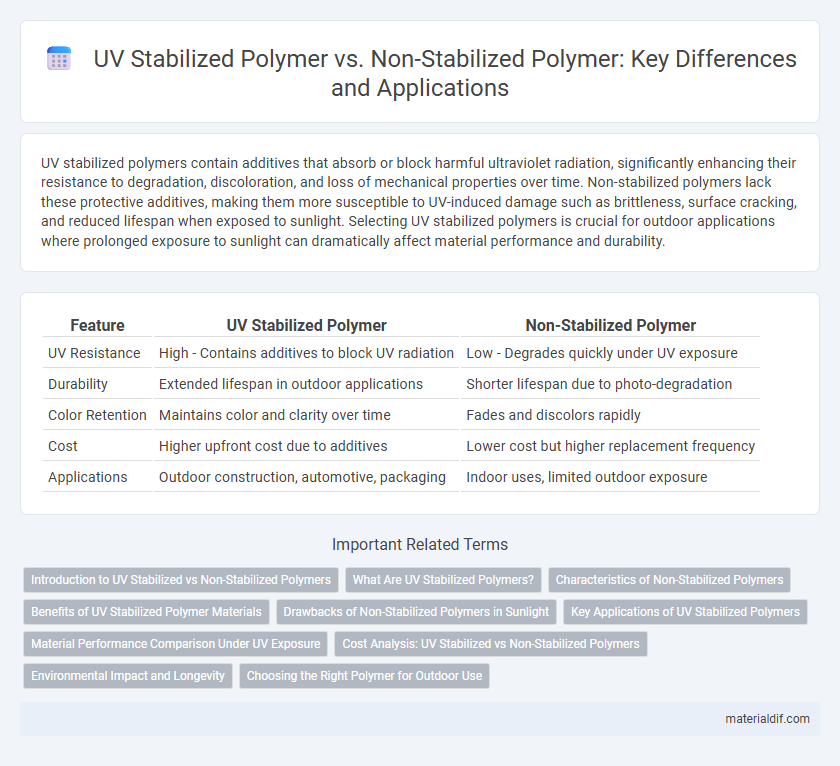
UV stabilized polymers contain additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing their resistance to degradation, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties over time. Non-stabilized polymers lack these protective additives, making them more susceptible to UV-induced damage such as brittleness, surface cracking, and reduced lifespan when exposed to sunlight. Selecting UV stabilized polymers is crucial for outdoor applications where prolonged exposure to sunlight can dramatically affect material performance and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UV Stabilized Polymer | Non-Stabilized Polymer |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | High - Contains additives to block UV radiation | Low - Degrades quickly under UV exposure |
| Durability | Extended lifespan in outdoor applications | Shorter lifespan due to photo-degradation |
| Color Retention | Maintains color and clarity over time | Fades and discolors rapidly |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to additives | Lower cost but higher replacement frequency |
| Applications | Outdoor construction, automotive, packaging | Indoor uses, limited outdoor exposure |
Introduction to UV Stabilized vs Non-Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers incorporate additives that absorb or screen ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing their resistance to photodegradation and color fading when exposed to sunlight. Non-stabilized polymers lack these protective agents, making them more susceptible to chain scission, embrittlement, and surface cracking under prolonged UV exposure. The distinction between UV stabilized and non-stabilized polymers is critical in applications like outdoor construction materials, automotive parts, and packaging, where durability and longevity are essential.
What Are UV Stabilized Polymers?
UV stabilized polymers contain specific additives that absorb or dissipate ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer degradation caused by prolonged sun exposure. These stabilizers enhance the material's durability, color retention, and mechanical properties by minimizing photo-oxidative damage. Non-stabilized polymers lack these protective compounds, leading to rapid discoloration, brittleness, and reduced lifespan under UV radiation.
Characteristics of Non-Stabilized Polymers
Non-stabilized polymers lack additives that protect against ultraviolet (UV) radiation, making them highly susceptible to photodegradation, which leads to discoloration, surface cracking, and loss of mechanical properties. These polymers exhibit poor resistance to UV exposure, resulting in accelerated aging and reduced lifespan when used in outdoor applications. The absence of UV stabilizers causes rapid chain scission and oxidation, compromising the material's structural integrity and performance over time.
Benefits of UV Stabilized Polymer Materials
UV stabilized polymers significantly enhance the durability and lifespan of products exposed to sunlight by resisting degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation. These materials prevent discoloration, loss of mechanical strength, and surface cracking, maintaining aesthetic and structural integrity over time. Their use reduces maintenance costs and extends service intervals in outdoor applications such as automotive parts, construction materials, and packaging.
Drawbacks of Non-Stabilized Polymers in Sunlight
Non-stabilized polymers exposed to sunlight undergo rapid degradation due to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, leading to discoloration, loss of mechanical strength, and surface cracking. These polymers lack protective additives, making them highly susceptible to photo-oxidation and polymer chain scission under UV exposure. Consequently, non-stabilized polymers exhibit reduced lifespan and structural integrity when used in outdoor applications without UV stabilization.
Key Applications of UV Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers are extensively used in outdoor applications such as automotive parts, roofing materials, and agricultural films where prolonged exposure to sunlight leads to degradation. These polymers incorporate UV absorbers or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) to enhance durability and prevent discoloration, cracking, and loss of mechanical properties. In contrast to non-stabilized polymers, UV stabilized variants provide superior weather resistance and extended service life in demanding environmental conditions.
Material Performance Comparison Under UV Exposure
UV stabilized polymers exhibit significantly enhanced resistance to photodegradation compared to non-stabilized polymers, maintaining mechanical strength, color stability, and surface integrity under prolonged UV exposure. Non-stabilized polymers tend to suffer from chain scission, discoloration, and embrittlement, leading to reduced service life and compromised material performance in outdoor applications. Incorporating UV stabilizers like hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) or UV absorbers effectively prolongs polymer durability by mitigating UV-induced damage.
Cost Analysis: UV Stabilized vs Non-Stabilized Polymers
UV stabilized polymers typically incur higher initial costs due to the inclusion of UV-absorbing additives and stabilizers, which enhance durability under prolonged sun exposure. Non-stabilized polymers have lower upfront expenses but often experience faster degradation, leading to increased maintenance, replacement, and overall lifecycle costs. Cost analysis reveals that UV stabilized polymers can offer greater long-term economic value by reducing material failure and minimizing service interruptions in outdoor applications.
Environmental Impact and Longevity
UV stabilized polymers significantly reduce environmental degradation by resisting photodegradation, thus extending the material's lifespan and minimizing waste accumulation. In contrast, non-stabilized polymers break down faster under UV exposure, releasing microplastics and harmful chemicals into ecosystems. Enhanced longevity of UV stabilized polymers contributes to lower resource consumption and reduced environmental pollution over time.
Choosing the Right Polymer for Outdoor Use
UV stabilized polymers contain additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing their resistance to discoloration, cracking, and mechanical degradation when exposed to sunlight. Non-stabilized polymers lack these protective compounds, making them prone to rapid deterioration and loss of structural integrity in outdoor environments. Selecting a UV stabilized polymer is essential for outdoor applications to ensure durability, maintain aesthetic appearance, and extend the lifespan of plastic products exposed to continuous UV exposure.
UV Stabilized Polymer vs Non-Stabilized Polymer Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com