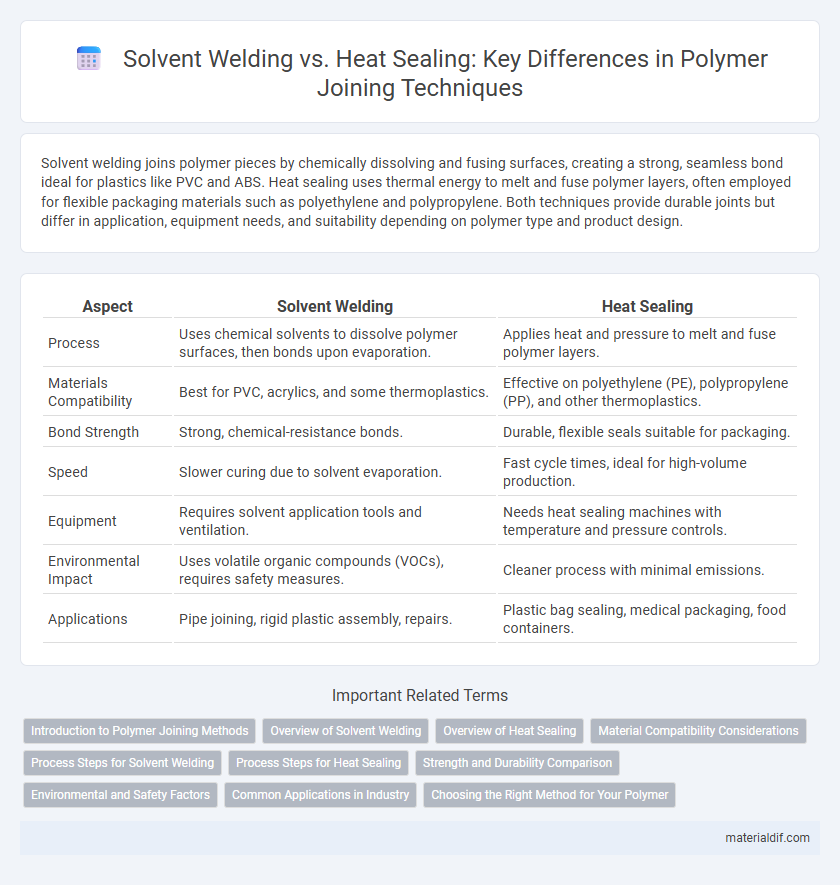
Solvent welding joins polymer pieces by chemically dissolving and fusing surfaces, creating a strong, seamless bond ideal for plastics like PVC and ABS. Heat sealing uses thermal energy to melt and fuse polymer layers, often employed for flexible packaging materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene. Both techniques provide durable joints but differ in application, equipment needs, and suitability depending on polymer type and product design.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Solvent Welding | Heat Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses chemical solvents to dissolve polymer surfaces, then bonds upon evaporation. | Applies heat and pressure to melt and fuse polymer layers. |
| Materials Compatibility | Best for PVC, acrylics, and some thermoplastics. | Effective on polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and other thermoplastics. |
| Bond Strength | Strong, chemical-resistance bonds. | Durable, flexible seals suitable for packaging. |
| Speed | Slower curing due to solvent evaporation. | Fast cycle times, ideal for high-volume production. |
| Equipment | Requires solvent application tools and ventilation. | Needs heat sealing machines with temperature and pressure controls. |
| Environmental Impact | Uses volatile organic compounds (VOCs), requires safety measures. | Cleaner process with minimal emissions. |
| Applications | Pipe joining, rigid plastic assembly, repairs. | Plastic bag sealing, medical packaging, food containers. |
Introduction to Polymer Joining Methods
Solvent welding and heat sealing are critical polymer joining methods used to create strong, durable bonds in plastic fabrication processes. Solvent welding chemically softens polymer surfaces, allowing polymer chains to intertwine and form a seamless joint ideal for materials like PVC and ABS. Heat sealing employs controlled heat and pressure to melt and fuse polymer layers, commonly used in thermoplastic films such as polyethylene and polypropylene for packaging applications.
Overview of Solvent Welding
Solvent welding is a joining technique that uses chemical solvents to soften and dissolve polymer surfaces, creating a strong, homogeneous bond once the solvent evaporates. This method is commonly applied to thermoplastics such as PVC, ABS, and acrylics, providing durable and leak-proof joints ideal for piping and automotive components. The process offers advantages over heat sealing by eliminating the need for elevated temperatures, reducing thermal stress and distortion in sensitive polymer materials.
Overview of Heat Sealing
Heat sealing joins polymer materials by applying heat and pressure to create a bond through melting the surfaces. This technique is widely used for thermoplastics, ensuring strong, airtight, and watertight seals without the need for adhesives. Heat sealing offers precise control over temperature and pressure, making it ideal for packaging applications requiring durability and reliability.
Material Compatibility Considerations
Solvent welding relies on the chemical dissolution of polymer surfaces, requiring materials such as PVC, ABS, and acrylic that are soluble in specific solvents to form strong, permanent bonds. Heat sealing demands thermoplastic polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene that melt and fuse under controlled temperature and pressure conditions without degrading. Selecting the appropriate technique depends on the polymer's chemical resistance and thermal properties to ensure optimal adhesion and structural integrity.
Process Steps for Solvent Welding
Solvent welding involves applying a solvent to polymer surfaces, softening the material to create a molecular bond upon drying. The process steps include cleaning the surfaces, applying the solvent with a brush or applicator, aligning the parts accurately, and holding them together until the joint solidifies. This technique is commonly used for PVC and acrylic polymers, ensuring strong, leak-proof joints in piping and plastic assemblies.
Process Steps for Heat Sealing
Heat sealing in polymer processing involves bringing two thermoplastic surfaces into contact and applying controlled heat and pressure to fuse them without melting the entire material. The process typically includes surface preparation, precise temperature regulation using heated bars or plates, and a dwell time where heat and pressure cause the polymer chains to interdiffuse and form a strong bond. Cooling under maintained pressure solidifies the joint, ensuring a durable, airtight, and watertight seal ideal for packaging, medical devices, and flexible films.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Solvent welding creates a strong, durable bond by chemically dissolving polymer surfaces and fusing them at the molecular level, resulting in joints that often outperform the base material in tensile strength and environmental resistance. Heat sealing fuses thermoplastic polymers by applying heat and pressure, producing bonds that are quick to form but may exhibit lower mechanical strength and are more susceptible to degradation over time under stress or chemical exposure. The strength and durability of solvent-welded joints make them preferable for critical applications requiring long-term structural integrity, whereas heat sealing is suited for less demanding, more rapid assembly processes.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Solvent welding involves chemical solvents that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing environmental pollution and health hazards if not properly managed, while heat sealing uses high temperatures to bond polymers without hazardous emissions. Heat sealing generally offers a safer and more environmentally friendly process by eliminating solvent disposal and reducing exposure to toxic fumes. However, energy consumption in heat sealing must be balanced with its benefits to minimize overall environmental impact.
Common Applications in Industry
Solvent welding is extensively used in the fabrication of PVC pipes and automotive components, providing strong, uniform joints ideal for plumbing and electrical conduit systems. Heat sealing dominates in flexible packaging industries, such as food and medical sectors, offering fast, reliable seals for plastic films and laminated materials. Both methods ensure durable polymer bonds but are selected based on substrate compatibility and application-specific performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Polymer
Solvent welding achieves strong, chemically bonded joints by dissolving polymer surfaces with specific solvents, making it ideal for polymers like PVC and ABS that respond well to solvent interaction. Heat sealing uses controlled temperature and pressure to fuse thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene, offering a faster, cleaner method without chemical use. Selecting the right method depends on the polymer type, desired joint strength, and application conditions, with solvent welding preferred for complex shapes and heat sealing favored for flexible packaging.
Solvent Welding vs Heat Sealing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com