Unpigmented polyethylene offers superior clarity and is ideal for applications requiring transparency and purity, such as food packaging and medical containers. Pigmented polyethylene contains added colorants that enhance UV resistance, improve aesthetic appeal, and provide branding opportunities, making it suitable for outdoor uses and consumer products. Both types maintain polyethylene's inherent durability and chemical resistance, but selection depends on specific visual and functional requirements.
Table of Comparison
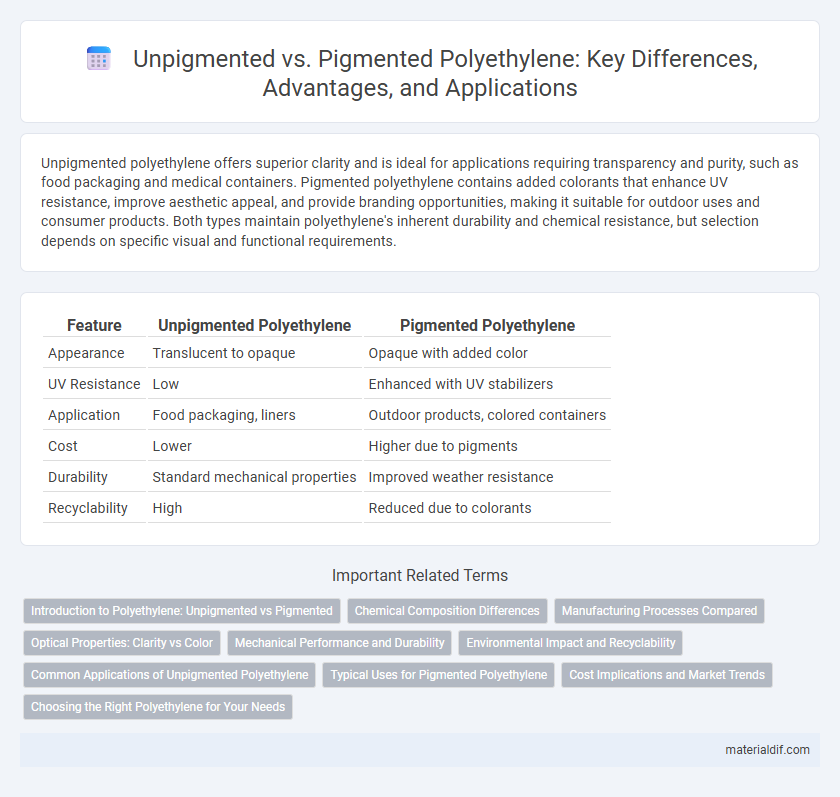
| Feature | Unpigmented Polyethylene | Pigmented Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Translucent to opaque | Opaque with added color |
| UV Resistance | Low | Enhanced with UV stabilizers |
| Application | Food packaging, liners | Outdoor products, colored containers |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to pigments |
| Durability | Standard mechanical properties | Improved weather resistance |
| Recyclability | High | Reduced due to colorants |
Introduction to Polyethylene: Unpigmented vs Pigmented
Unpigmented polyethylene offers high clarity and natural appearance, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and minimal color interference. Pigmented polyethylene incorporates colorants to enhance UV resistance, improve product aesthetics, and provide identification for various industrial uses. Both types maintain the core properties of polyethylene, including chemical resistance and durability, but pigmented varieties are preferred in environments where visual differentiation or extended weatherability is critical.
Chemical Composition Differences
Unpigmented polyethylene primarily consists of long chains of ethylene monomers with minimal additives, preserving its natural chemical purity and clarity. Pigmented polyethylene contains added colorants such as titanium dioxide or carbon black, which chemically interact with the polymer matrix to provide specific hues while affecting properties like UV resistance. The presence of pigments introduces molecular-level heterogeneity, altering the polymer's crystallinity and potentially influencing mechanical and barrier characteristics.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Unpigmented polyethylene undergoes a straightforward polymerization process with minimal additives, resulting in clear or translucent material properties ideal for applications requiring purity and flexibility. Pigmented polyethylene involves the incorporation of colorants and stabilizers during compounding, which necessitates precise dispersion techniques and additional quality control to ensure color consistency and UV resistance. Manufacturing pigmented polyethylene often requires modified extrusion or blending equipment to accommodate pigment compatibility without compromising the polymer's mechanical integrity.
Optical Properties: Clarity vs Color
Unpigmented polyethylene offers superior optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency such as packaging and medical containers. Pigmented polyethylene contains color additives that enhance UV resistance and aesthetic appeal but significantly reduce clarity and light transmission. The choice between unpigmented and pigmented polyethylene depends on the necessity for optical transparency versus color customization and durability.
Mechanical Performance and Durability
Unpigmented polyethylene exhibits superior mechanical performance with higher tensile strength and elongation at break compared to pigmented polyethylene, which may experience slight reductions due to the presence of additives. Durability of unpigmented polyethylene is generally enhanced, as it undergoes less UV degradation and maintains flexibility longer without colorants acting as potential sites for stress concentration. Pigmented polyethylene offers aesthetic advantages but requires UV stabilizers and antioxidants to achieve comparable durability and mechanical integrity over extended service life.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Unpigmented polyethylene typically exhibits higher recyclability due to the absence of dyes or additives that can interfere with mechanical recycling processes. Pigmented polyethylene may contribute to environmental pollution through the introduction of synthetic colorants, some of which can release harmful substances during degradation. Both forms require responsible disposal, but unpigmented variants generally have a lower environmental impact and facilitate more efficient closed-loop recycling systems.
Common Applications of Unpigmented Polyethylene
Unpigmented polyethylene is widely used in applications requiring high purity and chemical resistance, such as food packaging, medical containers, and pharmaceutical films. Its natural clarity and low additive content make it ideal for situations where contamination or color interference must be minimized. Common industrial uses include tubing, liners, and storage tanks where transparency and inertness are critical.
Typical Uses for Pigmented Polyethylene
Pigmented polyethylene is commonly used in applications requiring enhanced UV resistance and aesthetic appeal, such as outdoor furniture, automotive parts, and packaging materials. Its pigmentation provides color stability and protection against degradation caused by sunlight exposure. These properties make pigmented polyethylene ideal for products exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Implications and Market Trends
Unpigmented polyethylene typically costs less due to the absence of colorants and additives, reducing raw material expenses and simplifying production processes. Pigmented polyethylene attracts higher prices driven by demand for customization, UV resistance, and enhanced aesthetic appeal in industries like packaging and automotive. Market trends indicate a growing preference for pigmented variants in eco-friendly and premium segments, despite the steady volume dominance of unpigmented polyethylene in bulk applications.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Needs
Unpigmented polyethylene offers superior clarity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and minimal contamination risk. Pigmented polyethylene provides enhanced UV stability and improved aesthetics, suitable for outdoor use and colorful product designs. Selecting the right polyethylene depends on factors like exposure conditions, mechanical requirements, and visual preferences to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Unpigmented Polyethylene vs Pigmented Polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com