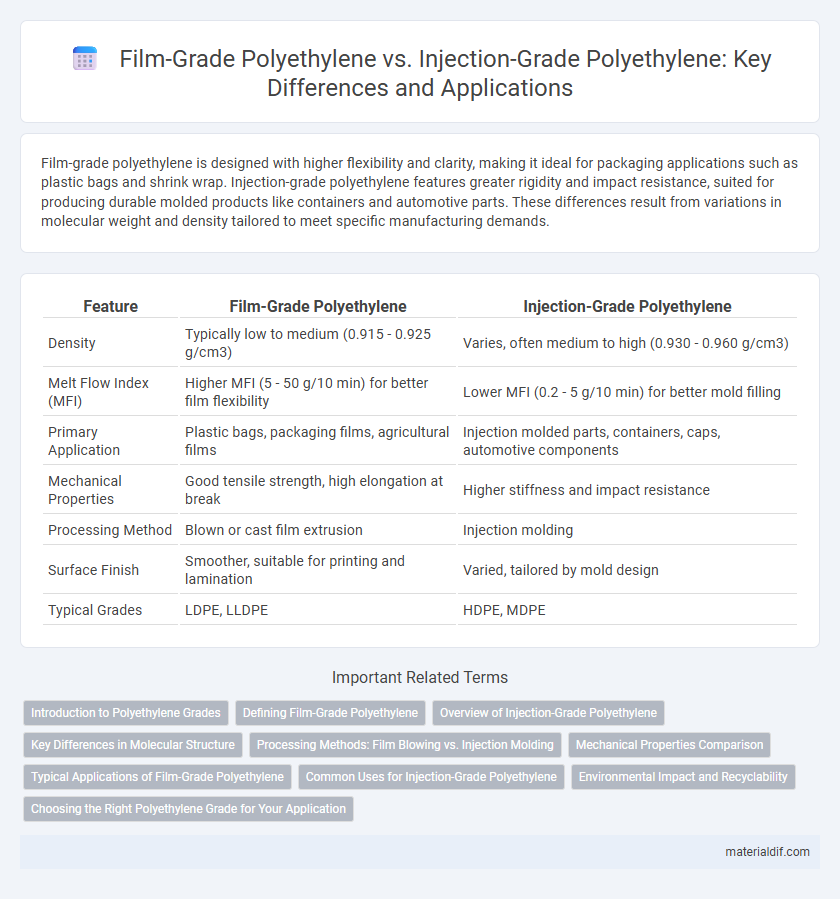
Film-grade polyethylene is designed with higher flexibility and clarity, making it ideal for packaging applications such as plastic bags and shrink wrap. Injection-grade polyethylene features greater rigidity and impact resistance, suited for producing durable molded products like containers and automotive parts. These differences result from variations in molecular weight and density tailored to meet specific manufacturing demands.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Film-Grade Polyethylene | Injection-Grade Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Typically low to medium (0.915 - 0.925 g/cm3) | Varies, often medium to high (0.930 - 0.960 g/cm3) |
| Melt Flow Index (MFI) | Higher MFI (5 - 50 g/10 min) for better film flexibility | Lower MFI (0.2 - 5 g/10 min) for better mold filling |
| Primary Application | Plastic bags, packaging films, agricultural films | Injection molded parts, containers, caps, automotive components |
| Mechanical Properties | Good tensile strength, high elongation at break | Higher stiffness and impact resistance |
| Processing Method | Blown or cast film extrusion | Injection molding |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, suitable for printing and lamination | Varied, tailored by mold design |
| Typical Grades | LDPE, LLDPE | HDPE, MDPE |
Introduction to Polyethylene Grades
Film-grade polyethylene is specifically engineered for applications requiring flexibility, clarity, and strength, such as packaging films, bags, and liners. Injection-grade polyethylene, on the other hand, is formulated for high melt flow properties suitable for injection molding processes used in manufacturing rigid containers, automotive parts, and household goods. These grades differ primarily in molecular weight distribution and density, impacting their mechanical properties and processing techniques.
Defining Film-Grade Polyethylene
Film-grade polyethylene is specifically formulated for the production of thin, flexible plastic films widely used in packaging, agricultural, and industrial applications. This grade features a lower density and higher molecular weight distribution, which enhances its clarity, tensile strength, and elongation properties essential for film durability and flexibility. In contrast, injection-grade polyethylene is designed for molding processes requiring higher rigidity and impact resistance, making it suitable for solid, intricate components rather than flexible films.
Overview of Injection-Grade Polyethylene
Injection-grade polyethylene is specifically engineered for high-performance molding applications, offering superior flow characteristics and mechanical strength compared to film-grade polyethylene. It exhibits enhanced thermal stability and impact resistance, making it ideal for manufacturing durable components through injection molding processes. This grade is commonly used in automotive parts, containers, and household items requiring precision and robustness.
Key Differences in Molecular Structure
Film-grade polyethylene typically features a higher molecular weight with linear chains, providing enhanced tensile strength and flexibility ideal for thin, stretchable films. Injection-grade polyethylene often has a lower molecular weight with more branched chains, resulting in improved flow characteristics and ease of molding into complex shapes. These molecular variations directly influence mechanical properties, processing behavior, and end-use applications.
Processing Methods: Film Blowing vs. Injection Molding
Film-grade polyethylene is specifically formulated for film blowing, a processing method that involves extruding molten polymer through a circular die to create thin, flexible films used in packaging and agriculture. Injection-grade polyethylene, on the other hand, is optimized for injection molding, where molten polymer is injected into molds to produce rigid, precise components like containers and automotive parts. The molecular weight distribution and additive package of film-grade polyethylene facilitate bubble stability and film clarity, whereas injection-grade polyethylene emphasizes flow properties and mechanical strength for complex shapes.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Film-grade polyethylene exhibits superior tensile strength and elongation at break compared to injection-grade polyethylene, making it ideal for flexible packaging applications requiring durability and stretchability. Injection-grade polyethylene features higher stiffness and impact resistance, suitable for molded products demanding dimensional stability and toughness. The mechanical property differences stem from molecular weight distribution and branching, influencing crystallinity and performance in respective processing methods.
Typical Applications of Film-Grade Polyethylene
Film-grade polyethylene is primarily used in the manufacturing of flexible packaging materials such as plastic bags, shrink wraps, and agricultural films due to its excellent clarity, flexibility, and moisture resistance. It also serves in the production of stretch films and liners, optimizing durability and tear resistance for industrial and consumer applications. The molecular structure of film-grade polyethylene is designed to enhance strength and elongation, making it ideal for lightweight, high-performance film products.
Common Uses for Injection-Grade Polyethylene
Injection-grade polyethylene is primarily used in manufacturing rigid and semi-rigid products such as containers, caps, and automotive parts due to its high melt flow index and excellent moldability. This type of polyethylene enables precise molding processes, making it ideal for producing complex shapes and thin-walled components in medical devices and consumer goods. Its superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance contribute to its widespread application in packaging, toys, and household items.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Film-grade polyethylene typically exhibits higher recyclability due to its lower density and simpler polymer structure, facilitating easier mechanical recycling processes compared to injection-grade polyethylene. Injection-grade polyethylene often contains additives and fillers that can complicate recycling and contribute to greater environmental footprint during production due to higher energy consumption. The environmental impact of film-grade polyethylene is generally reduced through efficient recycling streams and lower energy requirements, promoting a more sustainable lifecycle relative to injection-grade variants.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene Grade for Your Application
Film-grade polyethylene, characterized by its higher clarity, flexibility, and tensile strength, is ideal for packaging, plastic bags, and agricultural films requiring durability and transparency. Injection-grade polyethylene offers superior stiffness, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for molded products like containers, caps, and automotive parts. Selecting the right polyethylene grade depends on factors such as mechanical performance, processing method, and end-use requirements, ensuring optimal functionality and cost-effectiveness in the final application.
Film-grade polyethylene vs Injection-grade polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com